|
IO Configuration
|
|
|
|
|
Address
|
Element
|
Function
|
|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Tabs
|
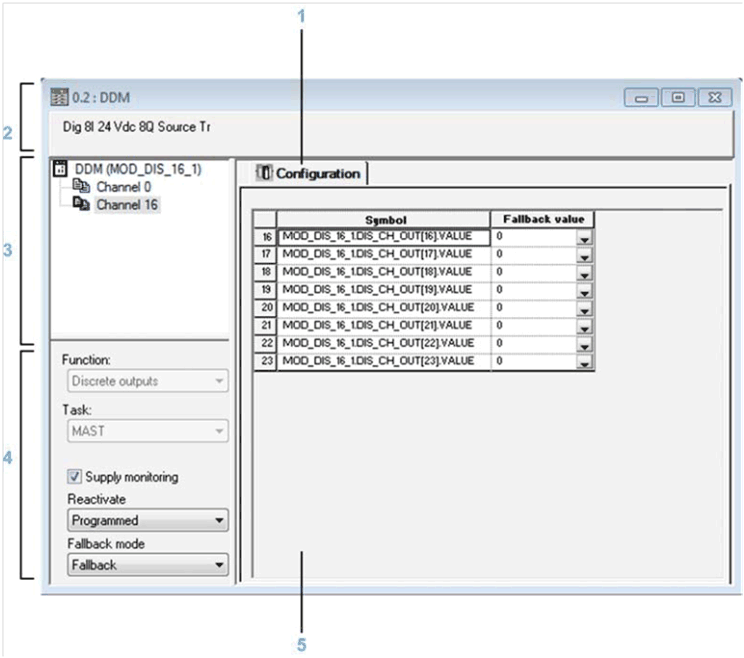
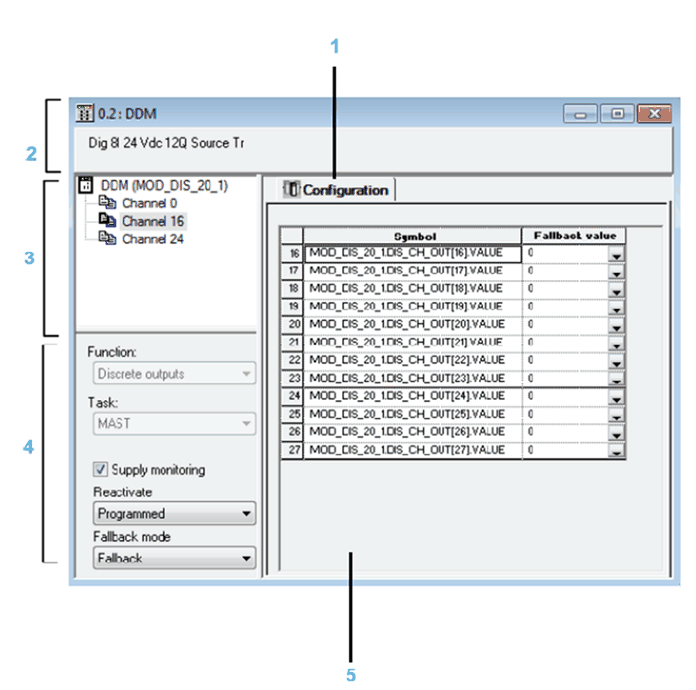
The tab in the foreground indicates the mode in progress (Configuration in this example). Every mode can be selected using the respective tab:
|
|
2
|
Module area
|
Specifies the abbreviated heading of the module.
|
|
3
|
Channel area
|
Allows you:
NOTE: All channels are activated and a channel cannot be de-activated to None. |
|
4
|
General parameters area
|
Allows you to select the associated function and task in groups of 8 channels:
The Supply monitoring check box defines the active or inactive state of the external power supply monitoring.
The Reactivate and Fallback mode drop-down menus enable you to configure the output reset and output fallback mode.
|
|
5
|
Configuration area
|
Enables the configuration of parameters for the various channels. This field includes various items, displayed according to the selected discrete module.
