|
|
Original instructions
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
|
|
2
|
Confirm that you already created client or server channels.
|
|
3
|
In the CONFIGURATION menu, expand (+) the Channels sub-menu.
|
|
4
|
Make a selection in the Channels sub-menu:
|
|
5
|
Select a specific channel in the sub-menu.
|
|
6
|
Select the DATA MAPPINGS tab for the channel.
|
|
7
|
Configure the data mapping parameters.
|
|
8
|
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
At Select Type Id, select a type ID.
NOTE: For this example, select Binary Input. |
|
2
|
Click Add to see the name of the binary input (DNP3_SERVER_BINARY_INPUT) in the Type Identification column.
|
|
3
|
Select the table row that corresponds to the new binary input to see the BINARY INPUT configuration options.
|
|
4
|
Modify the parameters.
NOTE: When the Control Expert window is active, you can hover the cursor over any field to see a description of the functionality and the available range of values. |
|
5
|
|
 WARNING WARNING |
|
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION
Do not create an instance of redundant data access.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Open the Project Settings (Tools → Project Settings).
|
|
2
|
Expand (+) the menu: Project Settings → General
|
|
3
|
Select the PLC Embedded Data setting to see the Property label and Property value columns.
|
|
4
|
In the Data label column, find the Data Dictionary row and check the corresponding box in the Property value column.
NOTE: Check this box when you program the PLC application. Otherwise, unlocated variables may not be mapped to RTU data points. However, a compiled application consumes more memory when the data dictionary is included, which can have an impact on unlocated variables that are implemented in RTU solutions. |
|
5
|
|
|
Data object type
|
Static variation
|
|---|---|
|
Binary Input
|
g1v1 Binary In
|
|
g1v2 Binary In Flag
|
|
|
Double Input
|
g3v1 Double In
|
|
g3v2 Double In Flag
|
|
|
Binary Output
|
g10v1 Binary Out
|
|
g10v2 Binary Out Flag
|
|
|
Binary Counter
|
g20v1 32bit Counter
|
|
g20v2 16bit Counter
|
|
|
g20v5 32bit Ctr No Flag
|
|
|
g20v6 16bit Ctr No Flag
|
|
|
Frozen Counter
|
g21v1 32bit Frozen Ctr Flag
|
|
g21v2 16bit Frozen Ctr Flag
|
|
|
g21v5 32bit Frozen Ctr Flag Time
|
|
|
g21v6 16bit Frozen Ctr Flag Time
|
|
|
g21v9 32bit Frozen Counter
|
|
|
g21v10 32bit Frozen Counter
|
|
|
Analog Input
|
g30v1 32bit Analog In
|
|
g30v2 16bit Analog In
|
|
|
g30v3 32bit AI No Flag
|
|
|
g30v4 16bit AI No Flag
|
|
|
g30v5 Short Float AI
|
|
|
Analog Input Deadband
|
g34v1 16bit AI Deadband
|
|
g34v2 32bit AI Deadband
|
|
|
g34v3 Short Float AI Deadband
|
|
|
Analog Input Dband_Ctrl
|
g34v1 16bit AI Deadband
|
|
g34v2 32bit AI Deadband
|
|
|
g34v3 Short Float AI Deadband
|
|
|
Analog Output
|
g40v1 32bit Analog Output
|
|
g40v2 16bit Analog Output
|
|
|
g40v3 Short Float AO
|
|
|
Read_Group
|
—
|
|
Read_Class
|
—
|
|
Write_Octet_String
|
—
|
|
Freeze_Counter
|
—
|
|
Unsolicited_Class
|
—
|
|
Time_Sync
|
—
|
|
Restart
|
—
|
|
Octet String
|
g110 Octet Strings
|
|
Integrity_Poll
|
—
|
|
Gen_Events
|
—
|
|
Clear_Events
|
—
|
|
Client Parameter
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Point Number
|
Indicates the start number of the point.
NOTE: Confirm that the DNP3 point number starts at 0 and is contiguous in slave/server mode. If this is not applied, the nonconsecutive points cannot work normally. |
|
|
Point Count
|
Indicates the number of points.
|
|
|
Store to CPU
|
Choose a source for the event time stamp and flag:
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register
|
|
|
Static Variation
|
Select the static variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Event Routing
|
Route Channel
|
|
|
Route Point
|
Point number to route. (This point number appears in the server side but cannot be modified on the server side.)
|
|
|
Event Class Mask
|
Defines the event class of points. Unsolicited is not allowed with class 0 only. In client, Channel is 0.
|
|
|
Default Event Variation
|
Indicates the default event variation for data point.
|
|
|
Routing Offline
|
Specify the flag when the routing channel is offline:
|
|
|
Server Parameter
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Point Number
|
Indicates the start number of the point.
