This topic describes the process of deriving an IP address from a MAC address and the times when you may need to derive the IP address.
Getting an IP Address from a MAC Address
NOTE: All Ethernet devices are assigned a unique ID. Therefore, your adapter was assigned an IP address at the Schneider factory. That IP address is derived from a MAC address.
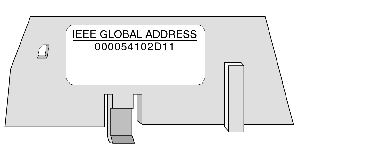
The MAC address, or IEEE global address, is stored as hex. The address appears on the outside of the adapter. As stated, each MAC address is unique. The address on the label below is one unique address and is the address for the adapter displayed below. Your adapter will have a different address.
To convert those hex numbers into decimal numbers, follow these steps:
-
There are six pairs of hex values displayed in the address above. Ignore the first two pairs, 00 and 00.
-
Identify a pair, for example: 54.
-
Multiply the first number (5) by 16. 5 x 16 = 80
-
Add the second number (4). 80 + 4 = 84
There are many sources for converting hex numbers to decimal numbers. We recommend searching on the Web or using the Windows calculator in scientific mode.
This table converts the hex pairs in the IEEE global address (MAC address) above into a decimal number which becomes one element of an IP address.
|
Hex Pair
|
Decimal Conversion
|
|
54
5 x 16 = 80 + 4 = 84
|
84
|
|
10
1 x 16 = 16 + 0 = 16
|
16
|
|
2D
2 x 16 = 32 + 13 = 45
D = 13 in hex
|
45
|
|
11
1 x 16 = 16 + 1 = 17
|
17
|
The IP address of the adapter above is 84.16.45.17.