The Symbol column displays the symbol associated with the channel.
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Open the desired module configuration screen.
|
|
2
|
Check the Supply monitoring check box in the General Parameters area.
Result : The I/O editor window appears. Click OK.
|
|
3
|
Validate the change by clicking Edit → Validate.
|
|
Mode
|
Meaning
|
|---|---|
|
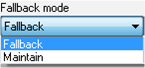
Fallback
|
Channels are set to 0 or 1 according to the defined fallback value for the corresponding 8-channel group.
|
|
Maintain
|
The outputs remain in the status they were in before switching to Stop.
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Open the desired module configuration screen.
|
|
2
|
For the desired channel group, click the arrow of the Fallback mode drop-down menu.
Result : The following list appears
 |
|
3
|
Select the desired fallback mode.
|
|
4
|
For Fallback mode, configure each channel of the selected group.
To do this, click the drop-down menu arrow of the channel to be configured, located in the Fall Back Value column.
|
|
5
|
Click the desired value (0 or 1).
|
|
6
|
Confirm the modification with the Edit → Validate menu command.
|
|
Mode
|
Meaning
|
|---|---|
|
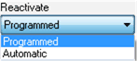
Programmed
|
Reactivation is executed with a command from the PLC application or through the appropriate debug screen.
Remark : In order to avoid repeated reactivations, the module implements an automatic 10 s delay between two resets.
|
|
Automatic
|
The reactivation is executed automatically every 10 s until the error disappears.
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Open the desired module configuration screen.
|
|
2
|
For the desired channel group, click the arrow of the Reactivate drop-down menu.
Result : The following list appears.
 |
|
3
|
Select the required reactivate mode.
|
|
4
|
Validate the modification by clicking Edit → Confirm.
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
bit #
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MOD_HEALTH
|
BOOL
|
-
|
0 = the module has a detected error
1 = the module is operating correctly
|
Read
|
|
|
MOD_FLT
|
BYTE
|
-
|
Internal detected errors bytes of the module
|
Read
|
|
|
DIS_CH_IN[0...7]
|
T_MC80_DIS_STD_CH_IN
|
-
|
Array [0...7] of T_MC80_DIS_STD_CH_IN
|
-
|
|
|
DIS_CH_OUT[16...23]
|
T_MC80_DIS_STD_CH_OUT
|
-
|
Array [16...23] of T_MC80_DIS_STD_CH_OUT
|
-
|
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
bit #
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MOD_HEALTH
|
BOOL
|
-
|
0 = the module has a detected error
1 = the module is operating correctly
|
Read
|
|
|
MOD_FLT
|
BYTE
|
-
|
Internal detected errors bytes of the module
|
Read
|
|
|
DIS_CH_IN[0...7]
|
T_MC80_DIS_STD_CH_IN
|
-
|
Array [0...7] of T_MC80_DIS_STD_CH_IN
|
-
|
|
|
DIS_CH_OUT[16...27]
|
T_MC80_DIS_STD_CH_OUT
|
-
|
Array [16...27] of T_MC80_DIS_STD_CH_OUT
|
-
|
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
bit #
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CH_HEALTH
|
BOOL
|
-
|
0 = the channel is inactive, including input power supply lose, input power supply under voltage, or over temperature
1 = the channel is active
|
Read
|
|
|
VALUE
|
EBOOL
|
|
indicates the status of the sensor controlling the input channel
|
Read
|
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
bit #
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CH_HEALTH
|
BOOL
|
-
|
0 = the channel is inactive.