NOTE: The DNP3 point number starts at 0 and is contiguous in slave/server mode. If this is not the case, the nonconsecutive points do not work normally. |
|
|
Point Count
|
indicates the number of points.
|
|
|
CPU Reg Mapping
|
Choose a source for the event time stamp and flag:
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register
|
|
|
Default Static Variation
|
Select the default static variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Default Event Variation
|
Select the default event variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Event Class Mask
|
Defines the event class of points. Unsolicited is not allowed with class 0 only. In client, Channel is 0.
|
|
|
PLC State
|
Specify the flag when the routing channel is offline:
|
|
|
Client Parameter
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Point Number
|
Indicates the start number of the point.
NOTE: Confirm that the DNP3 point number starts at 0 and is contiguous in slave/server mode. If this is not applied, the nonconsecutive points cannot work normally. |
|
|
Point Count
|
Indicates the number of points.
|
|
|
Store to CPU
|
Choose a source for the event time stamp and flag:
|
|
|
Static Variation
|
Select the static variation for the data point.,
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register
|
|
|
Display Deadband In Variable
|
Specify a deadband variable name.
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register when Display Deadband In Variable is selected (checked)
|
|
|
Event Routing
|
Channel
|
Enable or disable the routing of the channel number.
|
|
Route Point
|
Define the point number to route.
|
|
|
Event Class Mask
|
Defines the event class of points. Unsolicited is not allowed with class 0 only. In client, confirm that Channel is at 0.
|
|
|
Default Event Variation
|
Indicates the default event variation for data point.
|
|
|
Routing Offline
|
Specify the flag when the routing channel is offline:
|
|
|
Server Parameter
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Point Number
|
Indicates the start number of the point.
NOTE: Confirm that the DNP3 point number starts at 0 and is contiguous in slave/server mode. If this is not applied, the nonconsecutive points cannot work normally. |
|
|
Point Count
|
Indicates the number of points.
|
|
|
Event Class Mask
|
Defines the event class of points. Unsolicited is not allowed with class 0 only. In client, Channel is at 0 for normal operations.
|
|
|
Default Static Variation
|
Select the default static variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Default Event Variation
|
Select the default event variation for the data point.
|
|
|
CPU Reg Mapping
|
Choose a source for the event time stamp and flag:
|
|
|
Deadband
|
Deadband value of the analog input
|
|
|
Use Percent Data
|
Use low and high range for the percentage of deadband calculation when the check box is selected.
|
|
|
Low Range
|
Lowest value in the range when the Use Percent Data check box is selected.
|
|
|
High Range
|
Highest value in the range when the Use Percent Data check box is selected.
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register
|
|
|
PLC State
|
Specify the flag when the routing channel is offline:
|
|
|
Display Deadband In Variable
|
Specify a deadband variable name.
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register when the Display Deadband In Variable check box is selected.
|
|
|
Client Parameter
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Point Number
|
Indicates the start number of the point.
NOTE: Confirm that the DNP3 point number starts at 0 and is contiguous in slave/server mode. If this is not applied, the nonconsecutive points cannot work normally. |
|
|
Point Count
|
Indicates the number of points.
|
|
|
Operation Mode
|
The selected operation mode
|
|
|
Control Code Type
|
Specify the control code used by the CROB:
NOTE: Refer to the description of binary output behavior. |
|
|
Default Static Variation
|
Select the default static variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Pulse Duration
|
Specify the width of the pulse (ms).
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register
|
|
|
Add CMD_STATUS
|
Specify the CMD_STATUS variable name.
|
|
|
Server Parameter
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Point Number
|
Indicates the start number of the point.
NOTE: Confirm that the DNP3 point number starts at 0 and is contiguous in slave/server mode. If this is not applied, the nonconsecutive points cannot work normally. |
|
|
Point Count
|
Indicates the number of points.
|
|
|
TCC
|
When Trip_Close is enabled, the odd point in this configuration is a closed output, and the following point is a trip out when an outstation receives a close or trip command. Use an even number for the point count value when enabled.
|
|
|
Default Static Variation
|
Select the default static variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Default Event Variation
|
Select the default event variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Add Flag Variable
|
Specify the flag variable name.
