Introduction
This section describes the Ladder Diagram (LD) according to IEC 61131-3.
The structure of an LD section corresponds to a rung for relay switching.
The left power rail is located on the left-hand side of the LD editor. This left power rail corresponds to the phase (L ladder) of a rung. With LD programming, in the same way as in a rung, only the LD objects which are linked to a power supply, that is to say connected to the left power rail, are "processed". The right power rail corresponds to the neutral wire. However, all coils and FFB outputs are linked with it directly or indirectly, and this creates a power flow.
A group of objects which are linked together one below the other, and have no links to other objects (excluding the power rail), is called a network or a rung.
Representation of an LD Section
Representation:
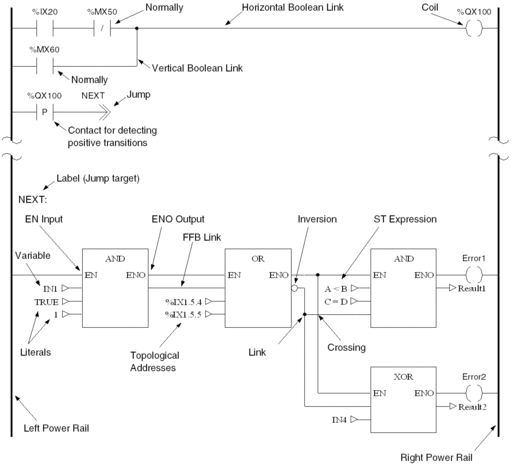
Objects
The objects of the LD programming language help to divide a section into a number of:
EFs and EFBs (Elementary Functions and Elementary Function Blocks)
DFBs (Derived Function Blocks)
Control Elements and
Operation and Comparison blocks that represent an extension to IEC 61131-3
These objects can be connected with each other by means of:
Links or
Actual Parameters (FFBs only).
Comments regarding the section logic can be provided using text objects (see Text Object).
Section Size
One LD section consists of a window containing a single page.
This page has a grid that divides the section into rows and columns.
A width of 11-63 columns and 17-3998 lines can be defined for LD sections.
The LD programming language is cell oriented, i.e. only one object can be placed in each cell.
Processing Sequence
The processing sequence of the individual objects in an LD section is determined by the data flow within the section. Networks connected to the left power rail are processed from top to bottom (link to the left power rail). Networks that are independent of each other within the section are processed according to their position (from top to bottom) (see also Execution Sequence and Signal Flow).
IEC Conformity
For a description of IEC conformity for the LD programming language, see IEC Conformity.