1 = the channel is active
|
Read
|
|
|
VALUE
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
indicates the status of the sensor controlling the output channel
|
Read /Write
|
|
|
CH_FLT [INT]
|
EXT_PS_FLT
|
BOOL
|
3
|
Internal detected error: module out of order
|
Read
|
|
SHORT_CIRCUIT
|
BOOL
|
8
|
External detected error: short-circuit on a channel
|
Read
|
|
|
REACTIVATION
|
BOOL
|
-
|
Reactivation
|
Read /Write
|
|
|
Address
|
Element
|
Function
|
|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Tabs
|
The tab in the foreground indicates the mode in progress (Configuration in this example). Every mode can be selected using the respective tab:
|
|
2
|
Module area
|
Specifies the abbreviated heading of the module.
|
|
3
|
Channel area
|
Allows you:
NOTE: All channel are activated and a channel cannot be de-activated to None. |
|
4
|
General parameters area
|
This is used to set up the channels using several fields:
Task: Defines the MAST task through which the exchanges between the processor and the module will be carried out.
Cycle: Allows you to define the scan cycle for inputs (only available on some analog modules).
|
|
5
|
Configuration area
|
This is used to define the configuration parameters of the different channels. This area includes several topics, whose display varies depending on the analog module you've selected.
The Symbol column displays the symbol associated with the channel.
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Access the hardware configuration screen for the appropriate module
|
|
2
|
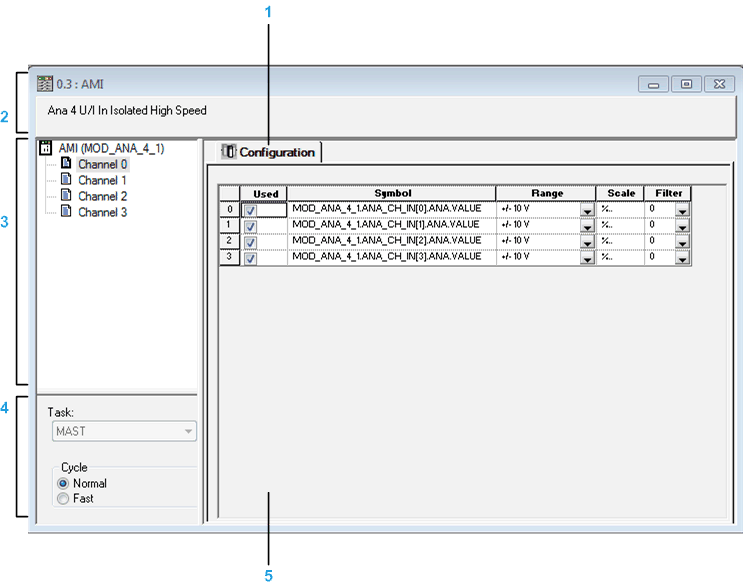
In the Range column, click the arrow of the drop-down menu pertaining to the channel you need to configure.
Result : The following list appears
 |
|
3
|
Select the appropriate range.
|
|
4
|
Validate the change by clicking Edit → Validate.
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Access the hardware configuration screen for the appropriate module.
|
|
2
|
Click the cell of the Scale column for the channel you need to configure.
Result: An arrow appears.
|
|
3
|
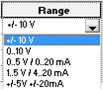
Click the arrow in the cell of the Scale column for the channel you need to configure.
Result: The Channel Parameters dialog box appears.
 NOTE: The display modification change only concerns the Scale area. The Overflow area enables the modification of the overflow control. |
|
4
|
Type in the values to be assigned to the channel in the two Display boxes situated in the Scale zone.
|
|
5
|
Confirm your changes by closing the dialog box.
NOTE: If default values have been selected (standardized display), the corresponding cell in the Scale column displays %... Otherwise it will show User (user display). |
|
6
|
Validate the change by clicking Edit → Validate.
|
|
Step
|
Action
|
|---|---|
|
1
|
Access the hardware configuration screen for the appropriate module.
|
|
2
|
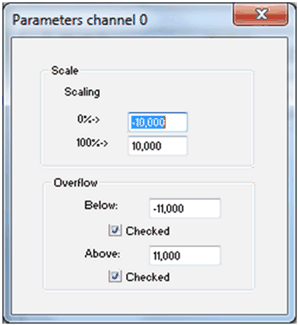
In the Filter column, click the arrow of the drop-down menu pertaining to the channel you need to configure.
