Introduction
With the programming language of structured text (ST), it is possible, for example, to call up function blocks, perform functions and assignments, conditionally perform instructions and repeat tasks.
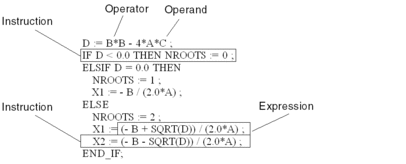
Expression
The ST programming language works with "Expressions".
Expressions are constructions consisting of operators and operands that return a value when executed.
Operator
Operators are symbols representing the operations to be executed.
Operand
Operators are used for operands. Operands are variables, literals, FFB inputs/outputs etc.
Instructions
Instructions are used to assign the values returned from the expressions to actual parameters and to structure and control the expressions.
Representation of an ST Section
Representation of an ST section:
Section Size
The length of an instruction line is limited to 300 characters.
The length of an ST section is not limited within the programming environment. The length of an ST section is usually limited by the size of the PLC memory.
Syntax
Identifiers and Keywords are not case sensitive.
Exception: Not allowed - spaces and tabs
keywords
literals
values
identifiers
variables and
limiter combinations [e.g.
(*for comments)]
Execution Sequence
The evaluation of an expression consists of applying the operators to the operands in the sequence as defined by the rank of the operators (see Table of Operators). The operator with the highest rank in an expression is performed first, followed by the operator with the next highest rank, etc., until the evaluation is complete. Operators with the same rank are performed from left to right, as they are written in the expression. This sequence can be altered with the use of parentheses.
If, for example, A, B, C and D have the values 1, 2, 3 and 4, and are calculated as follows:
A+B-C*Dthe result is -9.
In the case of the following calculation:
(A+B-C)*Dthe result is 0.
If an operator contains two operands, the left operand is executed first, e.g. in the expression
SIN(A)*COS(B)the expression SIN(A) is calculated first, then COS(B) and only then
is the product calculated.
Error Behavior
The following conditions are handled as an error when executing an expression:
Attempting to divide by 0.
Operands do not contain the correct data type for the operation.
The result of a numerical operation exceeds the value range of its data type
If an error occurs when executing the operation, the corresponding Systembit (%S) is set (if supported by the PLC being used).
IEC Conformity
For a description of IEC conformity for the ST programming language, see IEC Conformity.


