The following examples are presented in the following diagrams:
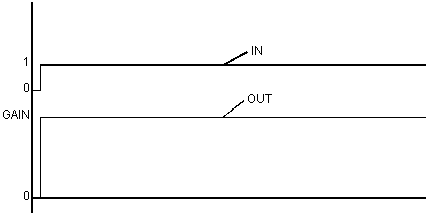
The function block behaves like a pure multiplication block with the multiplier GAIN.
Function block LDLG with LEAD = LAG
In this case the output OUT will jump to half the accumulated value in order to make the transition to the final value (GAIN * IN) with the delay time constant LAG.
Function block LDLG with LEAD/LAG = 0.5 and GAIN = 1
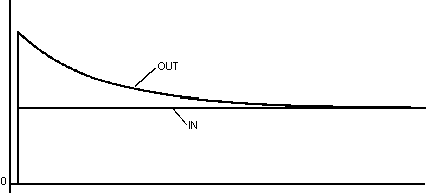
In this case the output OUT will jump to double the accumulated value in order to make the transition to the final value (GAIN * IN) with the delay time constant LAG.
Function block LDLG with LEAD/LAG = 2 and GAIN = 1