|
Description
|
|
|
(Original Document)
|
|
Name in LL984 Editor
|
Function Block Name
|
|---|---|
|
name of legacy 984 instruction
|
name in other tools and editors like:
|
 |
 |
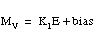
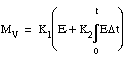

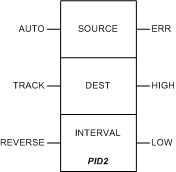
|
Input Pin
|
Name
|
Data Type
|
Address Range
|
Meaning
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Top
|
AUTO
|
–
|
0 = manual mode
1 = auto mode
|
|
|
Middle
|
TRACK
|
BOOL
|
–
|
0 = integral preload OFF
1 = integral preload ON
|
|
Bottom
|
REVERSE
|
BOOL
|
–
|
0 = output increases as E increases
1 = output decreases as E increases or output increases as E decreases
|
|
Node
|
Node Type
|
Name
|
Data Type
|
Address Range
|
Meaning
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Top
|
IN/OUT
|
SOURCE
|
ARRAY[1...21] OF UINT, see Parameter SOURCE below
|
%MW
|
source
first of 21 contiguous words in a source block
|
|
Middle
|
IN/OUT
|
DEST
|
ARRAY[1...9] OF UINT, see Parameter DEST below
|
%MW
|
destination
first of 9 contiguous words used for L9_PID2 calculation
NOTE: Do not load anything in these words. |
|
Bottom
|
IN
|
INTERVAL
|
UINT
|
1... 255
|
solution interval
Contains a number ranging from 1 ... 255, indicating how often the function will be performed.
For more information see INTERVAL (Solution Interval) paragraph below.
|
|
Output Pin
|
Name
|
Data Type
|
Address Range
|
Meaning
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Top
|
ERR
|
BOOL
|
–
|
1 = invalid user parameter or Loop ACTIVE but not being solved
|
|
Middle
|
HIGH
|
BOOL
|
–
|
1 = PV ≥ high limit indication
|
|
Bottom
|
LOW
|
BOOL
|
–
|
1 = PV ≤ low limit indication
|
|
Operation
|
Word 6
|
Word 7
|
Word 8
|
Word 9
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
P
|
ON
|
-
|
-
|
ON
|
|
PI
|
ON
|
ON
|
-
|
-
|
|
PID
|
ON
|
ON
|
ON
|
-
|
|
Word
|
Meaning
|
Content
|
Format
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Scaled PV
|
loaded by the block each time it is scanned
A linear scaling is done on %MWx + 13 using the high and low ranges from %MWx + 11 and %MWx + 12:
scaled PV = (%MWx13 / 4095) * (%MWx11 - %MWx12) + %MWx12
|
UINT
|
|
2
|
SP
|
Specify the set point in engineering units. The value must be < value in word 12 and > value in word 13.
|
UINT
|
|
3
|
Mv
|
loaded by the block every time the loop is solved
It is clamped to a range of 0 ... 4095, making the output compatible with an analog output module. The manipulated variable word may be used for further CPU calculations such as cascaded loops.
|
UINT
|
|
4
|
High Limit Indication
|
Load a value in this word to specify a high limit indication for PV (at or above SP). Enter the value in engineering units within the range specified in word 12 and word 13.
|
UINT
|
|
5
|
Low Limit Indication
|
Load a value in this word to specify a low limit indication for PV (at or below SP). Enter the value in engineering units within the range specified in word 12 and word 13
|
UINT
|
|
6
|
Proportional Band
|
Load this word with the desired proportional constant in the range 5 ... 500. The smaller the number, the larger the proportional contribution. A valid number is needed in this word for L9_PID2 to operate.
|
UINT
|
|
7
|
Reset Time Constant
|
Load this word to add integral action to the calculation. Enter a value between 0000 ... 9999 to represent a range of 00.00 ... 99.99 repeats/min. The larger the number, the larger the integral contribution. A value > 9999 stops the L9_PID2 calculation.
|
UINT
|
|
8
|
Rate Time Constant
|
Load this word to add derivative action to the calculation. Enter a value between 0000 ... 9999 to represent a range of 00.00 ... 99.99 min. The larger the number, the larger the derivative contribution. A value > 9999 stops the L9_PID2 calculation.
|
UINT
|
|
9
|
Bias
|
Load this word to add a bias to the output. The value must be between 000 ... 4095, and added directly to Mv, whether the integral term is enabled or not.
|
UINT
|
|
10
|
High Integral Windup Limit
|
Load this word with the upper limit of the output value (between 0 ... 4095) where the anti-reset windup takes effect. The updating of the integral sum is stopped if it goes above this value (this is normally 4095).
|
UINT
|
|
11
|
Low Integral Windup Limit
|
Load this word with the lower limit of the output value (between 0 ... 4095) where the anti-reset windup takes effect (this is normally 0).
|
UINT
|
|
12
|
High Engineering Range
|
Load this word with the highest value for which the measurement device is spanned, e.g. if a resistance temperature device ranges from 0 ... 500 degrees C, the high engineering range value is 500. The range must be given as a positive integer between 0001 ... 9999, corresponding to the raw analog input 4095.
|
UINT
|
|
13
|
Low Engineering Range
|
Load this word with the lowest value for which the measurement device is spanned. The range must be given as a positive integer between 0 ... 9998, and it must be less than the value in word 12. It corresponds to the raw analog input 0.
|
UINT
|
|
14
|
Raw Analog Measurement
|
The logic program loads this word with PV. The measurement must be scaled and linear in the range 0 ... 4095.
|
UINT
|
|
15
|
Pointer to LoopCounter Word
|
The value you load in this word points to the word that counts the number of loops solved in each scan. The entry is determined by discarding the most significant digit in the word where the controller will count the loops solved/scan, e.g., if the PLC does the count in word 41236, load 1236 into word 15. The same value must be loaded into word 15 in every L9_PID2 block in the logic program.
|
UINT
|
|
16
|
Maximum Number of Loops
|
solved in a scan
If word 15 contains a non-zero value, you may load a value in this word to limit the number of loops to be solved in one scan.
|
UINT
|
|
17
|
Pointer To Reset Feedback Input
|
The value you load in this word points to the memory word that contains the value of feedback (F). Drop the 4 from the feedback word and enter the remaining digits in this word. Integration calculations depend on the F value being connected to Mv - i.e., as the PID2 output varies from 0 ... 4095, so should F vary from 0 ... 4095. If there is no external feedback, set this register to point to Mv (Word 3).
|
UINT
|
|
18
|
Output Clamp - High
|
The value entered in this word determines the upper limit of Mv (this is normally 4095).
|
UINT
|
|
19
|
Output Clamp - Low
|
The value entered in this word determines the lower limit of Mv (this is normally 0).
|
UINT
|
|
20
|
Rate Gain Limit (RGL) Constant
|
The value entered in this word determines the effective degree of derivative filtering. The range is from 2 ... 30. The smaller the value, the more filtering takes place.
|
UINT
|
|
21
|
Pointer to Integral Preload
|
The value entered in this word points to the memory word containing the track input (T) value. Drop the 4 from the tracking word and enter the remaining four digits in this word. The value in the T word is connected to the input of the integral lag whenever the auto bit and integral preload bit are both true.
|
UINT
|
|
Word
|
Meaning
|
Content
|
Format
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
Loop Status
|
12 of the 16 bits in this word are used to define loop status (see below).
|
UINT
|
|
2
|
Detected Error (E) Status Bits
|
This word displays L9_PID2 Detected Error Status Bits.
|
UINT
|
|
3
|
Loop Timer
|
This word stores the real-time clock reading on the system clock each time the loop is solved. The difference between the current clock value and the value stored in the word is the elapsed time. If elapsed time ≥ solution interval (10 times the value given in INTERVAL of the L9_PID2 block), then the loop should be solved in this scan.
|
UINT
|
|
4
|
for internal use
|
integral (integer portion)
|
INT
|
|
5
|
for internal use
|
integral-fraction 1 (1/3 000)
|
UINT
|
|
6
|
for internal use
|
integral-fraction 2 (1/600 000)
|
UINT
|
|
7
|
Pv x 8 (filtered)
|
This word stores the result of the filtered analog input (from %MWx13) multiplied by 8. This value is useful in derivative control operations.
|
UINT
|
|
8
|
Absolute Value of E
|
This word, which is updated after each loop solution, contains the absolute value of (SP - PV). Bit 8 in %MWy indicates the sign of E.
|
UINT
|
|
9
|
for internal use
|
current solution interval
|
UINT
|
|
Control Expert-IEC bits
|
Function
|
|---|---|
|
0
|
Bit 16 is set after initial startup or installation of the loop. If you clear the bit, the following actions take place in one scan:
|
|
1
|
top input status (MAN / AUTO)
|
|
2
|
middle input status (tracking mode)
|
|
3
|
bottom input status (direct / reverse acting)
|
|
4
|
negative values in the equation
|
|
5
|
integral windup saturated
|
|
6
|
integral windup limit not set
|
|
7
|
rev B or higher
|
|
8
|
sign of E in %MWy + 7
|
|
9
|
%MWx14 word referenced by %MWx15 is valid.
|
|
10
|
loop in AUTO mode but not being solved
|
|
11
|
wind-down mod (for REV B or higher)
|
|
12
|
loop in AUTO mode and time since last solution ≥ solution interval
|
|
13
|
bottom output status (low limit exceeded)
|
|
14
|
middle output status (high limit exceeded)
|
|
15
|
top output status (parameter lockout or parameter detected error)
|