|
Example for the PWM block
|
|
|
Original instructions
|
|
Parameters
|
Specification
|
|---|---|
|
t_period
|
4 s
|
|
t_min
|
0.2 s
|
|
t_max
|
3.8 s
|
|
t_pause
|
0.1 s
|
|
t_brake
|
0.2 s
|
|
up_pos
|
10
|
|
up_neg
|
10
|

Xanalog signal
|
Parameters
|
Specification
|
|---|---|
|
t_period
|
4 s
|
|
t_min
|
0.5 s
|
|
t_max
|
4 s
|
|
t_pause
|
0 s
|
|
t_brake
|
0 s
|
|
up_pos
|
10
|
|
up_neg
|
10
|
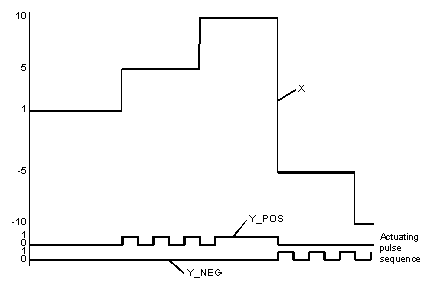
Xanalog signal