|
Configuring the DHCP and FDR Servers
|
|
|
(Original Document)
|
|
Step
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Select the Services node in the navigation tree located on the left side of the Device Editor. The Services page opens.
|
|
2
|
In the Services page, set the Address Server field to Enabled. The Address Server node appears in the navigation tree.
|
|
3
|
Select the Address Server node in the navigation tree.
|
|
Step
|
Description
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
1
|
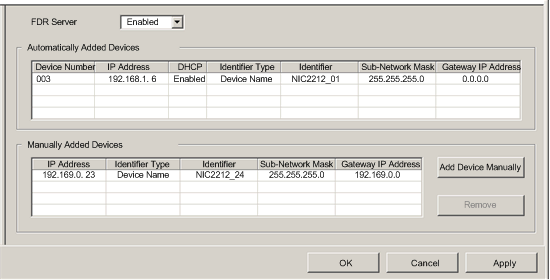
In the Address Server page, click the Add Device Manually button. Control Expert adds an empty row to the list of Manually Added Devices.
|
|
|
2
|
In the new row, configure the following parameters for the client device:
|
|
|
IP Address
|
Type in the IP address of the client device.
|
|
|
Identifier Type
|
Select the type of value the client device will use to identify itself to the FDR server:
|
|
|
Identifier
|
Depending upon the identifier type, type in the client device setting for the MAC address or Name.
|
|
|
Mask
|
Type in the client device subnet mask.
|
|
|
Gateway
|
Type in the gateway address used to access a remote client device. Use 0.0.0.0 if the device is located on the same subnet as the server.
|
|
|
3
|
Refer to the topic Configuring Properties in the Device Editor for instructions on how to apply edited properties to networked devices.
|
|
|
Property
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Device Number
|
The number assigned to the device in the Control Expert configuration.
|
|
IP Address
|
The client device IP address.
|
|
Enable DHCP
|
TRUE indicates that the device subscribes to the DHCP service.
|
|
Identifier Type
|
Indicates the mechanism used by the server to recognize the client (MAC address or DHCP device name).
|
|
Identifier
|
The actual MAC address or DHCP device name.
|
|
Mask
|
The client device subnet mask.
|
|
Gateway
|
The IP address a DHCP client device will use to access other devices that are not located on the local subnet. A value of 0.0.0.0 constrains the DHCP client device by allowing it to communicate only with devices on the local subnet.
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
1
|
In the DTM Browser, select the Ethernet communication module that is connected to the remote device that you want to add to the DHCP service. In the following example, the communication module with the alias name of ETC01 is selected:
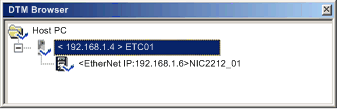 NOTE: The selected module is connected to the STB NIC 2212 network interface device bearing the alias name NIC2212_01, which is the module you want to add to the DHCP service. |
|
|
2
|
With ETC01 selected in the DTM Browser, click the right mouse button, and select Open in the pop-up menu.:
 The Device Editor opens.
|
|
|
3
|
In the navigation tree on the left side of the Device Editor, expand the Device List node and select the device for which you want to enable the DHCP service. In this example, select NIC2212_01:
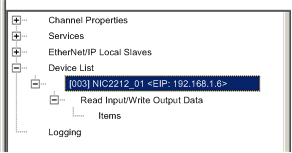 Control Expert displays the properties for the selected remote device in the right pane of the window.
|
|
|
4
|
In the right pane of the window, select the Address Setting tab to display the following page:
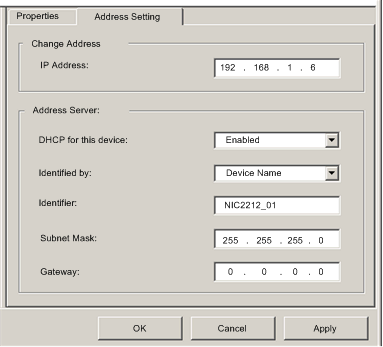 |
|
|
5
|
In the Address Server area of this page, configure the following properties:
|
|
|
DHCP for this device
|
Select Enabled
|
|
|
Identified by
|
The choices are:
Select Device Name.
|
|
|
Identifier
|
Control Expert has automatically added the device name NIC2212_01. For the purpose of this example, accept the default value.
|
|
|
Subnet Mask
|
Control Expert has automatically applied the same subnet mask used for the Ethernet communication module. For the purpose of this example, accept the default value of 255.255.255.0.
|
|
|
Gateway
|
Control Expert has automatically applied the same gateway used for the Ethernet communication module. For the purpose of this example, accept the default value of 0.0.0.0.
|
|
|
6
|
Click OK to save your edits.
NOTE: Refer to the topic Configuring Properties in the Device Editor for more information on editing and saving property settings in this window. |
|