|
Configuration of a Cam Profile (Channels 25 to 31)
|
|
|
(Original Document)
|
|
Parameters
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
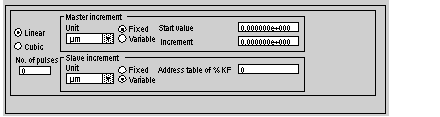
Linear
|
When this button is selected, interpolation between 2 consecutive cam profile points is linear. This button operates alternately with the Cubic button.
|
|
Cubic
|
When this button is selected, interpolation between 2 consecutive cam profile points is cubic. This button operates alternately with the Linear button.
|
|
No. of points
|
This field can be used to enter the number of points used to define the cam profile.
|
|
Parameters
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Unit
|
Used to define the unit used for the master increment. The unit selected can be a sub unit of the unit defined for the axes (for example, cm for the axes and mm for the increment).
|
|
Fixed
|
When this button is selected, the increment between 2 consecutive cam profile points is always the same. This button operates alternately with the Variable button.
|
|
Start value
|
For a fixed increment, this field can be used to enter the start value for the cam profile. This value is entered as a floating point.
|
|
Increment
|
For a fixed increment, this field can be used to define the value of the increment. This value is entered as a floating point.
|
|
Variable
|
When this button is selected, the increment between 2 consecutive cam profile points is variable. The value of the points is defined by a table of constant words %KF, whose length is equal to the number of points.
|
|
Address table of %KF
|
For a variable increment, this field can be used to enter the start address for the table of points for the master.
|
|
Parameters
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Unit
|
Used to define the unit, which is used for the slave increment. The unit selected can be a sub unit of the unit defined for the axes (for example, cm for the axes and mm for the increment).
|
|
Fixed
|
When this button is selected, the increment between 2 consecutive cam profile points is always the same. This button operates alternately with the Variable button.
|
|
Start value
|
For a fixed increment, this field can be used to enter the start value for the cam profile. This value is entered as a floating point.
|
|
Increment
|
For a fixed increment, this field can be used to define the value of the increment. This value is entered as a floating point.
|
|
Variable
|
When this button is selected, the increment between 2 consecutive cam profile points is variable. The value of the points is defined by a table of constant words %KF, whose length is equal to the number of points.
|
|
Address table of %KF
|
For a variable increment, this field can be used to enter the start address of the table of points for the slave.
|