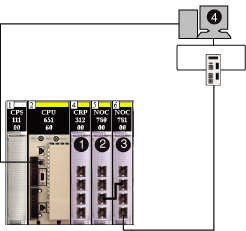
The 140NOC78100 control head module uses an IP forwarding service to provide network transparency between networks in a Quantum EIO system.
The IP forwarding service of the 140NOC78100 control head module is the interface between the and the other network (i.e., , ), with which you want to provide network transparency.
NOTE: In configurations that use the IP forwarding service (the 140NOC78100 control head module bridging the control network to the distributed I/O network via the 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module), we recommend that you use the 140NOC78100 module’s IP address to download the Control Expert application to the PLC.
If you download the application via the 140NOC78000 module, the 140NOC78100 resets at the end of the download, which resets the connection between Control Expert and the 140NOC78000 module. See the following figure showing the IP forwarding service feature in the 140NOC78100 module used to connect to the 140NOC78000 module.
1
140CRP31200 remote I/O head module
2
140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module
3
140NOC78100 control head module
4
Control Expert
How the IP Forwarding Service Manages Transparency between Networks
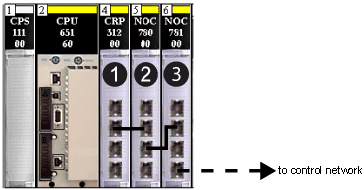
In order for the 140NOC78100 control I/O head module to manage transparency between networks, interlink the head modules on the .
Connect the
interlink port of the 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module (ETH 2) or the 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module (ETH 2 or ETH 3) to the
interlink port (ETH 2) of the 140NOC78100 module, as shown in this picture:
1
140CRP31200 remote I/O head module
2
140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module (interlinked with the 140CRP31200 module to support a device network)
3
140NOC78100 control head module (interlinked with the 140NOC78000 module to provide transparency between the control network and the device network)
IP Forwarding Topology
As an example, suppose you want to provide transparency between the control network and the device network:
-
On the control network, host A exists with a MAC address of aa-aa-aa-aa-aa-aa and an IP address of A.A.A.0.
-
On the device network, host B exists with a MAC address of bb-bb-bb-bb-bb-bb and an IP address of B.B.B.0.
In order for host A and B to communicate with each other, you need to connect the control network and device network physically, as well as logically. The IP forwarding service in the 140NOC78100 is the interface for the network connection.
The IP forwarding service gathers 3 types of information:
-
physical (example: 100BASE-T)
-
data link (example: MAC address)
-
network (example: IP address)
The IP forwarding service now has interface A with an IP address of A.A.A.1 on the control network, and it has interface B with an IP address of B.B.B.1 on the device network.
With this information, the routing table used for IP address forwarding looks like this:
|
Network
|
Interface
|
|
A.A.A.0 (control network)
|
A.A.A.1
|
|
B.B.B.0 (device network)
|
B.B.B.1
|
Now that you have established the IP forwarding service (i.e., gateway), add the IP address forwarding information to hosts A and B, which allows the hosts to send packets beyond their own IP network.
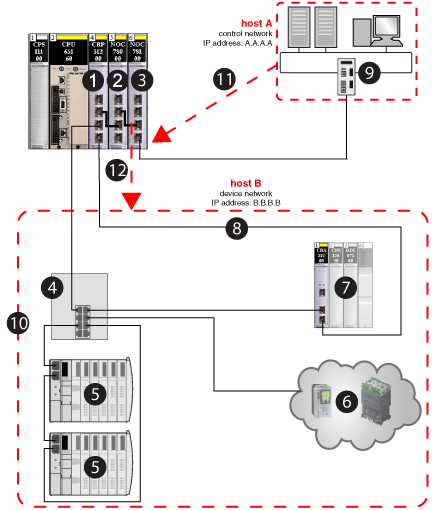
At this point, you can assume that host A is aware of host B and that host A wants to send a packet (example: Modbus message) to host B. Host A (IP address A.A.A.A sends the message to interface A (IP address A.A.A.1), which then sends it to interface B (IP address B.B.B.1) and finally to host B (IP address B.B.B.B) (as shown in the following graphic:
1
140CRP31200 remote I/O head module on the local rack
2
140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module (interface B)
3
140NOC78100 control head module (interface A)
4
DRS (with a C2 predefined configuration file loaded) connecting the distributed I/O sub-ring (5) and the distributed I/O cloud (6) to the main ring (8)
5
distributed I/O sub-ring
6
distributed I/O cloud
7
remote I/O drop on the main ring
8
main ring
9
control network (host A)
10
device network (host B)
11
control network (host A) with IP address A.A.A.A sends the message to interface A (140NOC78100 module) with IP address A.A.A.1
12
interface B (140NOC78000 module) sends the message to the device network (host B) with IP address B.B.B.1