|
Planning the Appropriate Network Topology
|
|
|
Original instructions
|
|
Network
|
Interface
|
|---|---|
|
A.A.A.0 (control network)
|
A.A.A.1
|
|
B.B.B.0 (device network)
|
B.B.B.1
|
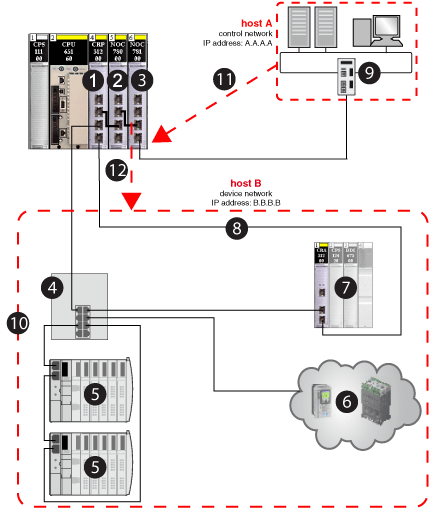
1140CRP31200 remote I/O head module on the local rack
2140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module (interface B)
3140NOC78100 control head module (interface A)
4DRS (with a C2 predefined configuration file loaded) connecting the distributed I/O sub-ring (5) and the distributed I/O cloud (6) to the main ring (8)
5distributed I/O sub-ring
6distributed I/O cloud
7remote I/O drop on the main ring
8main ring
9control network (host A)
10device network (host B)
11control network (host A) with IP address A.A.A.A sends the message to interface A (140NOC78100 module) with IP address A.A.A.1
12interface B (140NOC78000 module) sends the message to the device network (host B) with IP address B.B.B.1
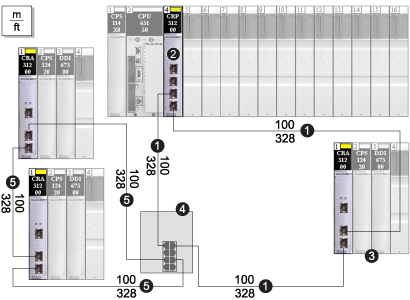
NoteThe solid line represents copper wire.
1the main ring
2the 140 CRP 312 00 head module in the local rack
3a remote I/O drop (including a 140 CRA 312 00 adapter module) on the main ring
4a DRS with a C1 predefined configuration to support a remote I/O sub-ring
5a remote I/O sub-ring
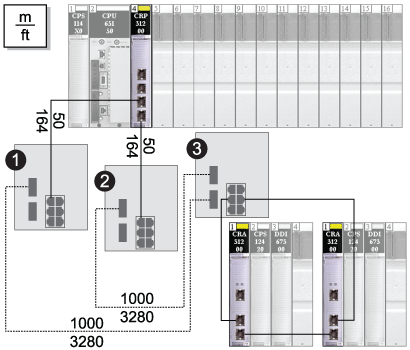
NoteThe dashed line represents fiber cable, and the solid line represents copper wire.
1 and 22 DRSs with C5 predefined configurations to use only 1 fiber port. They support a copper-to-fiber and a fiber-to-copper transition. They enable the fiber-based network to connect to the copper ports on the 140 CRP 312 00 head module in the local rack.
3A DRS with a C3 predefined configuration to use 2 fiber ports and support a remote I/O sub-ring and a distributed I/O cloud.
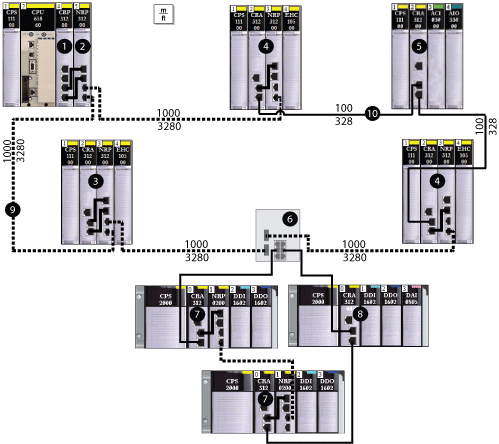
1Quantum local rack, showing a 140CRP31200 head module copper connection to the 140 NRP 312 00/01 fiber converter module (2)
2140 NRP 312 00/01 module connected to the local rack via fiber cable
3Quantum remote I/O drop connected to the main ring via fiber cable (140 NRP 312 00/01 module installed on drop)
4Quantum remote I/O drop connected to the main ring via copper and fiber cable (140 NRP 312 00/01 module installed on drop)
5Quantum remote I/O drop connected to the main ring via copper cable (no 140 NRP 312 00/01 module installed on drop)
6dual-ring switch (DRS) connecting the X80 sub-ring to the main ring
7X80 remote I/O drop connected to the main ring via copper cable and connected to the next drop in the sub-ring via fiber cable (BMX NRP 0200/01 fiber converter module installed on drop)
8X80 remote I/O drop connected to the next drop in the sub-ring and the main ring via copper cable (no BMX NRP 0200/01 module installed on drop)
9(dashed line) — fiber portion of the main ring
10(solid line) — copper portion of the main ring
|
To Insert in the Network...
|
Use...
|
Topology Type
|
|---|---|---|
|
distributed I/O devices with a single Ethernet port
|
a distributed I/O cloud (with devices in a star topology)
|
You can connect a distributed I/O cloud to a high-capacity daisy chain loop.
NOTE: A distributed I/O cloud that is connected to a 140NOC78000 module on the local rack within a simple daisy chain loop is isolated. The cloud is not physically part of the remote I/O network. |
|
distributed I/O devices with dual Ethernet ports
|
|
You can only connect a distributed I/O cloud or distributed I/O sub-ring via a DRS that resides on the main ring in a high-capacity daisy chain loop.
|
|
remote I/O devices with dual Ethernet ports
|
a Quantum remote I/O drop on the main ring or a remote I/O sub-ring
|
|
|
If Distributed I/O Devices Are in a...
|
Then...
|
|---|---|
|
isolated distributed I/O network or cloud — distributed I/O devices that are not a physical part of the remote I/O network
|
One or more 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head modules are required to manage the distributed I/O devices.
Each 140NOC78000 module can manage up to 128 isolated distributed I/O devices.
NOTE: A local rack manages a maximum of 6 communication modules. A 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module is not considered a communication module. You can install a maximum of five 140NOC78000 modules and one 140NOC78100 control head module. Instead of 140NOC78000 modules, you can also install 140 NO• 771 •• or 140 NOM 2•• 00 communication modules. |
|
distributed I/O sub-ring or cloud — distributed I/O devices that are a physical part of the remote I/O network
|
In addition to a 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module on the local rack:
The 140NOC78000 module (interlinked with the 140CRP31200 module) can manage up to a total of 128 devices in the remote I/O network.
NOTE: A local rack manages a maximum of 6 communication modules. A 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module is not considered a communication module. You can install a maximum of five 140NOC78000 modules and one 140NOC78100 control head module. Instead of 140NOC78000 modules, you can also install 140 NO• 771 •• or 140 NOM 2•• 00 communication modules. |
|
extended distributed I/O network or cloud — distributed I/O devices that do communicate with the Quantum EIO device network
|
Interlink a 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module with the extended port of the 140NOC78100 control head module. The 140NOC78100 is also interlinked with the 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module.
NOTE: Only one extended distributed I/O network is supported in a Quantum EIO system. |
|
independent distributed I/O network or cloud — distributed I/O devices that do not communicate with the Quantum EIO device network, but do communicate with the control network
|
Interlink a 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module with a 140NOC78100 control head module on the local rack. These modules are not interlinked with the 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module. An independent distributed I/O network is essentially an isolated distributed I/O network, but it communicates with a Quantum EIO control network.
NOTE: Only one independent distributed I/O network is supported in a Quantum EIO system. |
  DANGER DANGER |
|
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to follow these instructions will result in death or serious injury.
|