Introduction
Data types that are part of the DDT family can be nested. The nesting can be organized as follows:
in structures that contain arrays or structures
in arrays that contain arrays or structures
in a combination of these different nestings
Array, that contains structures
Carry out the following steps:
Step |
Action |
|---|---|
1 |
Double click in the Data Editor in the DDT Types tab on the empty field (marked by an arrow Name, and enter the name of the array type (e.g. PERSONNEL); the default type is <Struct>. Enter a comment (optional). |
2 |
Double click on the Typefield, select <Array>, and confirm by pressing . Result: The appears. |
3 |
The ARRAY checkbox is automatically checked:
See the following window: 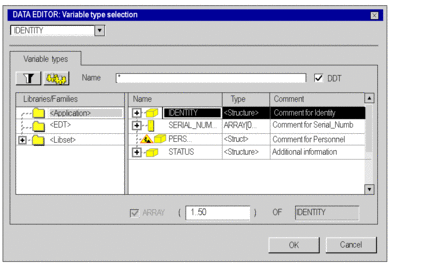 |
4 |
Enable the DDT checkbox, which will display the derived data types. |
5 |
Select the desired structure in the Name column and confirm with OK. |
6 |
Change to the name of the array type and go to the context menu and select Analyze Type. |
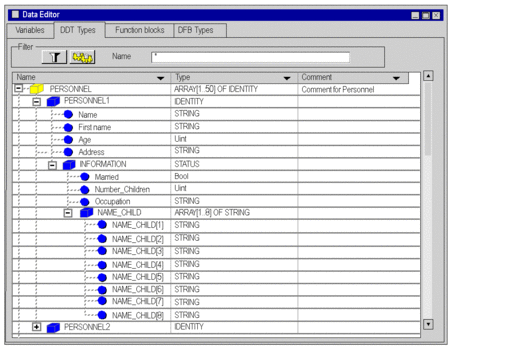
Array of the type PERSONNEL that contains structures of the type IDENTITY:
Structure containing a structure
Execute the following actions (provided a structure exists):
Step |
Action |
|---|---|
1 |
Click on + to display the type of the structure in the DDT Types tab in the data editor, to which you want to add an element. |
2 |
Double click on the empty Namefield and enter the name of the new structure type element. Enter a comment (optional). |
3 |
Double-click on the corresponding Type field and click on
 The following window appears. 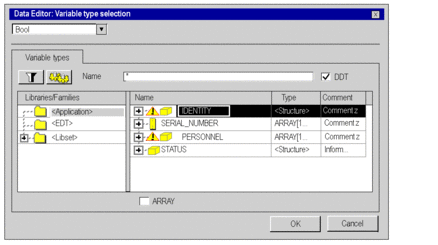 |
4 |
In the libraries/families area select:
See the following example: 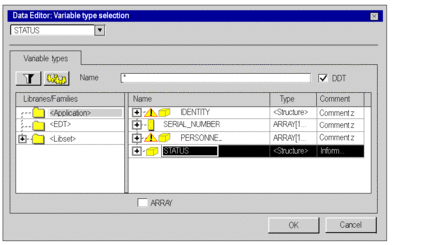 |
5 |
Enable the DDT checkbox, which will display the derived data types. |
6 |
Select the desired structure in the Name column and confirm with OK. |
7 |
Switch to the name of the structure type and select the Analyze Typeentry in the context menu. |
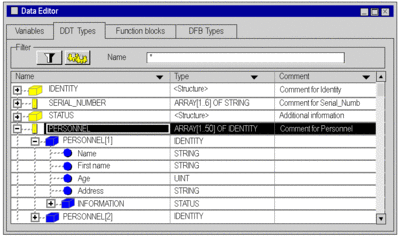
Example: IDENTITY structure that contains an INFORMATION structure of the STATUS type.
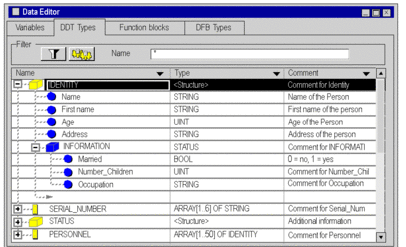
Combination of the different nestings.
The following example shows:
a PERSONNEL array consisting of IDENTITY type structures
IDENTITY structures containing STATUS type structures
STATUS structures containing arrays of the NAME_CHILD type
Example: