|
|
Original instructions
|
|
Word
Symbol
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
%SW60
HSB_CMD
|
Function
|
Quantum Hot Standby command register
|
|
|
Initial State
|
0
|
||
|
Different bits meaning of the word %SW60:
|
|||
|
%SW60
HSB_CMD
|
Function
|
Quantum Hot Standby command register
|
|
|
Initial State
|
0
|
||
|
Continued:
|
|||
|
%SW61
HSB_STS
|
Function
|
Quantum Hot Standby status register
|
|
|
Initial State
|
0
|
||
|
Meaning of the different bits of the word %SW61:
|
|||
|
%SW61
HSB_STS
|
Function
|
Quantum Hot Standby status register
|
|
|
Initial State
|
0
|
||
|
Continued:
|
|||
|
%SW62
HSBY_REVERSE0
%SW63
HSBY_REVERSE1
%SW64
HSBY_REVERSE2
%SW65
HSBY_REVERSE3
|
Function
|
Hot Standby reverse transfer word
|
|
|
Initial State
|
0
|
||
|
These 4 words are modified in the Hot Standby MAST task in first section of the user application program.
They are then transferred automatically from the standby processor to update the primary PLC.
They may be read on the primary PLC and used in the Hot Standby application.
|
|||
|
%SW68
HSBY_APP_STATUS
|
Function
|
Hot Standby application status
|
|
|
Initial State
|
0
|
||
|
%SW68.1: Applications:
%SW68.4: Init values:
|
|||
|
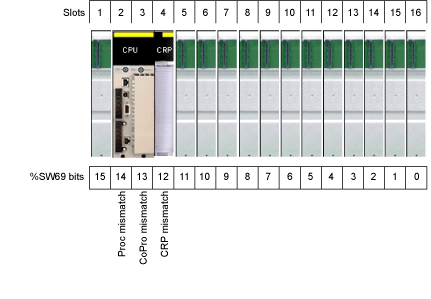
%SW69
HSBY_FW_MISMATCH
|
Function
|
Hot Standby firmware mismatch register
|
|
|
Initial State
|
0
|
||
|
Each bit of this word indicates the results of the comparison of firmware levels between primary and standby main rack slots that contain the same CPU, copro or Ethernet CRP. This word can handle the large 16-slots racks if smaller racks are used the excess bits are not valid. For example, if 8-slot racks are used, only the first 8 bits of the word are valid.
For the 16 bits:
NOTE: Bits 0 to 15 correspond to rack positions 16 to 1.
 |
|||