This section discusses specific cases when inductive loads at output points require additional protective circuits (directly on the actuator) and provides two examples of protective circuitry.
When there are contacted circuit elements (e.g. for safety interlocks) in the output conductors.
When the leads are very long.
Where inductive actuators are operated via relay contacts of the I/O base (to extend contact life and for EMC considerations).
In all three cases, the protective circuit is a clamping diode.
The following table provides generic selection guidelines.
|
Type of Load
|
Suppression Device
|
Minimum Component Rating
|
|
DC circuits
|
a reverse-biased clamping diode across the load
|
2 A and greater than twice the maximum load voltage
|
Consult relay and contactor manufacturers’ catalogs for commercial suppression devices matched to your particular products.
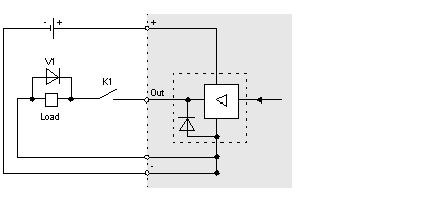
An example of a protective circuit for inductive DC actuators is illustrated below:
K1
contact, e.g., for safety interlocks
V1
clamping diode as the protective circuit
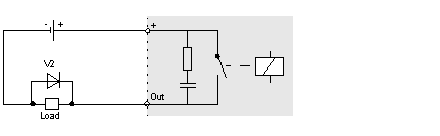
Another example of a protective circuit for inductive DC actuators is illustrated below:
V2
clamping diode as the protective circuit