Overview
The CONTROL and DATABUF output parameters define the operation performed by the MBP_MSTR function block.
For the Modbus TCP protocol, both the structure
and the content of the CONTROL output parameter vary,
depending upon the function code.
The structure
of the CONTROL parameter is described, below, for
each supported function code.
Refer to the Quantum Ethernet I/O System Planning Guide for an example of an MSTR block created in a Control Expert application to read the ports of a dual-ring switch (DRS) to diagnose a sub-ring break.
Control Parameter Routing Register
The CONTROL[5] routing register specifies the
source and destination node addresses for network data transfer, and
consists of the following 2 bytes:
Most Significant Byte (MSB): contains the source node address, for example, the slot number of the 140 NOC 78• 00
Least Significant Byte (LSB): contains the destination node address — a value representing either a direct or a bridge address. The LSB is required for devices that are reached through a bridge, for example, an Ethernet to Modbus bridge or an Ethernet to Modbus Plus bridge. The values of the LSB are as follows:
If no bridge is used: LSB is set to zero(0).
If a bridge is used: LSB contains the Modbus Plus on Ethernet Transporter (MET) mapping index value. This value, also known as the Unit ID, indicates the device to which the message is directed.
The CONTROL[5] routing register:
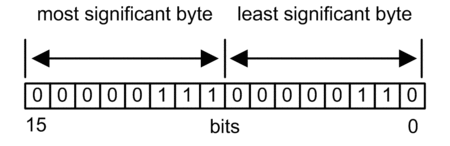
When the Ethernet communication module acts as a server, the LSB indicates the destination of a message received by the communication module:
messages with an LSB value from 0 to 254 are forwarded to and processed by the CPU
messages with an LSB value of 255 are retained and processed by the Ethernet communication module
Write Data
The control parameter consists of 9 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
1 = write data |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only) |
|
Data buffer length |
Number of addresses sent to the slave |
|
Starting register |
Start address of the slave to which the data is written, in 16-bit words |
|
Routing register |
High byte = Ethernet communication module slot |
Low byte = MBP on Ethernet transporter (MET) mapping index |
||
|
IP address |
Byte 4 of the IP address (MSB) |
|
Byte 3 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 2 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 1 of the IP address (LSB) |
|
1. For example, the control parameter handles the IP address 192.168.1.7 in the following order: Byte 4 = 192, Byte 3 = 168, Byte 2 = 1, Byte 1 = 7. |
||
Read Data
The control parameter consists of 9 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
2 = read data |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only) |
|
Data buffer length |
Number of addresses to be read from the slave |
|
Starting register |
Determines the %MW starting register in the slave from which the data is read. For example: 1 = %MW1, 49 = %MW49) |
|
Routing register |
High byte = Ethernet communication module slot |
Low byte = MBP on Ethernet transporter (MET) mapping index |
||
|
IP address |
Byte 4 of the IP address (MSB) |
|
Byte 3 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 2 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 1 of the IP address (LSB) |
|
1. For example, the control parameter handles the IP address 192.168.1.7 in the following order: Byte 4 = 192, Byte 3 = 168, Byte 2 = 1, Byte 1 = 7. |
||
Get Local Statistics
The control parameter consists of 9 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
3 = read local statistics |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only) |
|
Data buffer length |
Number of addresses to be read from local statistics (0...37) |
|
Starting register |
First address from which the statistics table is read (Reg1=0) |
|
Routing register |
High byte = Ethernet communication module slot |
Low byte = MBP on Ethernet transporter (MET) mapping index |
||
|
(not used) |
— |
|
||
|
||
|
Module
Response: A TCP/IP Ethernet module responds
to the Get Local Statistics command with the following
information:
Word |
Description |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
00...02 |
MAC Address |
|||
03 |
Board Status — this word contains the following bits: |
|||
Bit 15 |
0 = Link LED off; 1 = Link LED ON |
Bit 3 |
Reserved |
|
Bits 14...13 |
Reserved |
Bit 2 |
0 = half duplex; 1 = full duplex |
|
Bit 12 |
0 = 10 Mbit; 1 = 100 Mbit |
Bit 1 |
0 = not configured; 1 = configured |
|
Bits 11...9 |
Reserved |
Bit 0 |
0 = PLC not running; 1 = PLC or NOC running |
|
Bits 8...4 |
Module Type — this bit presents the following values: |
|||
|
|
|||
04 and 05 |
Number of receiver interrupts |
|||
06 and 07 |
Number of transmitter interrupts |
|||
08 and 09 |
Transmit_timeout detected error count |
|||
10 and 11 |
Collision_detect error count |
|||
12 and 13 |
Missed packets |
|||
14 and 15 |
(reserved) |
|||
16 and 17 |
Number of times driver has restarted |
|||
18 and 19 |
Receive framing detected error |
|||
20 and 21 |
Receiver overflow detected error |
|||
22 and 23 |
Receive CRC detected error |
|||
24 and 25 |
Receive buffer detected error |
|||
26 and 27 |
Transmit buffer detected error |
|||
28 and 29 |
Transmit silo underflow |
|||
30 and 31 |
Late collision |
|||
32 and 33 |
Lost carrier |
|||
34 and 35 |
Number of retries |
|||
36 and 37 |
IP address |
|||
Clear Local Statistics
The control parameter consists of 9 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
4 = clear local statistics |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only) |
|
