Definition
The system time stamping provides a consistent SOE (sequence of events), time stamped at the source, in order to allow the user to analyze the source of abnormal behavior in a distributed automation system.
The SOE is displayed in an alarm summary or SOE page of a client (such as a SCADA).
Each source of time stamped event of the SOE is a discrete I/O value change (transition) detected by a time stamping module or an internal variable value change detected by a PLC.
The following graphic shows an example of AVEVA Plant SCADA SOE page display:
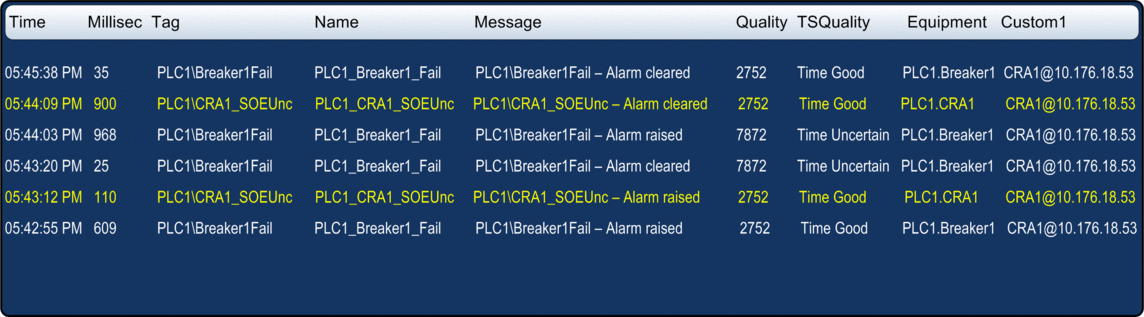
Benefits
The system time stamping benefits are:
No need for PLC programming.
Direct communication between the time stamping modules and the client. If the time stamping modules are in a Modicon Quantum or M580 Ethernet I/O drop, the PLC communication bandwidth is not used.
Consistency in the I/O values between the process (time stamping modules) and the client (SCADA).
Advanced diagnostic functions:
Signalization of uncertain SOE (sequence during which some events may be lost) to the client.
Time quality information associated with each time stamped event.
No loss of events in normal operating conditions:
A buffer is available to store the events in each time stamping module. The event storage is stopped when the buffer is full.
Rising and falling edges transitions are stored for each discrete I/O and PLC internal variables.
Hot Standby configurations on the PLC and/or redundant SCADA are managed.


