Cause of a Warm Restart
A warm restart may be caused:
by a power restoral without loss of context
by the system bit %S1 being set to 1 by the program
by Control Expert from the terminal
by pressing the RESET button of the power supply module of rack 0 (on Premium PLC)
Illustration
The diagram below describes how a warm restart operates.
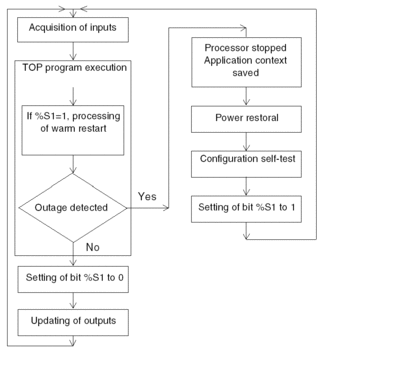
Operation
The table below describes the program execution restart phases on warm restart.
Phase |
Description |
|---|---|
1 |
Program execution resumes starting from the element where the power outage occurred, without updating the outputs. |
2 |
At the end of the restart cycle, the system carries out the following:
|
3 |
The system performs a restart cycle during which it:
|
Processing a Warm Restart by Program
In the event of warm restart, if you want the application to be processed in a particular way, you must write the corresponding program conditional on the test that %S1 is set to 1 at the start of the master task program.
For Quantum PLCs, the switch on the front panel of the processor can be used to configure operating modes. For further details, see Quantum documentation.
Output Changes, for Premium and Atrium
As soon as a power outage is detected, the outputs are set in the fallback position:
either they are assigned the fallback value, or
the current value is maintained.
depending on the choice made in the configuration.
After power restoral, the outputs remain in the fallback position until they are updated by the task.
Output Changes, for Quantum
As soon as a power outage is detected:
the local outputs are set to zero
the outputs of the remote or distributed extension racks are set in the fallback position
After power restoral, the outputs remain in the fallback position until they are updated by the task.
Output Changes, for Extension Rack
If power outage occurs on rack where CPU is located:
Fallback state as soon as CPU loss is detected
Security state during I/O configuration
State calculated by CPU after the first run of the task driving this output
After power is restored, the outputs remain in the fallback position until they are updated by the task


