For use in standalone SIL3 solutions, the 140 CPU 651 60S Quantum Safety CPU is certified.
The safety CPU includes a PCMCIA memory card, but its use and presence is not mandatory.
Description of the Internal CPU Architecture
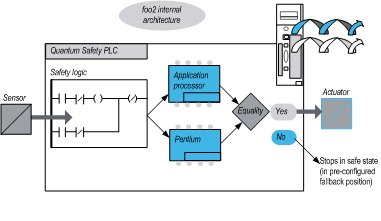
The Quantum Safety CPU contains 2 different processors, an Intel Pentium and an application processor. Each one executes the Safety logic in its own memory area and both compare the results of the execution at the end of each cycle.
Two CPUs are available:
The following figure shows the internal architecture of the Quantum Safety CPU:
Benefits of the Double Code Generation and Execution
The 2 processors inside the Quantum Safety PLC allow double code generation and execution.
This diversity provides the following advantages in error detection:
-
2 executable codes are generated independently. The diversity of compilers allows the detection of systematic error in the code generation.
-
The 2 generated codes are executed by 2 different processors. Thus, the CPU is able to detect both systematic errors in the code execution and random errors in the PLC.
-
2 independent memory areas are used for the 2 processors. Thus, the CPUs are able to detect random errors in the RAM and a full RAM test is not necessary at every scan.
Description of the Watchdog
A hardware and a firmware watchdog check the PLC activity and the time needed to execute the user logic.
NOTE: You must configure the software watchdog (maximum PLC cycle time) to be consistent with the application execution time, the filtering of the I/O communication error, and the process Safety time (PST) targeted.
Description of the Memory Check
Static memory areas, including the Flash memory, PCMCIA memory card (if any) and the RAM, are checked using the cyclic redundancy check (CRC) and the double code execution. Dynamic areas are protected by the double code execution and a periodic memory test. At cold start, these tests are re-initialized and fully performed before the CPU goes into Stop or Run mode.