At a Glance
That example deals with 2 Modicon M340 processors which communicate via Modbus serial link.
Description of the Example
The following example uses unlocated variables, and covers the
writing of an unlocated 50-word table named Tab_1 (declared as an ARRAY [0..49] OF INT) in the Modbus
slave. The management parameters are located in a table of 4 integers
called Management_Parameter (declared as ARRAY [0..3] OF INT).
In that example, the Modbus
slave’s number is 7, so the input ADDM parameter
is ‘0.0.0.7’:
0: rack number of the processor equal to 0
0: slot number of the processor within the rack, equal to 0 as the slot number of a Modicon M340 processor is always 0
0: channel number, equal to 0 as the serial link of a Modicon M340 processor is always channel 0
7: configured slave number is 7.
The values to write are in the variable Tab_1 of the sender.
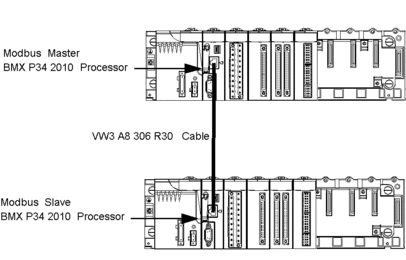
Illustration
The two Modicon 340 processors are connected via a Modbus link:
Programming
Programming in ST:
IF RE(%I0.3.1) AND NOT Management_Parameter[0].0 THEN WRITE_VAR(ADDM(’0.0.0.7’),’%MW’,0,50,Tab_1,Management_Parameter);END_IF;The request parameters are as follows:
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
ADDM(’0.0.0.7’) |
|
’%MW’ |
Type of object (internal word) |
0 |
address of the first object to write |
50 |
Number of consecutive objects to write |
Tab_1 |
Data to write |
Management_Parameter |
Management table |