Result : The drop-down menu appears.
 |
|
3
|
Select the filter value you need to assign to the selected channel.
|
|
4
|
Validate the change by clicking Edit → Validate.
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
Bit #
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MOD_HEALTH
|
BOOL
|
-
|
0 = the module has a detected error
|
Read
|
|
-
|
1 = the module is operating correctly
|
|||
|
MOD_FLT
|
BYTE
|
-
|
Internal detected errors bytes of the module
|
Read
|
|
ANA_CH_IN[0...3]
|
T_MC80_ANA_STD_CH_IN
|
-
|
Array of structure
|
-
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
Bit #
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
FCT_TYPE
|
WORD
|
-
|
0 = channel is not used
1 = channel is used
|
Read
|
|
|
CH_HEALTH
|
BOOL
|
-
|
0 = the channel is inactive
1 = the channel is active
|
Read
|
|
|
CH_WARNING
|
BOOL
|
-
|
0 = no detected warning on the channel
1 = detected warning on the channel
|
Read
|
|
|
ANA
|
T_MC80_ANA_VALUE_IN
|
-
|
Analog input structure
|
-
|
|
|
MEASURE_STS [INT]
|
CH_ALIGNED
|
BOOL
|
0
|
Aligned channel
|
Read
|
|
LOWER_LIMIT
|
BOOL
|
5
|
Measurement within lower tolerance zone
|
Read
|
|
|
UPPER_LIMIT
|
BOOL
|
6
|
Measurement within upper tolerance zone
|
Read
|
|
|
INT_OFFSET_ERROR
|
BOOL
|
8
|
Internal offset error
|
Read
|
|
|
IN_REF_ERROR
|
BOOL
|
10
|
Internal reference error
|
Read
|
|
|
POWER_COM_ERROR
|
BOOL
|
11
|
Power supply error
|
Read
|
|
|
SPI_COM_ERROR
|
BOOL
|
12
|
SPI communication error
|
Read
|
|
|
CH_FLT [INT]
|
SENSOR_FLT
|
BOOL
|
0
|
External fault: sensor link fault
|
Read
|
|
RANGE_UNF
|
BOOL
|
1
|
External fault: Range under fault
|
Read
|
|
|
RANGE_OVF
|
BOOL
|
2
|
External fault: Range overrun fault
|
Read
|
|
|
EXTERNAL_FLT
|
BOOL
|
3
|
External fault: channel error report
|
Read
|
|
|
INTERNAL_FLT
|
BOOL
|
4
|
Internal fault: channel inoperative
|
Read
|
|
|
CONF_FLT
|
BOOL
|
5
|
Hardware or software configuration fault
|
Read
|
|
|
COM_FLT
|
BOOL
|
6
|
Bus communication fault
|
Read
|
|
|
APPLI_FLT
|
BOOL
|
7
|
Application fault
|
Read
|
|
|
NOT_READY
|
BOOL
|
8
|
Channel not ready
|
Read
|
|
|
CALIB_FLT
|
BOOL
|
9
|
Calibration fault
|
Read
|
|
|
ALIGNMENT_CURRENT_VALUE
|
INT
|
-
|
Current value of alignment
|
Read
|
|
|
FILTER_CURRENT_VALUE
|
INT
|
-
|
Current value of filter
|
Read
|
|
|
ALIGNMENT_PRESET_VALUE
|
INT
|
-
|
Preset value of alignment
|
Write
|
|
|
FILTER_PRESET_VALUE
|
INT
|
-
|
Present value of filter (0...6)
|
Write
|
|
|
CMD_ALIGNMENT
|
BOOL
|
-
|
Rising edge: execute command to change alignment with the preset alignment value
|
Write
|
|
|
CMD_FILTER
|
BOOL
|
-
|
Rising edge: execute command to change filter with the preset filter value
|
Write
|
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
Bit #
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VALUE
|
INT
|
-
|
Analog input value
|
Read
|
|
FORCED_VALUE
|
INT
|
-
|
Forced value
|
Read/Write
|
|
FORCE_CMD
|
BOOL
|
-
|
Force command
|
Read/Write
|
|
FORCED_STATE
|
BOOL
|
-
|
Forced state
|
Read
|
|
TRUE_VALUE
|
INT
|
-
|
Physical value
|
Read
|

|
Address
|
Element
|
Function
|
|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Tabs
|
The tab in the foreground indicates the mode in progress (Configuration in this example). Every mode can be selected using the respective tab:
|
|
2
|
Module area
|
Displays the name and status of a function.
