Cause of a Warm Restart
A warm restart may be caused by a power restoral without loss of context.
| CAUTION | |
|---|---|
Illustration
The diagram below describes how a warm restart operates.
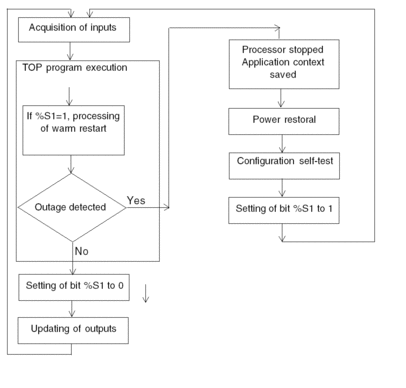
Operation
The table below describes the program execution restart phases on warm restart.
Phase |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Program execution doesn’t resume from the element where the power outage occurred. The remaining program is discarded during the warm start. Each task will restart from the beginning. |
2 |
At the end of the restart cycle, the system carries out the following:
|
3 |
The system performs a restart cycle during which it:
|
Processing a Warm Restart by Program
In the event of a warm restart, if you want the application to be processed in a particular way, you must write the corresponding program to test that %S1 is set to 1 at the start of the master task program.
SFC Warm start specific features
The Warm start on M340 PLCs is not considered as a real warm start by the CPU. SFC interpreter does not depend on tasks.
SFC publishes a memory area "ws_data" to the OS that contains SFC-section-specific data to be saved at a power fail. At the beginning of chart processing the currently active steps are saved to "ws_data" and processing is marked to be in "critical section". At the end of chart processing the "critical section" is unmarked.
If a power failure hits into "critical section" this could be detected if this state is active at the beginning (as the scan is aborted and MAST task is restarted from the beginning). In this case the workspace might be inconsistent and is restored from the saved data.
Additional information from SFCSTEP_STATE in located data area is used to reconstruct the state machine.
When a power failure occurs:
during first scan %S1 =1 Mast is executed but Fast and Event tasks are not executed.
On power restoral:
Clears chart, deregisters diagnostics, keeps set actions
sets steps from saved area
sets step times from SFCSTEP_STATE
restores elapsed time for timed actions
Output Changes
As soon as a power outage is detected, the outputs are set in the fallback position:
either they are assigned the fallback value,
or the current value is maintained,
depending on the choice made in the configuration.
After power restoral, the outputs stay in security mode (equal to 0) until they are updated by a running task.


