Introduction
Menu commands are used to execute commands or to call dialog boxes.
Example of a menu with menu commands:
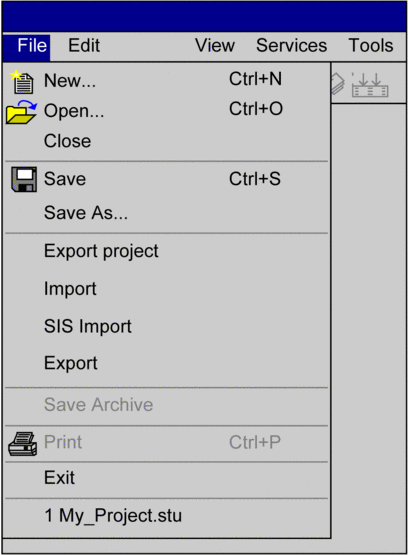
Keyboard shortcuts or mnemonics
Keyboard shortcuts (underlined letters) in menu commands allow you to select menu commands using the keyboard. A main menu (menu title) and subsequently a menu command can be selected by holding down Alt and simultaneously entering the underlined letter in the menu title and then that of the menu command.
For example, in the you want to use the menu command you must press Alt+D to open the menu and then Alt+S to execute the menu command.
Grayed out menu command
If a menu command is not available it is grayed out. One or more other commands must be executed before the desired menu command can be executed.
Periods () after the menu command
On execution of this menu command a dialog box is opened with options, which must be selected before execution.
Checkmark (√) in front of the menu command
The menu command is enabled. If the menu command is selected, the checkmark disappears and the menu command is disabled. The checkmark is mostly used to identify enabled modes (e.g. normal display, dial in mode etc.).
Shortcut keys
Shortcut keys (e.g. F8) or key combinations (e.g. Ctrl+R) after the menu command is a shortcut way for executing the menu command. You can select the menu command using this shortcut key or key combination without having to open the menu. For example, Ctrl+S to execute the menu command .
Starting external applications
Process the following steps to launch external applications from Control Expert:
Step |
Action |
|---|---|
1 |
Open the tab. |
2 |
Click the button. |
3 |
In the field, enter the name of the
menu item to be created (e.g. |
4 |
In the field, enter the path to the program to be launched (e.g. Microsoft Excel). |
5 |
In the field, enter the name of the file to be opened (e.g. Motor_Variables.xls). |
6 |
In the field, enter the path to the file to be opened. Display of the tab: 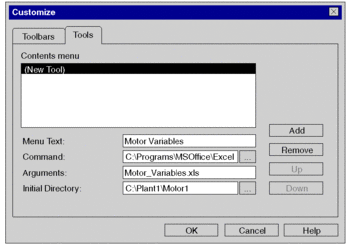 |
7 |
Confirm the entries with . Result: In the main menu a menu command to launch the selected application will be generated (in this example ). Example: 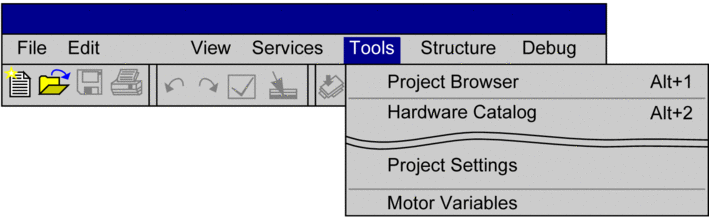 |