Is used:
|
|
3
|
Channel area
|
Allows you:
NOTE: All channels are activated and a channel cannot be de-activated to None. |
|
4
|
General parameters area
|
Allows you to select the counting function and the task associated with the channel:
Function: Counting function among those available for the modules involved. Depending on this choice, the headings of the configuration area may differ. By default, in Frequency Mode no function is configured.
Task: defines the MAST task through which the channel's implicit exchange objects will be exchanged. These choices are only possible in offline mode.
NOTE: In Configuration view, the events are not managed. |
|
5
|
Parameters in progress area
|
This area has various functionalities which depend upon the current mode:
Configuration: It is used to configure the channel parameters.
NOTE: The Input and Output fault parameters are set by default with the value Local or General IO Fault. |
|
Label
|
Configurable Values
|
|---|---|
|
IN_A input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: low,
2: medium,
3: high.
|
|
Input power supply fault
|
0:General input fault mode
1:Local input fault mode
|
|
Output power supply fault
|
0:General output fault mode
1:Local output fault mode
|
|
Scale factor
|
Edit (value in the range 1...255)
|
|
Output block 0
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
|
|
Output block 1
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
|
|
Pulse width 0
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Pulse width 1
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Polarity 0
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Polarity 1
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Fault recovery
|
Automatic reaction
Activated
|
|
Fallback 0
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback 1
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback value 0
|
0
1
|
|
Fallback value 1
|
0
1
|
|
Label
|
Configurable Values
|
|---|---|
|
IN_A input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_SYNC input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
Input power supply fault
|
0:General input fault mode
1:Local input fault mode
|
|
Output power supply fault
|
0:General output fault mode
1:Local output fault mode
|
|
Synchronization edge
|
0:Rising edge at IN_SYNC
1:Falling edge at IN_SYNC
|
|
Time base
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: 0.1 s,
1: 1 s,
2: 10 s,
3: 1 min.
|
|
Output block 0
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
|
|
Output block 1
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
|
|
Pulse width 0
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Pulse width 1
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Polarity 0
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Polarity 1
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Fault recovery
|
Automatic reaction
Activated
|
|
Fallback 0
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback 1
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback value 0
|
0
1
|
|
Fallback value 1
|
0
1
|
|
Label
|
Configurable Values
|
|---|---|
|
IN_A input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_SYNC input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
Input power supply fault
|
0:General input fault mode
1:Local input fault mode
|
|
Output power supply fault
|
0:General output fault mode
1:Local output fault mode
|
|
Resolution
|
This parameter can take the following values :
0: 1 ΅s,
1: 100 ΅s,
2: 1 ms.
|
|
Mode
|
This parameter can take the following values :
0: From one edge to the same edge at input IN_A,
1: From one edge to the opposite edge at input IN_A.
