|
|
Original instructions
|
|
Selected configuration
|
Upcounting condition
|
Downcounting condition
|
|---|---|---|
|
A = Up, B = Down
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input.
|
Rising edge at the IN_B input.
|
|
A = Impulse, B = Direction
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input and high state at the IN_B input.
|
|
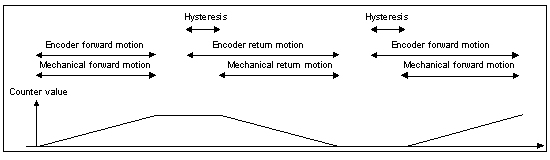
Normal Quadrature X1
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
|
Falling edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input
|
|
Normal Quadrature X2
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
Falling edge at the IN_A input and high state at the IN_B input.
|
Falling edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
Rising edge at the IN_A input and high level at the IN_B input.
|
|
Normal Quadrature X4
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
High state at the IN_A input and rising edge at the IN_B input.
Falling edge at the IN_A input and high state at the IN_B input.
Low state at the IN_A input and falling edge at the IN_B input.
|
Falling edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
Low state at the IN_A input and rising edge at the IN_B input.
Rising edge at the IN_A input and high level at the IN_B input.
High state at the IN_A input and falling edge at the IN_B input.
|
|
Reserve Quadrature X1
|
Falling edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
|
|
Reserve Quadrature X2
|
Falling edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
Rising edge at the IN_A input and high level at the IN_B input.
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
Falling edge at the IN_A input and high state at the IN_B input.
|
|
Reserve Quadrature X4
|
Falling edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
Low state at the IN_A input and rising edge at the IN_B input.
Rising edge at the IN_A input and high level at the IN_B input.
High state at the IN_A input and falling edge at the IN_B input.
|
Rising edge at the IN_A input and low state at the IN_B input.
High state at the IN_A input and rising edge at the IN_B input.
Falling edge at the IN_A input and high state at the IN_B input.
Low state at the IN_A input and falling edge at the IN_B input.
|
|
Bit
|
Label
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|
|
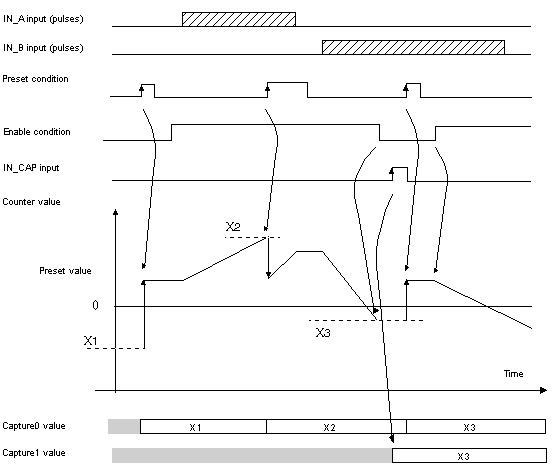
%IWr.m.c.0.1
|
MODULO_FLAG
|
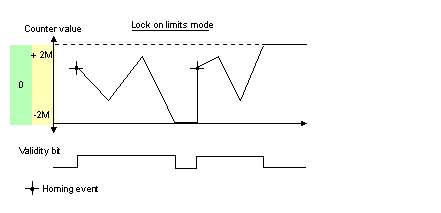
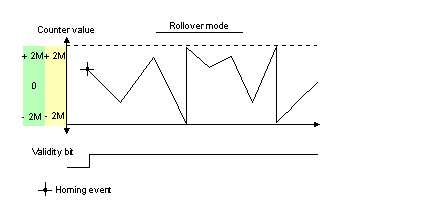
The bit status changes in the rollover mode.
The bit is set to 1 when the counter rollovers its limits (-2,147,483,648 or +2,147,483,647).
The bit is reset to 0 when the command MODULO_RESET (%Qr.m.c.9) is received (rising edge of the MODULO_RESET bit).
|
|
%IWr.m.c.0.2
|
SYNC_REF_FLAG
|
The bit is set to 1 when the counter have been set to the preset value and (re)started.
The bit is reset to 0 when the command SYNC_RESET (%Qr.m.c.8) is received (rising edge of the SYNC_RESET bit).
|
|
%IWr.m.c.0.3
|
VALIDITY
|
Validity bit is used to indicate that the counter current value and compare status registers contain valid data.
If the bit is set to 1, the data is valid.
If the bit is set to 0, the data is not valid.
|
|
%IWr.m.c.0.4
|
HIGH_LIMIT
|
The bit status changes in the lock on limits mode.
The bit is set to 1 when the counter reaches +2,147,483,647.
The bit is reset to 0 when the counter presets or resets.
|
|
%IWr.m.c.0.5
|
LOW_LIMIT
|
The bit status changes in the lock on limits mode.
The bit is set to 1 when the counter reaches -2,147,483,648.
The bit is reset to 0 when the counter presets or resets.
|