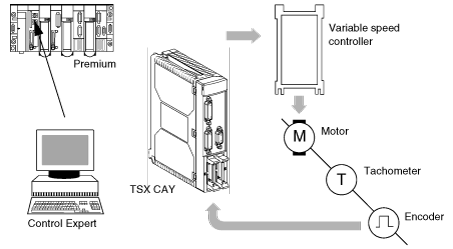
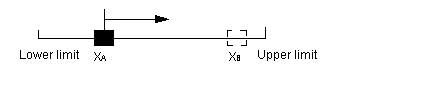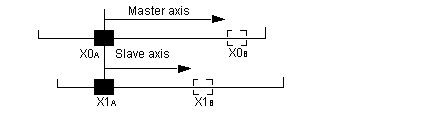Below is an overview of a motor operator axis control architecture:
The motor operator axis control range for Premium PLCs is made up of 5 modules: TSX CAY 21 / 41 / 22 / 42 / 33:
-
TSX CAY 21 (2 axes with limited run-time),
-
TSX CAY 41 (4 axes with limited run-time),
-
TSX CAY 22 (2 axes with unlimited run-time),
-
TSX CAY 42 (4 axes with unlimited run-time),
-
TSX CAY 33 (3 axes with limited or interpolated run-time),
The Control Expert software includes as standard the application-specific movement function for programming these axis control modules.
The basic movements are controlled via the machine’s principal sequential command program, but are made and checked by the TSX CAY modules, which ensure the position of the moving part is controlled.
The position of each channel is measured by either an incremental encoder or by an absolute encoder. The analog output is used to control a variable speed controller.
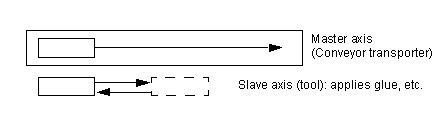
These modules (2 and 4 axes respectively) are used to control the movement of independent axes on machines with limited run-time. They are also used for master / slave applications.
|
At a Glance
|
|
The following diagram illustrates the movement of an axis between XA and XB on a machine with limited run-time (lower and upper limits):
|
|
The following diagram illustrates the movements of a master axis between X0A and X0B and those of a slave axis between X1A and X1B:
Master position / slave position = Constant
|
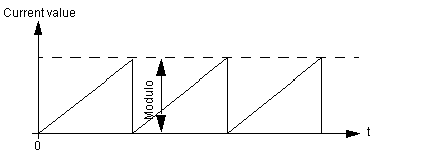
These modules (2 and 4 axes respectively) are used to control the movement of independent axes on machines with infinite run-time (usually rotational axes or similar). This type of application creates a measurement variation area called the "Modulo". These modules are also used to perform master-slave object tracking applications.
|
At a Glance
|
|
The following diagram illustrates the movement of an axis on a machine with unlimited run-time:
|
|
The following diagram provides an outline of the Modulo:
|
|
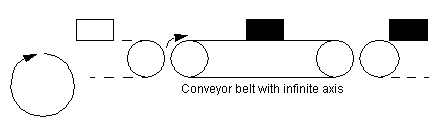
The following diagram illustrates a master-slave object tracking application:
|
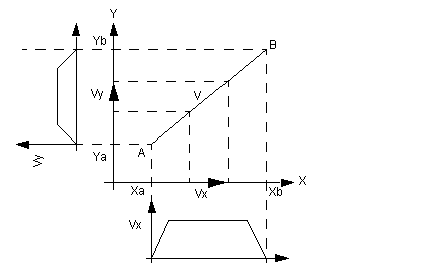
This module (3 axes) is used to control the movement of axes, which are linearly interpolated on Cartesian machines with limited run-time. It is used to follow trajectories, either on a plane (2 axes), or in space (3 axes).
|
At a Glance
|
|
The following diagram provides an outline of an interpolation of 2 axes:
|
The TSX CAY 33 module can be used in the following configurations:
This module does not provide the necessary circular interpolation to process bypass applications.