|
|
Time out
|
1... 1073741823
|
|
Output block 0
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
|
|
Output block 1
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
|
|
Pulse width 0
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Pulse width 1
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Polarity 0
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Polarity 1
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Fault recovery
|
Automatic reaction
Activated
|
|
Fallback 0
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback 1
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback value 0
|
0
1
|
|
Fallback value 1
|
0
1
|
|
Label
|
Configurable Values
|
|---|---|
|
IN_A input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_B input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
Input power supply fault
|
0:General input fault mode
1:Local input fault mode
|
|
Output power supply fault
|
0:General output fault mode
1:Local output fault mode
|
|
Absolute limit
|
Edit
|
|
Output block 0
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
|
|
Output block 1
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
|
|
Pulse width 0
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Pulse width 1
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Polarity 0
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Polarity 1
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Fault recovery
|
Automatic reaction
Activated
|
|
Fallback 0
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback 1
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback value 0
|
0
1
|
|
Fallback value 1
|
0
1
|
|
Label
|
Configurable Values
|
|---|---|
|
IN_A input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_SYNC input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_EN input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
Input power supply fault
|
0:General input fault mode
1:Local input fault mode
|
|
Output power supply fault
|
0:General output fault mode
1:Local output fault mode
|
|
Scale factor
|
Edit (value in the range 1...255)
|
|
Synchronization edge
|
0:Rising edge at IN_SYNC
1:Falling edge at IN_SYNC
|
|
Output block 0
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
8: Counter Stop
9: Counter Run
|
|
Output block 1
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
8: Counter Stop
9: Counter Run
|
|
Pulse width 0
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Pulse width 1
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Polarity 0
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Polarity 1
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Fault recovery
|
Automatic reaction
Activated
|
|
Fallback 0
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback 1
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback value 0
|
0
1
|
|
Fallback value 1
|
0
1
|
|
Label
|
Configurable Values
|
|---|---|
|
IN_A input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_B input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_SYNC input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_EN input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
Input power supply fault
|
0:General input fault mode
1:Local input fault mode
|
|
Output power supply fault
|
0:General output fault mode
1:Local output fault mode
|
|
Interface mode
|
0: A = High, B = Low,
1: A = Pulse, B = Direction,
2: normal quadrature 1,
3: normal quadrature 2,
4: normal quadrature 4,
5: inverse quadrature 1,
6: inverse quadrature 2,
7: inverse quadrature 4.
|
|
Scale factor
|
Edit (value in the range 1...255)
|
|
Synchronization edge
|
0:Rising edge at IN_SYNC
1:Falling edge at IN_SYNC
|
|
Output block 0
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
10: Capture0 Low Out is High level if Capture value < LT
11: Capture0 In window Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
12: Capture0 High Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
|
|
Output block 1
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
10: Capture0 Low Out is High level if Capture value < LT
11: Capture0 In window Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
12: Capture0 High Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
|
|
Pulse width 0
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Pulse width 1
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Polarity 0
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Polarity 1
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Fault recovery
|
Automatic reaction
Activated
|
|
Fallback 0
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback 1
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback value 0
|
0
1
|
|
Fallback value 1
|
0
1
|
|
Label
|
Configurable Values
|
|---|---|
|
IN_A input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_B input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_SYNC input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_EN input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_REF input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
IN_CAP input filter
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: Without,
1: Low,
2: Medium,
3: High.
|
|
Input power supply fault
|
0:General input fault mode
1:Local input fault mode
|
|
Output power supply fault
|
0:General output fault mode
1:Local output fault mode
|
|
Interface mode
|
0: A = High, B = Low,
1: A = Pulse, B = Direction,
2: normal quadrature 1,
3: normal quadrature 2,
4: normal quadrature 4,
5: inverse quadrature 1,
6: inverse quadrature 2,
7: inverse quadrature 4.
|
|
Scale factor
|
Edit (value in the range 1...255)
|
|
Preset mode
|
The least significant byte can take the following values:
0: rising edge at IN_SYNC
1: rising edge at IN_REF
2: rising edge at IN_SYNC and IN_REF
3: first rising edge at IN_SYNC and IN_REF at 1
4: first rising edge at IN_SYNC and IN_REF at 0
|
|
Present edge
|
0:Rising edge at IN_SYNC
1:Falling edge at IN_SYNC
|
|
Counter behavior
|
0:Lock on limits
1:Rollover
|
|
Capture 0 settings
|
0:Preset condition
1:Falling edge at the IN_CAP input
|
|
Output block 0
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
10: Capture0 Low Out is High level if Capture value < LT
11: Capture0 In window Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
12: Capture0 High Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
13: Capture1 Low Out is High level if Capture value < LT
14 :Capture1 In window Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
15 :Capture1 High Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
|
|
Output block 1
|
This parameter can take the following values:
0: Off,
1: Low counter,
2: Counter in a window,
3: High counter,
4: Pulse = less than the lower threshold (LT),
5: Pulse = greater than the lower threshold (LT),
6: Pulse = less than the upper threshold (UT),
7: Pulse = greater than the upper threshold (UT).
