Connecting to Control Expert
To download the PLC application for the first time, connect Control Expert to one of the following:
-
the terminal port of the Quantum CPU (USB or Modbus)
-
the Ethernet embedded port of the CPU (not available on CPU)
-
the Modbus Plus port of the CPU (if the Ethernet embedded port of the CPU is configured and running)
-
the service port on the 140CRA31200 or BMXCRA31210 remote I/O adapter module (Interlink a 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module with a 140CRP31200 remote I/O head module on the .)
NOTE: Do not connect a device with a speed in excess of 100 Mbps to the service port. If the device is configured for a speed that exceeds 100 Mbps, the Ethernet link may not be established between the device and the module through the service port.
-
a in the ring (Interlink a configured 140NOC78000 module with a 140CRP31200 module on the local rack.)
-
switches in the remote I/O (Interlink a configured 140NOC78000 module with a 140CRP31200 module on the local rack.)
-
legacy solutions with 140 NOE 771 •• modules
NOTE: In configurations that use the IP forwarding service (the 140NOC78100 control head module bridging the control network to the distributed I/O network via the 140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module), we recommend that you use the 140NOC78100 module’s IP address to download the Control Expert application to the PLC.
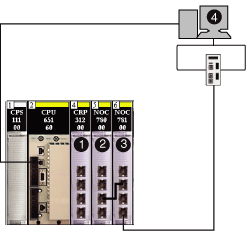
If you download the application via the 140NOC78000 module, the 140NOC78100 resets at the end of the download, which resets the connection between Control Expert and the 140NOC78000 module. See the following figure showing the IP forwarding service feature in the 140NOC78100 module used to connect to the 140NOC78000 module.
1
140CRP31200 remote I/O head module
2
140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module
3
140NOC78100 control head module
4
Control Expert
NOTE:
-
Control Expert is the only tool that can download the PLC application.
-
You can connect Control Expert to any Ethernet port.
-
If Control Expert is connected over Ethernet to a PLC that has no configuration, the of the CPU is used.
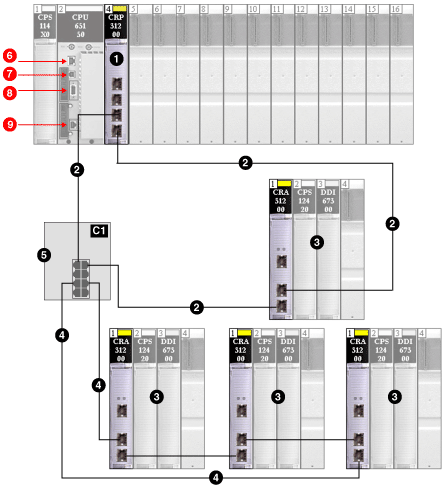
This example shows where you can connect Control Expert when you have only a 140CRP31200 module on the local rack, supporting remote I/O drops only (no distributed I/O devices).
1
140CRP31200 module on the local rack
2
main ring
3
remote I/O drop (including the 140CRA31200 adapter module)
4
remote I/O sub-ring
5
DRS with a C1 predefined configuration file connecting the remote I/O sub-ring to the main ring
6
Control Expert connection using the Modbus port on the CPU
7
Control Expert connection using the USB port on the CPU
8
Control Expert connection using the Modbus Plus port on the CPU
9
Control Expert connection using the Ethernet port on the CPU
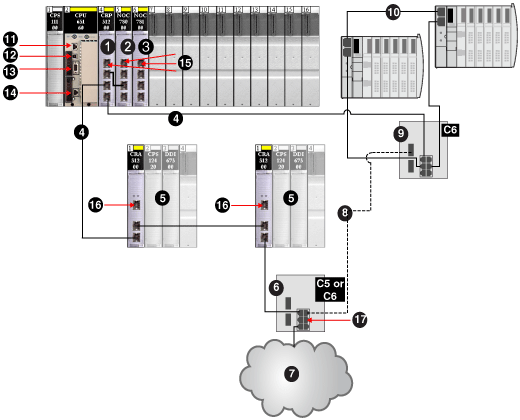
This example shows where you can connect Control Expert when you have a 140CRP31200 module interlinked with a 140NOC78000 module on the local rack, supporting remote I/O drops and distributed I/O devices.
1
140CRP31200 remote I/O head module on the local rack
2
140NOC78000 distributed I/O head module interlinked with the 140CRP31200 module
3
140NOC78100 control head module interlinked with the 140NOC78000 module
4
copper portion of the main ring
5
remote I/O drops (including the 140CRA31200 adapter module)
6
DRS with a C5 or C6 predefined configuration file (connecting a distributed I/O cloud to the main ring)
7
distributed I/O cloud
8
fiber portion of the main ring (to extend distance beyond 100 m)
9
DRS with a C6 predefined configuration file (connecting a distributed I/O sub-ring to the main ring)
10
distributed I/O sub-ring
11
Control Expert connection using the Modbus port on the CPU
12
Control Expert connection using the USB port on the CPU
13
Control Expert connection using the Modbus Plus port on the CPU
14
Control Expert connection using the Ethernet port on the CPU
15
Control Expert connection using the service port on the 140CRP31200, 140NOC78000, or 140NOC78100 modules
16
Control Expert connection using the service port on the 140CRA31200 adapter module
17
Control Expert connection using a distributed I/O cloud port on a DRS