Principle
In Structured Text, a user function block is called by a DFB call: name of the DFB instance followed by a list of arguments. Arguments are displayed in the list between brackets and separated by commas.
The DFB call can be of one of two types:
a formal call, when arguments are assignments (parameter = value). In this case, the order in which the arguments are entered in the list is not important.
The EN input parameter and the ENO output parameter can be used to control the execution of the function block
an informal call, when arguments are values (expression, object or an immediate value). In this case, the order in which the arguments are entered in the list must follow the order of the DFB input parameters, including for non-assigned inputs (the argument is an empty field)
It is not possible to use EN and ENO parameters.
DFB_Name (argument 1,argument 2,....,argument n)
Use of EN\ENO Parameters
Example of a DFB
The following simple example explains the different DFB calls
in Structured Text language. This is the instance Cpt_1 of the Cpt_parts: type DFB.
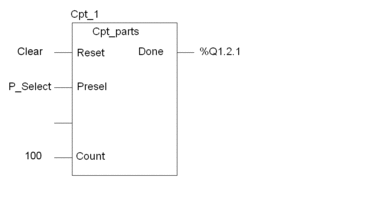
Formal DFB Call
The
formal DFB call Cpt_1 is performed with the following
syntax:
Cpt_1 (Reset:=Clear, Presel:=P_Select, Count:=100,
Done=>%Q1.2.1);
Where the input parameters assigned by a value (expression, object or immediate value) are entered in the list of arguments, the syntax is:
Cpt_1 (Reset:=Clear,
Presel:=P_Select, Count:=100);
...
%Q1.2.1:=Cpt_1.Done;
Elements of the Sequence
The following table lists the different elements of the program sequence, when a formal DFB call is made.
Element |
Meaning |
|---|---|
Cpt_1 |
Name of the DFB instance |
Reset, Presel, Count |
Input parameters |
:= |
Assignment symbol of an input |
Clear |
Assignment object of an input (symbol) |
100 |
Assignment value of an input |
Done |
Output parameter |
=> |
Assignment symbol of an output |
%Q1.2.1 |
Assignment object of an output (address) |
; |
End of sequence symbol |
, |
Argument separation symbol |
Informal DFB Call
The
informal DFB call Cpt_1 is performed with the following
syntax:
Cpt_1 (Clear, %MD10, , 100);
...
%Q1.2.1:=Cpt_1.Done;
Elements of the Sequence
The following table lists the different elements of the program sequence, when a formal DFB call is made.
Element |
Meaning |
|---|---|
Cpt_1 |
Name of the DFB instance |
Clear, %MD10, ,100 |
Assignment object or value of the inputs. Non-assigned inputs are represented by an empty field |
; |
End of sequence symbol |
, |
Argument separation symbol |