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register when the Add Flag Variable check box is selected.
|
|
|
PLC State
|
Specify the flag when the routing channel is offline:
|
|
|
Prefix
|
This prefix for the variable name is followed with an underscore (_). Configure the prefix in the server advanced parameters.
Example: RTU001_Point1.
|
|
|
CPU Register Type
|
The only available option for the binary output is %MW.
|
|
|
CPU Register Address
|
This is the start %MW address in the CPU. This field applies only to located variables.
To create a variable without a %MW address, use the value -1.
Considerations:
|
|
|
Client Parameter
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Point Number
|
Indicates the start number of the point.
NOTE: Confirm that the DNP3 point number starts at 0 and is contiguous in slave/server mode. If this is not applied, the nonconsecutive points cannot work normally. |
|
|
Point Count
|
Indicates the number of points.
|
|
|
Operation Mode
|
Selected operation mode
|
|
|
Default Static Variation
|
Select the default static variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register
|
|
|
Add CMD_STATUS
|
Specify the CMD_STATUS variable name.
|
|
|
Server Parameter
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
Point Number
|
Indicates the start number of the point.
NOTE: Confirm that the DNP3 point number starts at 0 and is contiguous in slave/server mode. If this is not applied, the nonconsecutive points cannot work normally. |
|
|
Point Count
|
Indicates the number of points.
|
|
|
Event Class Mask
|
Defines the event class of points. Unsolicited is not allowed with class 0 only. In client, confirm that Channel is at 0.
|
|
|
Default Static Variation
|
Select the default static variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Default Event Variation
|
Select the default event variation for the data point.
|
|
|
Deadband
|
Deadband value of the analog point
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register
|
|
|
Add Flag Variable
|
Specify the flag variable name.
|
|
|
Point Name
|
Name of the unlocated register when the Add Flag Variable check box is selected.
|
|
|
PLC State
|
Specify the flag when the routing channel is offline:
|
|
|
Prefix
|
This prefix for the variable name is followed with an underscore (_). Configure the prefix in the server advanced parameters.
The final variable name follows this format:
Prefix_VariableName.Pointx.value
Example: RTU001_AO01.Point[10].value
|
|
|
CPU Register Type
|
The only available option for the analog output is %MW.
|
|
|
CPU Register Address
|
This is the start %MW address in the CPU. This field applies only to located variables.
To create a variable without a %MW address, use a start address of the type float/32 bit. A valid analog output type value is an even number. Use address -1.
Considerations:
|
|
|
TCC (Trip-Close Code)
|
Operation type field
|
Control code
|
Point model in outstation
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
None
|
pulse on
|
01 hex
|
activation
|
|
latch on
|
03 hex
|
latch complement
|
|
|
latch off
|
04 hex
|
||
|
Close
|
pulse on
|
41 hex
|
two’s complement
|
|
Trip
|
81 hex
|
|
CROB sent in DNP3 master
|
Point number in DNP3 master
|
Point number in DNP3 outstation
|
|---|---|---|
|
Pulse on
|
0
|
0
|
|
Trip/Pulse on
|
0
|
1
|
|
Close/Pulse on
|
2
|
2
|
|
Trip/Pulse on
|
2
|
3
|
|
Close/Pulse on
|
n+2
|
n+2
|
|
Trip/Pulse on
|
n+2
|
n+2+1
|
|
Op type field
|
Trigger mechanism
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|
|
Close/Pulse_on
|
any value change (0...65535)
|
pulse on if value change
|
|
Latch_on
|
0 to 1
|
latch on
|
|
Latch off
|
1 to 0
|
latch off
|
|
Close/Pulse_on
|
0 to 1
|
pulse on for close output
|
|
Trip/Pulse_on
|
1 to 0
|
pulse on for trip output
|
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Local Address
|
This field contains the source address for this session.
|
|
Master Address
|
This field contains the remote master (destination) address for this session.
|
|
Parameter
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Link Status Periodic
|
Configure the frequency (ms) for the transmission of status requests when no DNP3 frames are received during this session.
|
|
Validate Source Address
|
Check this box to validate the source address in received frames.
|
|
Enable Self Address
|
Check this box to have the slave respond to address 0xfffc as if it received a request at its configured address. The slave responds with its own address so that the master can automatically discover the slave address.
