|
Clock Synchronization with the NTP Protocol
|
|
|
Original instructions
|
|
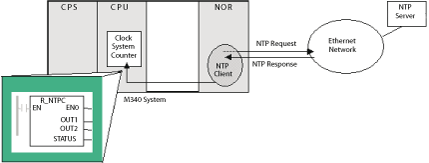
The NTP Client...
|
Result
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
1
|
... requests a clock synchronization signal from the NTP server over an Ethernet network.
|
The NTP server sends a signal.
|
|
2
|
... stores the time.
|
|
|
3
|
... sends a message to the clock system counter in the CPU.
|
The CPU updates its internal clock. The CPU clock is now typically within 5 ms of the NTP server, with a worst case of 10 ms.
Before the next clock synchronization signal, the CPU clock is updated each ms by an internal timer.
|
|
Term
|
Description of Service
|
|---|---|
|
local clock offset
|
Accurate local time adjustments are made via a local clock offset. The local clock offset is calculated as:
((T2 - T1) + (T4 - T3))/2
where:
|
|
time accuracy
|
The local time margin is < 10 ms compared to the referenced NTP server time.
|
|
settling time
|
Maximum accuracy is obtained after 2 updates from the NTP server.
|
|
polling period dependency
|
Accuracy depends on the polling period. Less than 10 ms of margin is achieved for polling periods of 120 ms or less. To obtain a high degree of accuracy (when your network bandwidth allows), reduce the polling period to a small value—for example, a polling time of 5 s provides better accuracy than a time of 30 s.
|
|
time zone
|
The default format is universal time, coordinated (UTC). Optionally you may configure the service to use a local time zone—e.g., GMT+1 for Barcelona or Paris
|
|
daylight saving time
|
The module automatically adjusts the time change in the spring and fall.
|
|
leap second
|
To compensate for the deceleration of the earth rotation, the module automatically inserts a leap second in the UTC time every 18 months via an international earth rotation service (IERS).
Leap seconds are inserted automatically as needed. When needed, they are inserted at the end of the last minute in June or December, as commanded by the NTP server.
|
|
Model
|
Starting Date
|
|---|---|
|
M340 with Control Expert
|
January 1, 1980 00:00:00.00
|