Introduction
The data types in Binary format belong to the EDT (Elementary data type) family, which includes single rather than derived data types (tables, structures, function blocks).
Reminder Concerning Binary Format
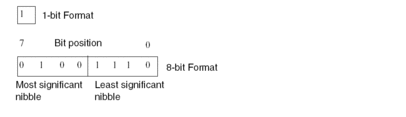
A data item in binary format is made up of one or more bits, where each of these is represented by one of the base 2 figures (0 or 1).
The scale of the data item depends on the number of bit(s) of which it is made.
Example:
A data item can be:
signed. Here the highest ranking bit is the sign bit:
0 indicates a positive value
1 indicates a negative value
The range of values is: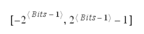
unsigned. Here all the bits represent the value
The range of values is: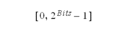
Bits=number of bits (format).
Data Types in Binary Format
List of data types:
Type |
Designation |
Format (bits) |
Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
BOOL |
Boolean |
8 |
0=(False) |
EBOOL |
Boolean with forcing and edge detection |
8 |
0=(False) |
INT |
Integer |
16 |
0 |
DINT |
Double integer |
32 |
0 |
UINT |
Unsigned integer |
16 |
0 |
UDINT |
Unsigned double integer |
32 |
0 |
TIME |
Unsigned double integer |
32 |
T=0s |