10: Capture0 Low Out is High level if Capture value < LT
11: Capture0 In window Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
12: Capture0 High Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
13: Capture1 Low Out is High level if Capture value < LT
14 :Capture1 In window Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
15 :Capture1 High Out is High level if LT ≤ capture value ≤ UT
|
|
Pulse width 0
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Pulse width 1
|
Are a number of 2 ms in a range 1
32,767 (Even value from 2 ms to 65,534 ms)
|
|
Polarity 0
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Polarity 1
|
0:Polarity +
1:Polarity -
|
|
Fault recovery
|
Automatic reaction
Activated
|
|
Fallback 0
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback 1
|
0:Without
1:With
|
|
Fallback value 0
|
0
1
|
|
Fallback value 1
|
0
1
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
MOD_HEALTH
|
BOOL
|
0 = the module has a detected error
|
Read
|
|
1 = the module is operating correctly
|
|||
|
MOD_FLT
|
BYTE
|
Internal detected errors bytes of the module
|
Read
|
|
CPT_CH_IN[0
1]
|
T_MC80_CPT_STD_CH_IN
|
Array of structure
|
-
|
|
Standard Symbol
|
Type
|
Bit #
|
Meaning
|
Access
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
FCT_TYPE
|
WORD
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
CH_HEALTH
|
BOOL
|
-
|
0 = channel is inactive
|
Read
|
|
|
1 = channel is active
|
|||||
|
ST_OUTPUT_0_ECHO
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
logical state of output 0
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_OUTPUT_1_ECHO
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
logical state of output 1
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_OUTPUT_BLOCK_0
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
status of physical counting output block 0
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_OUTPUT_BLOCK_1
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
status of physical counting output block 1
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_INPUT_A
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
status of physical counting input A
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_INPUT_B
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
status of physical counting input B
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_INPUT_SYNC
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
physical state of the IN_SYNC input (or IN_AUX)
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_INPUT_EN
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
physical state of IN_EN input (enable)
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_INPUT_REF
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
physical state of the IN_REF input (preset)
|
Read
|
|
|
ST_INPUT_CAPT
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
physical state of IN_CAP input (capture)
|
Read
|
|
|
COUNTER_STATUS [INT]
|
RUN
|
BOOL
|
0
|
the counter operates in counting mode only
|
Read
|
|
MODULO_FLAG
|
BOOL
|
1
|
flag set to 1 by a modulo switch event
|
Read
|
|
|
SYNC_REF_FLAG
|
BOOL
|
2
|
flag set to 1 by a preset or synchronization event
|
Read
|
|
|
VALIDITY
|
BOOL
|
3
|
the current numerical value is valid
|
Read
|
|
|
HIGH_LIMIT
|
BOOL
|
4
|
the current numerical value is locked at the upper threshold value
|
Read
|
|
|
LOW_LIMIT
|
BOOL
|
5
|
the current numerical value is locked at the lower threshold value
|
Read
|
|
|
COMPARE_STATUS [INT]
|
COUNTER_LOW
|
BOOL
|
0
|
current counter value less than lower threshold (LOWER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
COUNTER_WIN
|
BOOL
|
1
|
current counter value is between lower threshold (LOWER_TH_VALUE) and upper threshold (UPPER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
|
COUNTER_HIGH
|
BOOL
|
2
|
current counter value greater than upper threshold (UPPER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
|
CAPT_0_LOW
|
BOOL
|
3
|
Value captured in register 0 is less than lower threshold (LOWER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
|
CAPT_0_WIN
|
BOOL
|
4
|
