-
select a Configuration mode, which specifies how the communication module obtains its IP addressing settings, and
-
edit the IP addressing settings that will be used if the Configuration mode is set to Static
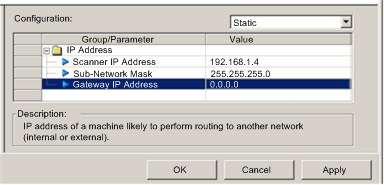
The TCP/IP page looks like this:
To display this page, select the Channel Properties → TCP/IP node in the navigation tree located on the left side of the Device Editor.
Selecting a Configuration Mode
Use the Configuration list to specify a configuration mode. The configuration mode setting determines how the communication module obtains its IP address at startup. Choices are:
|
Configuration Mode
|
Description
|
|
Static
|
The module uses the scanner IP address, gateway IP address, and sub-network mask configured in this page.
|
|
Flash Memory
|
The module uses the IP address configured via the TCP/IP object and stored flash memory. An IP address configured by this process survives both a warm and a cold re-start.
|
|
BOOTP
|
The module uses an IP address assigned by a BOOTP server.
|
Setting the Module Addresses in Static Mode
Three IP address properties need to be configured for the Ethernet communication module in Static configuration mode:
|
Property
|
Description
|
|
Scanner IP Address
|
The 32-bit identifier—consisting of both a network address and a host address—assigned to a device connected to a TCP/IP Internet network using the Internet Protocol (IP).
|
|
Sub-Network Mask
|
The 32-bit value used to hide (or mask) the network portion of the IP address and thereby reveal the host address of a device on a network using the IP protocol.
|
|
Gateway Address
|
The address of a device, if any, that serves as a gateway to the communication module.
|
Default Address Configurations
The communication module uses a default address configuration when it is not configured or when a duplicate IP address is detected. The default address is based on the MAC address of the module and makes it possible for several Schneider Electric devices to use their default network configuration on the same network.
The module uses the following default address configurations:
-
Default IP Address
This default address starts with 10.10 and uses the last two bytes of the MAC address. As an example, a device with the MAC address of 00:00:54:10:8A:05 has a default IP address of 10.10.138.5 (0x8A=138, 0x05=5).
-
Default Sub-Network Mask
The default address is 255.0.0.0 (a class A mask).
-
Default Gateway Address
The default gateway address is identical to the default IP address.
Duplicate Address Checking
Before going online, the module sends out at least four ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) messages with a proposed IP address:
NOTE: When powering up an entire network, some switches may be slow to complete the power up process. THis slow switch responce can cause some ARP messages to be dropped. To help improve performance when powering up an entire network, confirm that the network switches complete their power up cycle before powering up the PLCs.