Types of Topologies Created Based on Port Connections
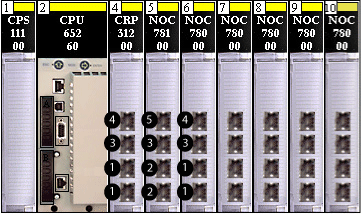
The following illustration shows a Quantum EIO local rack with a 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module, a 140NOC78100 control head module, and five 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head modules. Their ports are labeled as follows:
1
device network port
2
control network port
3
interlink port
4
service port
5
service/extended network port
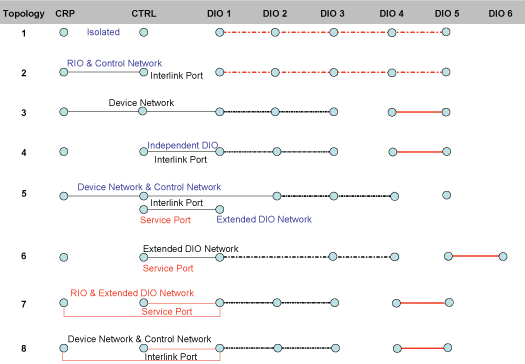
The following illustration shows the possible port connections between Quantum EIO head modules on the local rack and the type of topologies that are created as a result.
1
The 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module, the 140NOC78100 control head module, and the 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module(s) are not connected to each other. The 140NOC78000 modules may be connected to each other via interlink ports to form one isolated distributed I/O network. This port connection type (or lack of connection) creates an isolated remote I/O network and an isolated control network.
2
The 140CRP31200 module and the 140NOC78100 are connected via interlink ports. There are no 140NOC78000 module connections. This port connection type creates transparency between the control network and the remote I/O network.
3
The 140NOC78000 module is connected to the interlink port of the 140CRP31200 module, and the 140NOC78100 module is connected to the interlink/device network port of the 140NOC78000 module. This port connection type creates a device network. (The remaining 140NOC78000 modules may be connected to each other via interlink ports to form one isolated distributed I/O network.)
4
The 140CRP31200 module is not connected to the 140NOC78100 module, nor the 140NOC78000 module(s). The 140NOC78100 module and the 140NOC78000 module(s) are connected via interlink ports. This port connection type creates an independent distributed I/O network. (The remaining 140NOC78000 modules may be connected to each other via interlink ports to form one isolated distributed I/O network.)
5
The 140NOC78000 module is connected to the interlink port of the 140CRP31200 module, and the 140NOC78100 module is connected to the interlink/device network port of the 140NOC78000 module. This port connection type creates a device network and control network transparency. The 140NOC78100 module is also connected to another 140NOC78000 module via the service/extended network port to create an extended distributed I/O network. (The remaining 140NOC78000 module can be an isolated distributed I/O network.)
6
The 140CRP31200 module is not connected to the 140NOC78100 module, nor the 140NOC78000 module. The 140NOC78100 module is connected to the 140NOC78000 module(s) via the service/extended network port. This port connection type creates an extended distributed I/O network. (The remaining 140NOC78000 modules may be connected to each other via interlink ports to form one isolated distributed I/O network.)
7
The 140CRP31200 module is connected to the 140NOC78000 module(s) only; it is not connected to the 140NOC78100 module. The 140NOC78100 module is connected to the 140NOC78000 module(s) via the service/extended network port. These port connection types create a remote I/O network and an extended distributed I/O network. (The remaining 140NOC78000 modules may be connected to each other via interlink ports to form one isolated distributed I/O network.)
8
The 140CRP31200 module is connected to the 140NOC78000 module(s) only; it is not connected to the 140NOC78100 module. The 140NOC78100 module is connected to the interlink/device network port of the 140NOC78000 module. These port connection types create a device network and control network transparency. (The remaining 140NOC78000 modules may be connected to each other via interlink ports to form one isolated distributed I/O network.)