Using Fiber Optics in a RIO System
The following represent four typical configurations that show the wide range of the network architecture:
Point-to-Point Topology with Fiber Optic Repeater
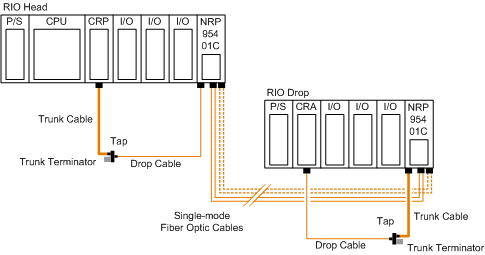
Point-to-point configuration (see the following figure) allows communication over the distance of up to 16 km through harsh industrial environments. The following figure shows the point-to-point configuration.
NOTE:
-
Using 2 optical fiber pairs provides a better service and diagnostics.
-
Using only one fiber pair, looping back the unused optical ports with a short fiber helps using the diagnostics.
For more details on the diagnostics, refer to the Modicon 140 NRP 954 00 and 140 NRP 954 01C Fiber Optic Repeater Modules User Guide.
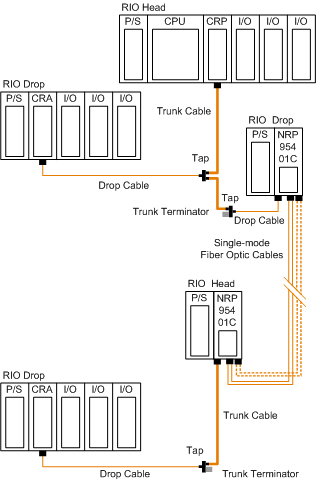
Bus Topology with Fiber Optic Repeater
This type of configuration is used when it is required to increase the length of the fiber link and increase the distance between drops on the RIO network.
The following figure shows the bus topology:
NOTE: The total distance between the first and the last fiber optic repeater is limited by the maximum allowable power loss from end-to-end (16 km over 9/125 µm fiber). Power loss includes the fiber optic cable attenuation, connector losses at the fiber optic receiver and transmitter ports, and the system margin of 3 dB.
NOTE: At each end of the bus, looping back the unused optical ports with a short fiber helps using the diagnostics. For more details on the diagnostics, refer to the Modicon 140 NRP 954 00 and 140 NRP 954 01C Fiber Optic Repeater Modules User Guide.
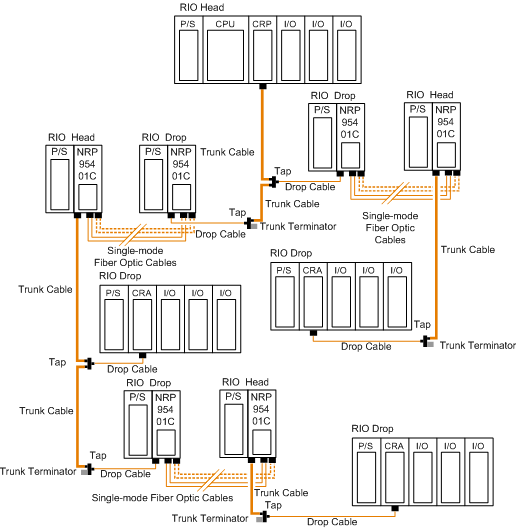
Tree Topology with Fiber Optic Repeater
Tree topologies, which cannot be established with coaxial cable alone can be built legally using fiber optic repeaters.
NOTE: The
limitations in bus and self-healing configurations are applicable for each drop in tree topology.
The following illustration shows an example of a tree topology:
NOTE:
-
Using 2 optical fiber pairs provides a better service and diagnostics.
-
Using only one fiber pair, looping back the unused optical ports with a short fiber helps using the diagnostics.
For more details on the diagnostics, refer to the Modicon 140 NRP 954 00 and 140 NRP 954 01C Fiber Optic Repeater Modules User Guide.
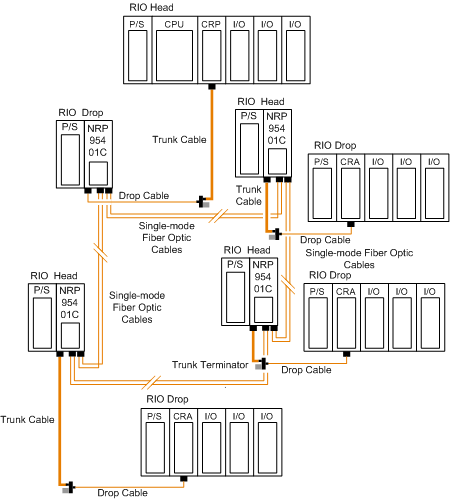
Self-Healing Ring Topology with Fiber Optic Repeater
This configuration can be achieved by connecting the unused fiber optic ports of the first and last 140 NRP 954 01C directly or through the fiber optic repeater. This type of connection has all the advantages of the previously described configurations, along with built-in redundancy. A broken connection between any two Quantum NRP modules in the ring will automatically reconfigure the RIO network and continue the communication.
NOTE: The maximum length of the fiber cable in a ring configuration, 16 km, is calculated in the the case of a break that occurs anywhere (back-loop included).
