About Dual-Bus Backplanes
The dual-bus interface on the back of the BMENOR2200H module connects to the X Bus and Ethernet bus connectors across the backplane when you mount the module in the rack.
BMEXBP••0• backplanes are compatible with Modicon X80 modules in an M580 system.
Communications across the dual-bus backplane of this sample local rack (which includes an M580 CPU) implement both the Ethernet (red line) and X-Bus (blue line) protocols:
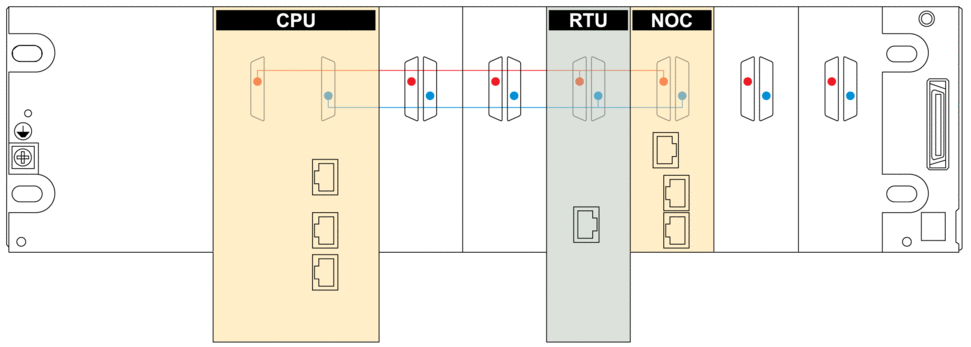
Red The red dot/line indicates Ethernet.
Blue The blue dot/line indicates X Bus.
BMXXPB••00 X Bus backplanes do not have connections that support eX80 modules.
Ethernet racks are described in detail in the Modicon M580, Hardware, Reference Manual.
Connection Protocols
The module supports communications over a BMEXBP••0• backplane using these protocols:
Bus |
Description |
|---|---|
X Bus |
The module uses X Bus communications to obtain and exchange the following through the CPU:
|
Ethernet |
NOTE: The Ethernet backplane port is always enabled for the BMENOR2200H module. Confirm your network topology
design to help avoid network loop issues.
The module uses Ethernet communications to provide an access path to the BMENOR2200H module for the following:
|
The data exchange uses implicit messaging to facilitate memory sharing between the module and the CPU. For each CPU scan cycle, the CPU publishes all data at the same time to share the most current information with the RTU.
I/O Data Exchange with the CPU
Observe these maximum input and output sizes when the module exchanges I/O data with the CPU:
Protocol |
Characteristics |
|---|---|
|
Memory consumption:
NOTE:
|
Minimum MAST Cycle Time
Use this formula to achieve the recommended minimum MAST task cycle time for a single BMENOR2200H module:
Tcycle min= ((DataInB
+ 128)*2+(DataOutB + 32)) / 23500B/S)*30ms
The result is approximately a 30ms MAST task cycle with 8Kb in and 8Kb out.


