Modicon M580 system and the traffic managed in its network is strictly regulated by switch configuration parameters like Identifier (VLAN-ID), , and . This along with protocol helps to ensure deterministic RIO performance.
Hence, to integrate Modicon M580 system in an open Ethernet network, it is imperative that the industrial Ethernet managed switches incorporate management of these features in its configuration.
Then design your architecture following the principles described in:
Point-to-Point Connection
The first principle is a point-to-point connection only using the service port of the M580 CPU and BM•CRA31210 adapter modules to connect to the industrial Ethernet managed switches.
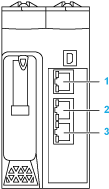
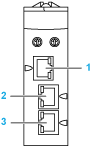
The following figures show the location of the service port of the modules:
|
M580 CPU
|
BM•CRA31210 adapter module
|
|
|
|
1 Service port (ETH1)
2 Device Network port (ETH2)
2 Device Network port (ETH3)
|
The device network ports have VLAN tagging as well as RSTP enabled whereas the service ports are configured to strip existing VLAN tags and do not support RSTP.
By using the service port only, you eliminate the possibility of device modification of packets with VLAN tagging and RSTP-based network recovery.
The service port of each module in the open Ethernet network (M580 CPU and BM•CRA31210 adapter modules) is connected to its dedicated port of the industrial Ethernet managed switch.
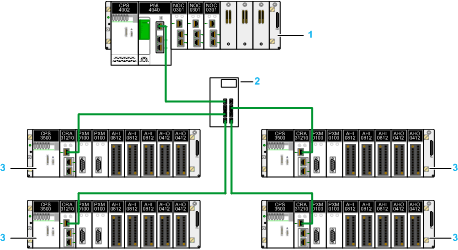
The following figure illustrates the point-to-point connection principle using only the service port of the modules in the network:
1
Modicon M580 CPU
2
Industrial Ethernet managed switch
3
X80 RIO drop
To prevent from interference with pre-existing device network port parameter configuration, make sure that only the service ports of the M580 CPU and BM•CRA31210 adapter modules are connected to the industrial Ethernet managed switching. If this verification is not done you can have a bandwidth overload of service port of the switch.
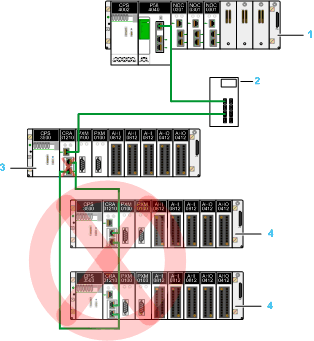
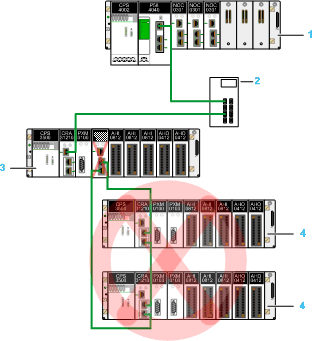
You cannot create a daisy chain loop from an RIO drop connected to the industrial Ethernet managed switch:
1
Modicon M580 CPU
2
Industrial Ethernet managed switch
3
X80 RIO drop connected to the open Ethernet network
4
X80 RIO drops in a daisy chain loop using the device network ports of the X80 adapter module.
When M580 system is integrated in an open Ethernet network, Schneider Electric recommends not to use BMENOS0300 modules to connect RIO/DIO devices and/or RIO/DIO sub-ring:
1
Modicon M580 CPU
2
Industrial Ethernet managed switch
3
X80 RIO drop connected to the open Ethernet network
4
X80 RIO drop in a sub-ring connected to the BMENOS0300 module.
The second principle is to assign dedicated and unique VLAN-IDs to separate the traffic generated by the M580 system in the open Ethernet network.
For example, if the network has a process M580 CPU that scans several X80 RIO drops, assign the same VLAN-ID to the ports of the switch to which the adapter modules of the RIO drops are connected. This assignment creates a VLAN isolation for the process M580 CPU and its scanned modules.
Create as many as necessary group of participants by assigning a dedicated and unique VLAN-ID to:
-
Process CPU and its scanned RIO drops (VLAN-x)
-
Safety CPU and its scanned safety RIO drops and CIP safety devices (VLAN-y)
-
BMENOC•••• module and its connected DIO devices (VLAN-z)
-
And so on
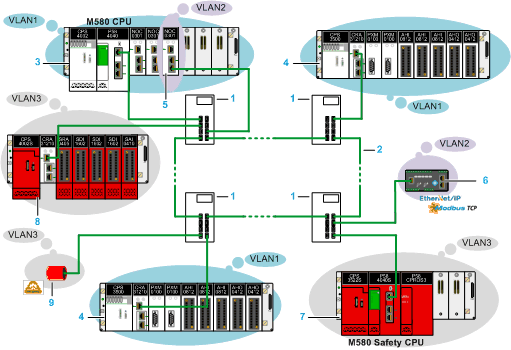
The following figure illustrates the VLAN isolation for three groups of network participants:
1
Industrial Ethernet managed switch
2
Ring configuration and operation configured as per the switch manufacturer recommendations
3
Modicon M580 CPU with Ethernet I/O scanner assigned to VLAN1
4
X80 RIO drop scanned by the Modicon M580 CPU
5
Modicon BMENOC•••• module assigned to VLAN2
6
DIO device (for example, EtherNet/IP or Modbus TCP) scanned by the BMENOC•••• module
7
Modicon M580 safety CPU with Ethernet I/O scanner assigned to VLAN3
8
Safety X80 RIO drop scanned by the Modicon M580 safety CPU
9
CIP Safety device