Predefined Configuration File Name
C5_RIOMainRingFxTx_RIOSubRingTx_DIOCloudsVx.xx.cfg, where
Vx.xx references the version number of the file.
Use of this Predefined Configuration
Common uses of this predefined configuration are to transition from a copper cable to a fiber cable on the main ring or to transition back from fiber to copper. An alternative use is to provide a long-haul return path for a basically copper network where the last RIO drop or RIO sub-ring in the daisy chain is far away from the local rack.
In any of the above scenarios, this predefined configuration allows you the opportunity to install an RIO sub-ring and/or some DIO clouds on the you are configuring.
Devices Supported by this Predefined Configuration
The DRS predefined configuration described here can be used with either of 2 switch types:
-
A TCSESM063F2CU1 ConneXium extended managed switch, which supports multi-mode fiber cable
-
A TCSESM063F2CS1 ConneXium extended managed switch, which supports single-mode fiber cable
Both switches have 2 fiber ports and 6 copper ports.
With single-mode fiber cable, you can achieve distances on the main ring up to 15 km. With multi-mode fiber cable, you can achieve distances up to 2 km.
Predefined Port Connections
The top fiber port (labeled 1 in the following figure) makes the connection to the fiber cable on the main ring (A). The other fiber port (port 2) is disabled in this predefined configuration; do not connect to this port.
The top left copper port (port 3) makes the connection to the copper cable on the main ring (A). Copper ports 5 and 6 are used to connect to the RIO sub-ring (B).
Ports 4 and 7 on the DRS are available for additional optional connections, and can be used to connect DIO clouds to the M580 system. Port 8 is reserved for
port mirroring, i.e., for monitoring the status of the ports you previously selected in the switch’s port mirror web page.
NOTE: The default configuration of port 8 has port mirroring disabled.
A
main ring (with copper/fiber connections)
B
RIO sub-ring
This table describes the functionality of the ports in the above illustration:
|
Port
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
1
|
FX
|
fiber main ring connection
|
|
3
|
100Base-TX
|
copper main ring connection
|
|
2
|
FX
|
disabled fiber port; do not use
|
|
4
|
100Base-TX
|
DIO cloud connection
|
|
5
|
100Base-TX
|
RIO sub-ring connection
|
|
6
|
100Base-TX
|
RIO sub-ring connection
|
|
7
|
100Base-TX
|
DIO cloud connection
|
|
8
|
100Base-TX
|
port mirroring connection
|
Except when enabling or disabling ports that are not connected to either a main ring or a sub-ring, do not adjust the configuration parameters or alter the port usage in the predefined configuration file. Changing the configuration parameters or the port assignments can compromise the effectiveness and accuracy of the switch, as well as the performance of the RIO network.
Port mirroring is disabled by default. If you enable port mirroring, you can select the ports on which you want to analyze traffic as the source ports. Ports 1-7 can be selected as source ports. Port 8 is the destination port, and it cannot be changed.
Supporting the Fiber-to-Copper Transition on the Main Ring
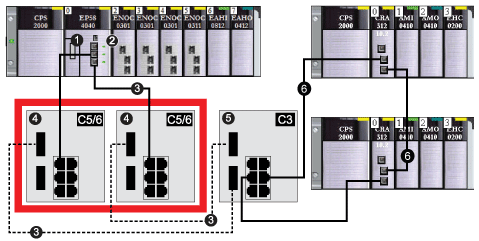
RIO devices in the main ring often do not come equipped with fiber connectors. Therefore, some part of the main ring requires copper cable. Typically, 2 DRSs are each configured to support 1 fiber and 1 copper connection to the main ring.
Connect the DRS directly to the in the local rack:
1
CPU with Ethernet I/O scanner service on the local rack
2
BMENOC0301/11 Ethernet communication module
3
copper/fiber main ring
4
two DRSs with a C5 or C6 predefined configuration file that use only 1 fiber port to support copper-to-fiber or fiber-to-copper transitions
5
DRS with a C3 predefined configuration file that uses both of the main ring fiber ports and both of the RIO sub-ring copper ports
6
RIO sub-ring
NOTE: A BMENOC0301/11 module can support distributed equipment via its Ethernet backplane connection to the CPU and via its device network port(s) on the front panel, respecting the limitation of 128 devices scanned per BMENOC0301/11 module.
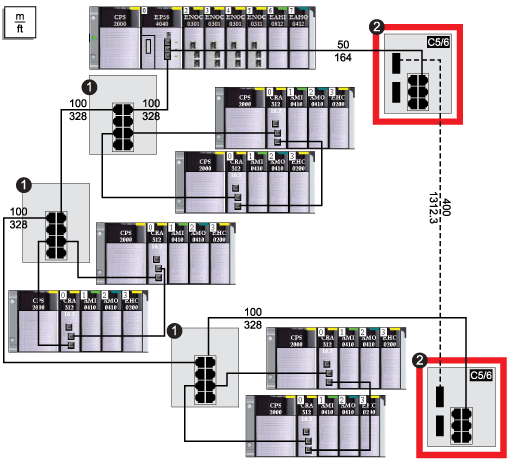
Suppose your application calls for several RIO drops. The distance between the first drop and local rack is no more than 100 m, and the distance between consecutive RIO drops is not more than 100 m. The overall distance between the CPU and the last drop, however, is significantly more than 100 m, for example, a distance of 400 m from the local rack.
In this case, you may be able to get the distance you need using less expensive copper connections on the front end of the high capacity daisy chain, and then closing the loop with 1 fiber optic connection:
1
These 3 DRSs are configured for a copper main ring and a copper sub-ring.
2
These 2 DRSs have C5 or C6 predefined configuration files to facilitate a fiber-to-copper transition on the main ring. 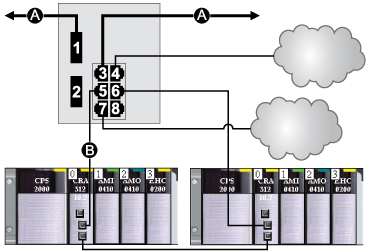
 WARNING
WARNING