Command DNP3 and Integrity Poll: Integrity poll retrieves all event (class 123) and static (Class 0) data from the device. It is typically sent after device restart, loss of communication, or on a periodic basis to check data accuracy.
Command IEC and General Interrogation: The General Interrogation command retrieves all or a specified group of static data. It is typically sent after device restart, loss of communication, or on a periodic basis so that no changes are missed in the spontaneous data reporting.
The BMXNOR0200H module has three communication ports, one serial port, one Ethernet port, and a backplane interface.
The serial port and the Ethernet port are mainly used to communicate with the remote master or slaves with RTU protocols. The backplane interface is used to communicate with the CPU. The main activity of the backplane interface is synchronizing data between CPU registers and the RTU point database inside the module. The synchronization cycle can be one or more PLC application scan cycles, depending on the data amount and backplane load.
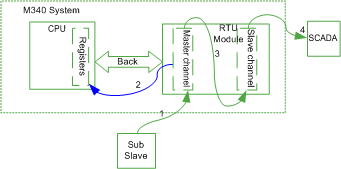
When Master Channel Receives Events from Sub Slave
When something significant changes in sub slave, such as a value of a point, the sub slave sent out an event. The system receives this event and the event needs to be routed to SCADA system.
Events routing example:
1
Sub slave sends out events to the master channel.
2
Master channel updates the point values in the module and the database of the logic slave channel and synchronizes the value to CPU registers.
3
Events are routed to slave channels according to point configuration.
4
Slave channel buffers these events and sends events to SCADA if communication link is established.
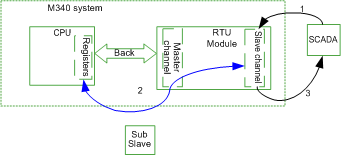
When Slave Channel Receives Request from SCADA
In the RTU system, SCADA sends requests (commands) like an Integrity Poll to slaves connected to it. The slave channel receives this request and sends a response to SCADA. In the routing system, the behavior of the slave channel is exactly the same as a standalone (without events routing) slave channel. The master channel and sub slaves are not involved in this case.
Response to the request from SCADA example:
1
SCADA sends an Integrity Poll request to the slave channel.
2
Points values are synchronized cyclically between the database of the slave channel and CPU registers.
3
The slave channel responds to the SCADA request with the points value in the database.
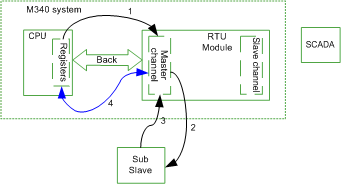
When Master Channel Sends Request to Sub Slave
The master channel can send requests to a sub slave connected to it, and a sub slave sends the response back to as the master channel. The behavior of the master channel in this case is exactly the same as a standalone master channel. The points in the logic slave channel should be synchronized with the updated point in the master channel.
Send request to sub slave example:
1
PLC application in the M340 CPU sends a Integrity Poll command to the master channel.
2
The master channel send Integrity Poll request to the sub slave.
3
The sub slave responds to the request with the value of the latest points.
4
The logic slave data base is synchronized while the master channel updates the database.
5
Points value are synchronized cyclically between the database of the master channel and CPU registers.