|
Channel Properties — TCP/IP Page
|
|
|
Original instructions
|
|
Property
|
Description
|
Configuration Mode Options
|
|---|---|---|
|
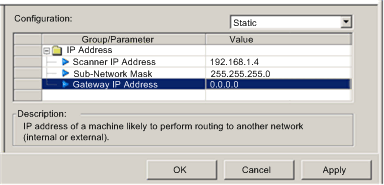
Scanner IP Address
|
The 32-bit identifier — consisting of both a network address and a host address — assigned to a device connected to a TCP/IP Internet network using the Internet Protocol (IP).
|
|
|
Sub-Network Mask
|
The 32-bit value used to hide (or mask) the network portion of the IP address and thereby reveal the host address of a device on a network using the IP protocol.
|
|
|
Gateway Address
|
The address of a device, if any, that serves as a gateway to the communication module.
|
|
|
Name
|
The device name.
NOTE: The default device name, based on the rotary switch settings is BMX_0401_xxy. where:
|
|
|
Configuration Mode
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Static
|
The module uses the scanner IP address, gateway IP address, and sub-network mask configured in this page.
|
|
Flash Memory
|
The module uses the IP address configured via the TCP/IP object and stored flash memory. An IP address configured by this process survives both a warm and a cold re-start.
|
|
BOOTP
|
The module uses an IP address assigned by a BOOTP server.
|
|
DHCP1
|
The module uses an IP address assigned by a DHCP server.
|
|
Application:
Configuration Mode
|
Rotary Switch Position
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DHCP1
|
BOOTP
|
STORED
|
CLEAR IP
|
|
|
<no configuration>
|
No Conflict: Get IP address from DHCP server using device name from rotary switches.
Start basic services only.
|
No Conflict: Get IP address from BOOTP server.
Start basic services only.
|
No Conflict: Get IP address from:
Start basic services only.
|
No Conflict: Use default IP address.
Start basic services only.
|
|
Static or Flash memory
|
Conflict: Get IP address from DHCP server using device name from rotary switches.
Start basic services only.
|
Conflict: Get IP address from BOOTP server.
Start basic services only.
|
No Conflict: Get IP address from the application.
Start services configured in the application.
|
|
|
DHCP or BOOTP with no configured device name
|
No Conflict: Get IP address from DHCP server using device name from rotary switches.
Start services configured in the application.
|
No Conflict: Get IP address from BOOTP server.
Start services configured in the application.
|
No Conflict: Get IP address from BOOTP server.
Start services configured in the application.
|
|
|
DHCP with a configured device name
|
Conflict (if device name on switches differs from name in application) or No Conflict: if names are equal.
Get IP address from DHCP server using device name from rotary switches.
If conflict, start basic services only; If no conflict, start services configured in the application.
|
Conflict: Get IP address from BOOTP server.
Start basic services only.
|
No Conflict: Get IP address from DHCP server using device name from application.
Start services configured in the application.
|
|
|
1. Based on device name BMX_0401_xxy, where x = the top rotary switch, and y represents the bottom rotary switch.
|
||||