Introduction
Dialog boxes are displayed if additional information is required from you in order to perform a particular task. Information that you may require is also communicated in this way.
Most dialog boxes contain options which can be selected, text boxes in which text can be entered, and buttons which can be pressed.
Grayed out options are currently not available. One or more other commands must be executed, or options selected or deselected, before the desired option can be activated.
The information contained in dialog boxes is separated into different areas. The different area in a dialog box can be selected using the F6 key.
Basic elements of a window:
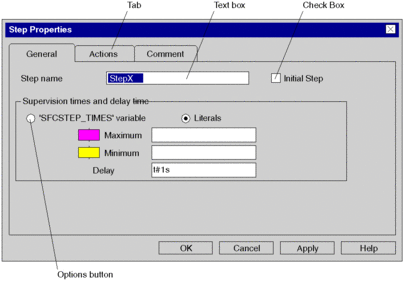
Tab
If the amount of information contained in a dialog box is too complex to be displayed in one dialog box, the dialog box is split into several tabs.
The different tabs in a dialog box can be selected using the Ctrl+Tab key combination.
button
buttons are used to initiate actions immediately, e.g. executing or aborting a command. buttons are e.g. , and .
buttons followed by three dots (...), open another dialog box. A button with a "greater than" sign (>>) extends the active dialog box.
The default setting is identified by a darker border. This default button can also be selected by pressing Enter.
If the name of the button contains an underlined letter, the button can be activated from any position in the dialog box by holding down the Alt key and entering the underlined letter.
To close a dialog box without executing a command, select the button.
Text box
Information (text) is entered in a text box.
If you go to an empty text box the cursor appears in the far left of the box. The entered text begins at the cursor position. If text is already present within the respective text box, the text will be selected and replaced by the new text automatically. The text can, however, also be deleted by pressing the Del or backspace key.
If the name of the text box contains an underlined letter, the text box can be activated from any position in the dialog box by holding down the Alt key and entering the underlined letter.
List box
The available options to select are given in list form in a list box. If more options are available than fit into the list, then the scrollbar or arrow keys can be used to move around the list.
Normally only a single entry can be chosen form the list. There are, however, some cases in which several entries can be chosen, e.g. when opening sections.
If the name of the list box contains an underlined letter, the list box can be activated from any position in the dialog box by holding down the Alt key and entering the underlined letter.
Single line list boxes
A single line list box initially appears as a rectangular box, in which the current selection (the default value) is selected. If the arrow in the right of the box is selected, a list of the available options to select opens. If more options are available than fit into the list, then the scrollbar or arrow keys can be used to move around the list.
If the name of the list box contains an underlined letter, the list box can be activated from any position in the dialog box by holding down the Alt key and entering the underlined letter.
Data selection boxes
See section Data selection boxes
Directory structures
See section Directory Structures
Option buttons
Option buttons represent mutually exclusive options. In each case only one option can be chosen.
The selected option button is identified by a black dot.
If the option name contains an underlined letter, the option button can be activated from any position in the dialog box by holding down the Alt key and entering the underlined letter.
Check boxes
A checkbox next to an option means that the option can be activated or deactivated. Any number of checkbox options can be activated.
Activated options are identified by an X or a check mark ( √ ).
If the name of the option contains an underlined letter, the checkbox can be activated from any position in the dialog box by holding down the Alt key and entering the underlined letter.