|
|
Multi Frag Resp Allowed
|
Check this box to allow the application to send multi-fragment responses.
|
|
Multi Frag Confirm
|
Check this box to request application layer confirmations for non-final fragments of a multi-fragment response. (Application layer confirmations are always requested for responses that contain events.)
|
|
Respond Need Time
|
Check this box to tell the device to set the Need Time IIN bit in response to this session at start-up after the clock valid period elapses.
|
|
Clock Valid Period
|
Configure the length of time (ms) that the local clock remains valid after it receives a time synchronization.
|
|
Application Confirm Timeout
|
Configure the length of time (ms) that the slave DNP3 device waits for an application layer confirmation from the master for a solicited response.
|
|
Select Before Operation (SBO) Timeout
|
Configure the maximum amount of time (ms) that a selection remains valid before the corresponding operate is received.
|
|
Warm Restart Delay
|
Configure the length of time that the master waits after it receives a response to a warm restart request. This value is encoded in a time delay fine object in the response of a warm restart request.
|
|
Cold Restart Delay
|
Configure the length of time (ms) that the master waits after it receives a response to a cold restart request. This value is encoded in a time delay fine object in the response of a cold restart request.
|
|
Allow Multi CROB Requests
|
Check this box to allow multiple control relay block objects (CROBs) in a single request.
|
|
Max Control Requests
|
Configure the maximum number of binary (CROB) or analog control outputs that are allowed in a single request.
|
|
Unsol Allowed
|
Check this box to allow unsolicited responses.
|
|
Send Unsol When Online
|
Check this box to send unsolicited null responses when the session comes online.
|
|
Unsol Class 1 Max Events
|
When unsolicited responses are enabled, configure this value to specify the maximum number of events in the corresponding class (1, 2, or 3) that are allowed before an unsolicited response is generated.
|
|
Unsol Class 2 Max Events
|
|
|
Unsol Class 3 Max Events
|
|
|
Unsol Class 1 Max Delay
|
Configure the maximum amount of time (ms) after an event in the corresponding class (1, 2, or 3) is received before an unsolicited response is generated.
|
|
Unsol Class 2 Max Delay
|
|
|
Unsol Class 3 Max Delay
|
|
|
Unsol Max Retries
|
Configure the maximum number of unsolicited retries before changing to the offline retries value.
|
|
Unsol Retry Delay
|
Configure the length of the delay (ms) after an unsolicited response.
|
|
Unsol Offline Retry Delay
|
Configure the length of the delay (ms) after an unsolicited timeout before retrying the unsolicited response after the configured number of Unsol Max Retries.
|
|
Delete Oldest Event
|
Configure the behavior for an event queue that is full:
|
|
Counts to Class0 Poll
|
Configure the type of value that is returned in a poll of class 0 data:
|
|
SBO Mode
|
Select a mode for a before-and-after operation:
|
|
Unsol Confirm Timeout
|
Configure the value for an unsolicited confirm timeout.
|
|
Data Synch Mode
|
Select a data synchronization mode:
|
|
Prefix
|
This string is part of the variable name for analog or binary output points when you select Synch On Demand as the Data Synch Mode (range: 1 ... 6).
Considerations:
|
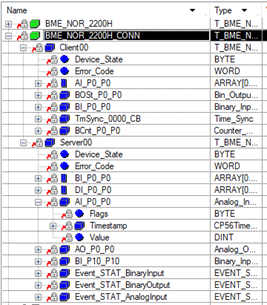
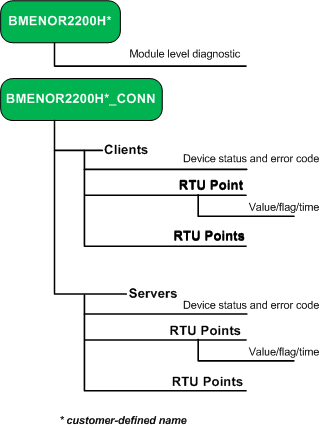
|
Parameter
|
Value Scope
|
Definition
|
|---|---|---|
|
Object Group
|
All Objects
Binary Input
Double Input
Binary Counter
Analog Input
Binary Output
Analog Output
|
Specifies the object group whose event is cleared o. demand
|
|
Variable Name
|
—
|
Indicates the name of the located register.
|
|
maximum
|
255 characters
|
|
default
|
16 characters
|