In a classic process control using PID, the loop controller reacts to the process output variations (closed loop process control). Therefore, in the occurrence of a disruption, the loop controller starts reacting only when the process value moves away from the setpoint.
Use the Feed Forward function to compensate for a measurable disruption as soon as it appears.
This open loop function anticipates the disruption's effects: this procedure is referred to as anticipating action (or Feed Forward).
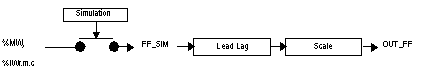
Block Diagram of the Branch
Block Diagram for Feed Forward Processing Branch
How the Initialization Works
If the Feed Forward branch address is undefined, processing is performed on the simulated value initially set to zero.
Operation of Execution Check
Setpoint processing checks for two types of errors: parameter errors (not written in floating point format) and internal calculation errors (division by zero, overflow, etc.). When such a fault appears:
-
The result of processing this setpoint is frozen.
-
These errors are not considered to be serious at the control loop level; loop controller and output value calculation is performed with the frozen Feed Forward value.
-
Specific warnings are displayed.
-
The OUT_FF value, on the loop controller input, is updated as soon as the error is resolved.
-