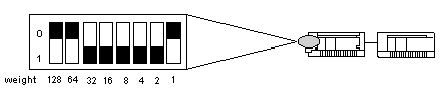
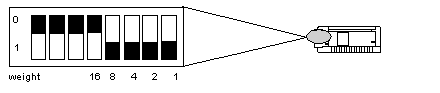
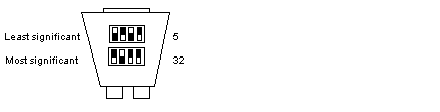|
Coding Addresses
|
|
|
(Original Document)
|
|
Type of processor
|
Max no. of TBX addresses
|
TBX addresses
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
IP20 monobloc
|
IP20 modular
IP65 monobloc
|
||
|
TSX P57 154
|
62
|
1 to 31
|
1 to 62
|
|
TSX P57 •54
TSX PCI 57 •54
|
127
|
1 to 31
|
1 to 62, 64 to 127
|
 WARNING WARNING |
|
UNEXPECTED SYSTEM BEHAVIOR
Do check the addresses of the devices to ensure:
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
|
|
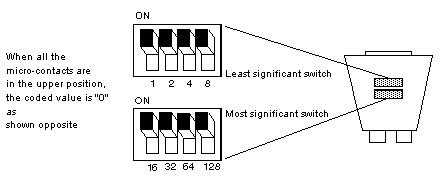
Least significant switch
|
Value
|
Most significant switch
|
Value
|
|---|---|---|---|
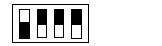 |
1
|
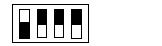 |
16
|
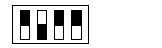 |
2
|
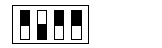 |
32
|
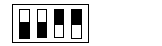 |
3
|
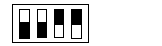 |
48
|