Introducing Bandwidth Monitoring
You can use the Bandwidth Monitoring service to monitor the 171 CBU 98090 and 171 CBU 98091 processor CPU allocation for each of the following services:
Global Data (for the 171 CBU 98091 processor)
Accessing and Configuring the Bandwidth Tab
The following procedure shows how to access the tab:
Step |
Action |
|---|---|
1 |
In the , navigate to the subdirectory. |
2 |
Double-click the appropriate Ethernet network to open its configuration dialog. |
3 |
Select the tab to open the Bandwidth Monitoring screen: |
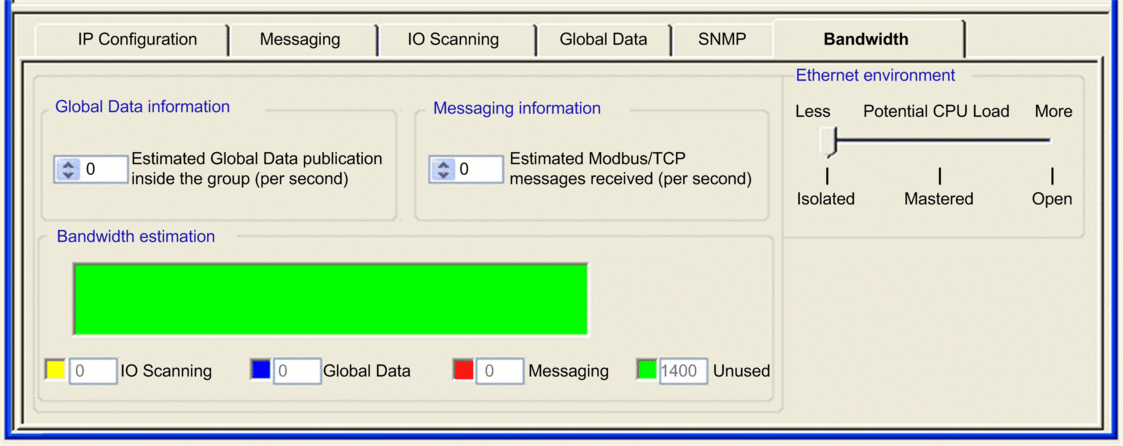
|
|
4 |
Configure the Global Data, I/O Scanning, and Modbus Messaging services before configuring the Bandwidth Monitoring parameters. |
5 |
Enter the parameter settings for the Bandwidth Monitoring. Refer to the Bandwidth Monitoring Properties section, below, for a description of Bandwidth Monitoring settings. |
Bandwidth Monitoring Properties
The tab includes the following properties:
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Select the environment that describes your Ethernet network:
|
|
Enter an estimate of the number of publication periods. The value entered is the estimated average publication frequency of the distribution (local and remote) group stations. |
|
Enter an estimate of the number of transactions per second. |
Controlling Ethernet Messaging
During runtime, Control Expert executes both master (MAST) tasks and Ethernet messaging (ETH) tasks. Control Expert prioritizes ETH tasks, and executes ETH tasks before it executes MAST tasks. Because Control Expert prioritizes ETH tasks, you need to configure Ethernet communications so that sufficient bandwidth remains for the execution of the MAST tasks.
To accomplish this, you need to:
separately configure each component of Ethernet communications (Global Data, I/O Scanning, and Modbus Messaging) to control the bandwidth used by each service, and
limit the number of Ethernet messages per second that the CPU may handle. As indicated above, set the value to one of the following limits:
: 500 messages per second
: 1000 messages per second
: Either:
⇒ 1600 messages per second for the 171 CBU 98090
⇒ 2200 messages per second for the 171 CBU 98091
To decrease the message load contributed by the Global Data service, increase the setting. Each device on the network can publish 1 variable, and subscribe to up to 63 variables. The estimated loads, below, are presented in messages per second:
Distribution Period (ms) |
Global Data Variables |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
8 |
16 |
32 |
64 |
|
20 |
400 |
800 |
1600 |
– |
30 |
267 |
533 |
1067 |
– |
40 |
200 |
400 |
800 |
1600 |
50 |
160 |
320 |
640 |
1280 |
60 |
133 |
267 |
533 |
1067 |
70 |
114 |
229 |
457 |
914 |
80 |
100 |
200 |
400 |
800 |
90 |
89 |
178 |
356 |
711 |
100 |
80 |
160 |
320 |
640 |
– indicates a value beyond the upper limit of 1600 messages per second |
||||
To decrease the message load contributed by the I/O Scanning service, increase the setting. The estimated loads, below, are presented in messages per second:
Repetitive rate (ms) |
I/O Scanned Devices |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
8 |
16 |
32 |
64 |
|
10 |
800 |
1600 |
– |
– |
20 |
400 |
800 |
1600 |
– |
30 |
267 |
533 |
1067 |
– |
40 |
200 |
400 |
800 |
1600 |
50 |
160 |
320 |
640 |
1280 |
60 |
133 |
267 |
533 |
1067 |
70 |
114 |
229 |
457 |
914 |
80 |
100 |
200 |
400 |
800 |
90 |
89 |
178 |
356 |
711 |
100 |
80 |
160 |
320 |
640 |
– indicates a value beyond the upper limit of 1600 messages per second |
||||
To decrease the message load contributed by the Modbus Messaging service, increase the of the several Modbus clients operating on the network. The messaging rate can be calculated as follows:
Messaging Rate = ((1/ Message Sampling
period) x Objects
This formula includes the following elements:
Element |
Description |
|---|---|
Messaging Sampling period |
The interval at which messages are processed |
Objects |
The number of devices, either client or server, that are actively communicating |