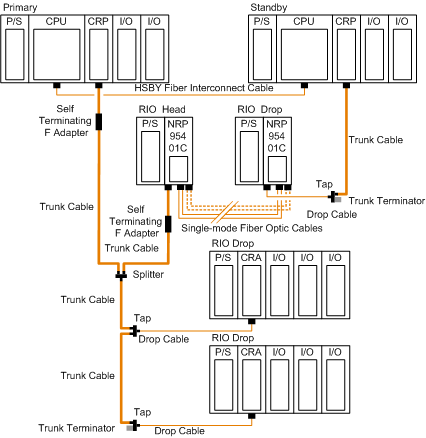
Hot Standby Systems with Fiber Optic Repeater
The following figure shows an example of hot standby systems using fiber optic repeaters:
NOTE:
-
Using 2 optical fiber pairs provides a better service and diagnostics.
-
Using only one fiber pair, looping back the unused optical ports with a short fiber helps using the diagnostics.
For more details on the diagnostics, refer to the Modicon 140 NRP 954 00 and 140 NRP 954 01C Fiber Optic Repeater Modules User Guide.
Instead of placing each fiber optic repeater modules with its own power supply module(s) in a standalone backplane, you can take the advantage of the quantum form factor.
The following figure shows two segments of RIO coaxial cable connected point-to-point by two 140 NRP 954 01C fiber optic repeaters placed on the Quantum racks where the RIO head and RIO drop modules are located:
NOTE:
-
Using 2 optical fiber pairs provides a better service and diagnostics.
-
Using only one fiber pair, looping back the unused optical ports with a short fiber helps using the diagnostics.
For more details on the diagnostics, refer to the Modicon 140 NRP 954 00 and 140 NRP 954 01C Fiber Optic Repeater Modules User Guide.
Recommended Materials for Fiber Optic Links
Modicon does not manufacture fiber optic products such as cables, connectors, or special tools. However, we have experience with third party suppliers of materials and can give some guidelines on what will work with our products.
Observing Safety Precautions
Before installing the 140 NRP 954 01C fiber optic repeater module, read the warning messages below. Follow them at all times during the installation of the fiber optic repeater.
Prior to installing 140 NRP 954 01C fiber optic repeater, network cables must be prepared and installed to the repeater’s site with their connectors.
To prepare optic cables:
-
Follow the cable manufacturer’s recommendations for routing, installing, and testing the cable. Take care when terminating the ends of each fiber optic cable in order to minimize loss of optical signal. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for installing optical connectors.
-
Test the cable for proper attenuation prior to the connection of the fiber optic repeaters. The cable ends should be accessible at each fiber optic installation site. Allow sufficient cable length for a service loop and strain reliefs.
-
Label each cable end to facilitate future maintenance.
To prepare and install coaxial cables, refer to Remote I/O Cable System Planning and Installation Guide.
Connecting the Fiber Optic Cable
Install the fiber optic cable to the 140 NRP 954 01C module’s LC duplex connectors as described in the following table:
|
Step
|
Action
|
|
1
|
Remove the dust plugs from the LC connectors of the fiber optic cable as shown in the following figure. Save the dust plugs for future use.
|
|
2
|
Inspect and clean the fiber optic end faces of the LC connectors.
|
|
3
|
Remove the dust plugs from the LC duplex connector as shown in the following figure:
|
|
4
|
Immediately attach the fiber optic cable to the LC duplex connector of the module as shown in the following figure:
|
Depending on the PV (Product Version) and SV (Software Version) of the CRA modules, the 140 NRP 954 01C may be incompatible.
The following table gives the compatibility rules between the 140 NRP 954 01C and CRA modules:
|
CRA Module Reference
|
PV
|
SV
|
Compatibility
|
|
Communication
|
Remote OS Update via S908 Bus
|
|
140 CRA 93• 00
|
≤ 08
|
2.0
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
|
09
|
2.0
|
No(1)
|
No(2)
|
|
≥ 10
|
2.01
|
Yes
|
No(2)
|
PV Product version
SV Software version
(1)
An upgrade of the SV to 2.01 makes the module communication compatible.
NOTE: Upgrading the software version of the CRA module from 2.0 to 2.01 for CRA modules PV 09 is mandatory before using 140 NRP 954 01C in the RIO network.
(2)
For CRA module with SV ≥2.0, OS update is only possible out of the RIO network.
|
The 140 CRA 93• 00 firmware upgrade is done through Modbus or Modbus Plus using the Control Expert OS loader tool. The procedure to follow is described in the Quantum Operating System Upgrade and Update Procedure.
 CAUTION
CAUTION 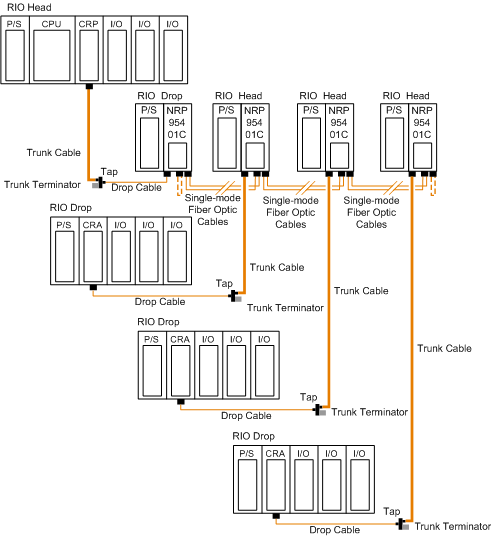
 DANGER
DANGER