|
|
Original instructions
|
|
Area
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
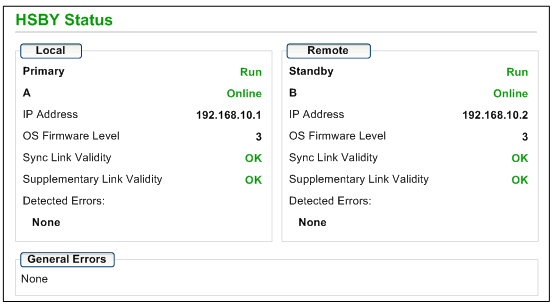
Local/Remote
|
This area displays the state of Hot Standby settings for the local and remote CPUs:
|
|
|
<Hot Standby Role>
|
The Hot Standby system role of the CPU. Valid values include:
|
|
|
<Operating State>
|
The operating state of the CPU. Valid values include:
|
|
|
A/B switch setting
|
The designation of the CPU, defined by the rotary switch on the back of the CPU. Valid values include:
|
|
|
<Run Mode>
|
The designation of the CPU, defined by the rotary switch on the back of the CPU. Valid values include:
|
|
|
IP Address
|
The IP address used to communicate with the CPU for web page access:
|
|
|
OS Firmware Level
|
Firmware version of the CPU operating system.
|
|
|
Sync Link Validity
|
The status of the Hot Standby link:
|
|
|
Supplementary Link Validity
|
The status of the Ethernet RIO link:
|
|
|
Detected Errors
|
Detected errors for the CPU, including:
|
|
|
General Errors
|
Detected errors for the Hot Standby system, including:
|
|