(not used) |
— |
|
(not used) |
— |
|
Routing register |
High byte = Ethernet communication module slot |
Low byte = MBP on Ethernet transporter (MET) mapping index |
||
|
(not used) |
— |
|
||
|
||
|
Get Remote Statistics
The control parameter consists of 9 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
7 = get remote statistics |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only) |
|
Data buffer length |
Number of addresses to be read from the statistics data field (0...37) |
|
Starting register |
First address from which the node statistics table is read |
|
Routing register |
High byte = Ethernet communication module slot |
Low byte = MBP on Ethernet transporter (MET) mapping index |
||
|
IP address |
Byte 4 of the IP address (MSB) |
|
Byte 3 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 2 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 1 of the IP address (LSB) |
|
1. For example, the control parameter handles the IP address 192.168.1.7 in the following order: Byte 4 = 192, Byte 3 = 168, Byte 2 = 1, Byte 1 = 7. |
||
Clear Remote Statistics
The control parameter consists of 9 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
8 = clear remote statistics |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only) |
|
(not used) |
— |
|
(not used) |
— |
|
Routing register |
High byte = Ethernet communication module slot |
Low byte = MBP on Ethernet transporter (MET) mapping index |
||
|
IP address |
Byte 4 of the IP address (MSB) |
|
Byte 3 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 2 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 1 of the IP address (LSB) |
|
1. For example, the control parameter handles the IP address 192.168.1.7 in the following order: Byte 4 = 192, Byte 3 = 168, Byte 2 = 1, Byte 1 = 7. |
||
Reset Module
The control parameter consists of 9 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
10 = reset module |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only) |
|
(not used) |
— |
|
(not used) |
— |
|
Routing register |
High byte = Ethernet communication module slot |
Low byte = MBP on Ethernet transporter (MET) mapping index |
||
|
(not used) |
— |
|
||
|
||
|
Read/Write Data
The control parameter consists of 11 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
23 = read / write data |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only) |
|
Data buffer length |
Number of addresses sent to the slave |
|
Starting register |
Determines the %MW starting register in the slave to which the data will be written. For example: 1 = %MW1, 49 = %MW49) |
|
Routing register |
High byte = Ethernet communication module slot |
Low byte = MBP on Ethernet transporter (MET) mapping index |
||
|
IP address |
Byte 4 of the IP address (MSB) |
|
Byte 3 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 2 of the IP address |
|
|
Byte 1 of the IP address (LSB) |
|
|
Data buffer length |
Number of addresses to be read from the slave |
|
Starting register |
Determines the %MW starting register in the slave from which the data is read. For example: 1 = %MW1, 49 = %MW49) |
1. For example, the control parameter handles the IP address 192.168.1.7 in the following order: Byte 4 = 192, Byte 3 = 168, Byte 2 = 1, Byte 1 = 7. |
||
Enable/Disable HTTP or FTP/TFTP Services
When HTTP or FTP/TFTP has been enabled using Control Expert configuration tools, an MSTR block can be used to change the enabled state of the service while the application is running. The MSTR block cannot change the state of the HTTP or FTP/TFTP services if the service was disabled using one of the configuration tools.
The control parameter consists of 9 contiguous words, as described below:
Register |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Operation |
FFF0 (hex) 65520 (dec) = enable / disable HTTP or FTP/TFTP |
|
Detected error status |
Holds the event code (read-only). Codes returned include: 0x000 (Success): MSTR block with operational code 0xFFF0 was called and the enabled state of HTTP or FTP/TFTP was changed. 0x5068 (Busy): MSTR block with operational code 0xFFF0 was called within 2 seconds of the previous call (regardless of return code from previous call). 0x4001 (Same state): MSTR block with operational code 0xFFF0 was called to change the enabled state of HTTP and FTP/TFTP to the states they were already in. 0x2004 (Invalid data): MSTR block with operational code 0xFFF0 was called and the data in the control block did not match the specifications. 0x5069 (Disabled): If the HTTP or FTP/TFTP service was already disabled via the Control Expert interface when the MSTR block with operational code 0xFFF0 was called to change the state of the disabled service. |
|
Set this register to 1. |
|
|
||
|
Module slot number and destination ID |
High byte = Module slot number communication module slot |
Low byte = Destination ID |
||
|
Request mode |
Bit 0 (LSB) = 1: Enable FTP/TFTP Bit 0 (LSB) = 0: Disable FTP/TFTP Bit 1 = 1: Enable HTTP Bit 1 = 0: Disable HTTP |
|
Set this register to 0. |
|
|
||
|
HTTP, FTP, and TFTP service state changes made by MSTR with operation code FFF0 (hex) are overridden by the configured value when the module is power-cycled or reset and when a new application is downloaded to the module.
Here are some examples:
State Configured By Control Expert |
Action attempted using MSTR with operation code FFF0 (hex) |
Result |
|---|---|---|
Disabled |
Any |
MSTR returns detected error code 0x5069 (service was already disabled by configuration) |
Enabled |
Disable |
MSTR returns code 0x000 (success).
|
Enable |
MSTR returns detected error code 0x4001 (same state). No change made. |


