SNMP defines network management solutions in terms of network protocols and the exchange of supervised data.
The structure relies on the following elements:
-
Manager: The manager allows entire or partial network supervision.
-
Agents: Each supervised device has one or more software modules named "Agent" that are used by the SNMP protocol.
-
MIB: The Management Information Base is a database or collection of objects.
The is implemented on the RTU module. This allows a manager to access MIB-II standardized objects from the Modicon X80 agent through the SNMP protocol. The MIB-II allows management of TCP/IP communication layers.
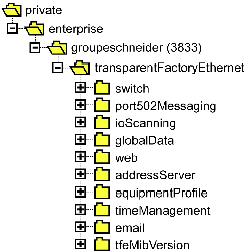
On the modules that support Ethernet communications, it is possible to access objects from the MIB Transparent Factory, which provides specific information about Messaging.
The following figure shows the tree structure of the Ethernet MIB:
The source file of the
TFE private MIB is available on modules and CPUs that support Ethernet communications. The MIB can be uploaded from the module web page by selecting
Upload MIB File. This file may be compiled by the major SNMP managers on the market.
The SNMP protocol defines 5 types of messages between the agent and the manager. These messages are encapsulated in datagrams.
Messages from the manager to an agent:
-
Get_Request: message used to obtain the value of one or more variables
-
Get_Next_Request: obtains the value of the next variables
-
Set_Request : sets the value of a variable
Messages from an agent to the manager: