|
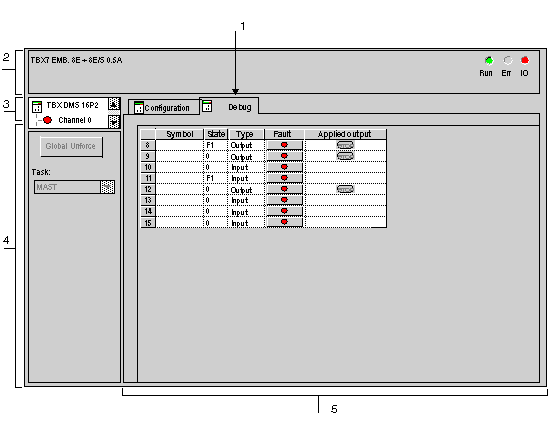
Description of the Debug Screen for a Discrete Remote Module
|
|
|
(Original Document)
|
|
Number
|
Element
|
Function
|
|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Tabs
|
The tab in the foreground indicates the mode in progress (Debug in this example). Every mode can be selected using the respective tab.
|
|
2
|
Module area
|
Specifies the abbreviated heading of the module.
In the same area there are 3 LEDs which indicate the module’s operating mode:
|
|
3
|
Channel area
|
Is used:
|
|
4
|
General parameters area
|
Gives a reminder of the channel setting:
|
|
5
|
Parameters in progress zone
|
This zone displays the state of the inputs and outputs, and the different parameters in progress.
For each of the channels, there are five columns:
|