Introduction
The LD editor is used for graphical ladder diagram programming according to IEC 61131-3.
Representation
Representation of an LD section:
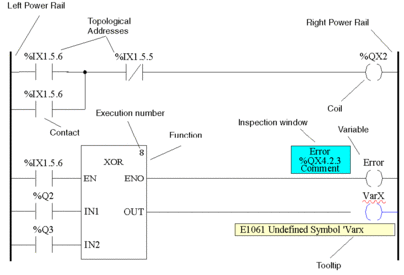
Objects
The objects of the LD programming language help to divide a section into a number of:
Contacts,
Coils,
Elementary Functions (EFs)
Elementary Function Blocks (EFBs),
Derived Function Blocks (DFBs)
Procedures
Control elements
Operation and compare blocks which represent an extension to IEC 61131-3
Subroutine calls
Jumps
Links
Actual Parameters
Text objects to comment on the logic
Properties
LD sections have a background grid that divides the section into lines and columns.
The LD programming language is cell oriented, i.e. only one object can be placed in each cell.
LD sections can be 11-63 columns and 17-3998 lines in size.
The program can be entered using the mouse or the keyboard.
Input Aids
The LD editor offers the following input aids:
Objects can be selected from the toolbar, the menu or directly using shortcut keys
Syntax and semantics are checked as the program is being written.
Incorrect objects are displayed in blue
Unknown words (e.g. undeclared variables) or unsuitable data types are marked with a red wavy line
Brief description of errors in the Quickinfo (Tooltip)
Information for variables and for elements of an LD section, that can be connected to a variable (pins, contacts, coils, operation and compare blocks), can be displayed in a Quickinfo (Tooltip)
type, name, address and comment of a variable/expression
type, name and comment of FFB pins, contacts etc.
Tabular display of FFBs
Actual parameters can be entered and displayed as symbols or topological addresses
Different zoom factors
Tracking of FFB links
Optimizing the link routes of FFB links
Display of inspection windows