Value captured in register 0 is between lower threshold (LOWER_TH_VALUE) and upper threshold (UPPER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
|
CAPT_0_HIGH
|
BOOL
|
5
|
Value captured in register 0 is greater than upper threshold (UPPER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
|
CAPT_1_LOW
|
BOOL
|
6
|
Value captured in register 1 is less than lower threshold (LOWER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
|
CAPT_1_WIN
|
BOOL
|
7
|
Value captured in register 1 is between lower threshold (LOWER_TH_VALUE) and upper threshold (UPPER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
|
CAPT_1_HIGH
|
BOOL
|
8
|
Value captured in register 1 is greater than upper threshold (UPPER_TH_VALUE)
|
Read
|
|
|
COUNTER_CURRENT_VALUE_S
|
DINT
|
-
|
Current counter value during event
|
Read
|
|
|
COUNTER_CURRENT_VALUE_US
|
UDINT
|
-
|
Current counter value during event
|
Read
|
|
|
CAPT_0_VALUE_S
|
DINT
|
-
|
Value captured in register 0
|
Read
|
|
|
CAPT_1_VALUE_S
|
DINT
|
-
|
Value captured in register 1
|
Read
|
|
|
OUTPUT_0
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
forces OUTPUT_0 to level 1
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
OUTPUT_1
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
forces OUTPUT_1 to level 1
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
OUTPUT_BLOCK_0_ENABLE
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
implementation of output 0 function block
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
OUTPUT_BLOCK_1_ENABLE
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
implementation of output 1 function block
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
FORCE_SYNC
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
counting function synchronization and start, which is valid only on rising edge
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
FORCE_REF
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
set to preset counter value, which is valid only on rising edge
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
FORCE_ENABLE
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
implementation of counter, which is valid only on rising edge
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
FORCE_RESET
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
reset counter, which is valid only on rising edge
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
SYNC_RESET
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
reset SYNC_REF_FLAG
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
MODULO_RESET
|
EBOOL
|
-
|
reset MODULO_FLAG
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
FUNCTIONS_ENABLING [INT]
|
VALID_SYNC
|
BOOL
|
0
|
synchronization and start authorization for the counting function via the IN_SYNC input
|
Read / Write
|
|
VALID_REF
|
BOOL
|
1
|
operation authorization for the internal preset function
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
VALID_ENABLE
|
BOOL
|
2
|
authorization of the counter enable via the IN_EN input
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
VALID_CAPT_0
|
BOOL
|
3
|
capture authorization in the capture 0 register
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
VALID_CAPT_1
|
BOOL
|
4
|
capture authorization in the capture 1 register
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
COMPARE_ENABLE
|
BOOL
|
5
|
comparators operation authorization
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
COMPARE_SUSPEND
|
BOOL
|
6
|
comparator frozen at its last value
|
Read / Write
|
|
|
CH_FLT(Diagnostic)
|
EXTERNAL_FLT_INPUTS
|
BOOL
|
0
|
external detected error at inputs
|
Read
|
|
EXTERNAL_FLT_OUTPUTS
|
BOOL
|
1
|
external detected error at outputs
|
Read
|
|
|
INTERNAL_FLT
|
BOOL
|
2
|
internal detected error: channel inoperative
|
Read
|
|
|
CONF_FLT
|
BOOL
|
3
|
hardware or software configuration detected error
|
Read
|
|
|
SENSOR_SUPPLY
|
BOOL
|
4
|
low input power supply for the sensors
|
Read
|
|
|
ACTUATOR_SUPPLY
|
BOOL
|
5
|
output power supply loss
|
Read
|
|
|
SHORT_CIRCUIT_OUT_0
|
BOOL
|
6
|
short circuit on output 0
|
-
|
|
|
SHORT_CIRCUIT_OUT_1
|
BOOL
|
7
|
short circuit on output 1
|
Read
|
|