Introduction
M580 safety PACs - both standalone and Hot Standby - include a mechanism for producing an SHA256 algorithmic fingerprint of the safe application: the SourceSafeSignature. When transferring the application from the PC to the PAC, Control Expert compares the SourceSafeSignature in the PC with the SourceSafeSignature in the PAC to determine if the safe application in the PC is the same as, or different from the safe application in the PAC.
The safe signature feature is optional. Generating a SourceSafeSignature can be a time-consuming process, depending on the size of the safe application. Using the safe signature management options, you can generate a SourceSafeSignature value that creates an algorithmic value for your safe application
on every build, or
only when you want to manually generate a SourceSafeSignature and add it to the most recent build, or
not at all
Actions that Change the SourceSafeSignature
Both configuration edits and variable value changes can cause the SourceSafeSignature to change.
Configuration changes: The following configuration actions lead to a signature change:
Device |
Action |
|---|---|
Safety CPU |
Change CPU reference via |
Change CPU version via |
|
Edit any parameter on the CPU or configuration tabs. |
|
Edit any parameter on any tab of the CPU Ethernet Communicator Head (, , , , , , ..). |
|
Safety Coprocessor |
Not applicable, as the coprocessor is not configurable. |
Other Safety Module |
// a module, either:
|
Edit of any safety module parameter, located on the tab (for example , ) and on the left pane of the editor (for example , ). |
|
Modification of module ID via command. |
|
Modification of Device DDT instance name. |
|
CIP Safety Module |
/ a module. |
Modification of any CIP Safety module parameter in either the CIP Safety device DTM editor, or the of the CPU master DTM editor. |
|
Modification of Device DDT instance name. |
|
Safety Power Supply |
/ a safety power supply. |
Other Safety-Related Equipment |
Modification of any topological address of equipment supporting a safety device, for example:
|
Except as noted, the following items are included in the SourceSafeSignature computation. A change to their values causes a SourceSafeSignature change:
Type |
Items |
|---|---|
Program |
SAFE task and related code sections. |
Variables |
All safe area variables and their attributes. |
DDTs |
Each safe DDT attribute, except date and version attributes. |
The variables inside each DDT, including their attributes. |
|
The safe DDTs, even if they are not used in the safe application. |
|
DFBs |
Each safe DFB attribute, except date and version attributes. |
The variables inside each DFB, including their attributes. |
|
The safe DFBs, even if they are not used in the safe application. |
|
Safe Scope Settings |
All for = safe. |
Common Scope Settings |
The following for = common: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
1. These variables are not exported, but any change to their values change the configuration partial signature. |
|
Managing the SourceSafeSignature
The SourceSafeSignature is managed in Control Expert in the window, by selecting , then selecting one of the following settings:
(default): generates a new SourceSafeSignature every time a command is executed.
: generates a new SourceSafeSignature when the command is executed.
Transferring an Application from the PC to the PLC
When you download an application from the PC to the PAC, Control Expert compares the SourceSafeSignature in the downloaded application with one in the PAC. Control Expert behaves as follows:
New Safe Signature |
PAC Safe Signature |
Control Expert Displays |
|---|---|---|
Any |
No application |
Transfer confirmation |
Any (except 0) |
0 |
Transfer confirmation |
0 |
0 |
Transfer confirmation |
0 |
Any (except 0) |
Transfer confirmation; Followed by a notice “This will reset the Safe Signature”; Followed by a new transfer confirmation |
XXXX = YYYY2 |
YYYY |
Transfer confirmation |
XXXX ≠ YYYY3 |
YYYY |
Transfer confirmation; Followed by a notice “This will modify the Safe Signature”; Followed by a new transfer confirmation |
1. The value “0” indicates a SourceSafeSignature was not generated automatically or manually. 2. The safe application in the PC (XXXX) and the safe application in the PAC (YYYY) are EQUAL. 3. The safe application in the PC (XXXX) and the safe application in the PAC (YYYY) are DIFFERENT. |
||
Viewing the SourceSafeSignature
When used, each SourceSafeSignature consists of a series of hexadecimal values, and can be very long, which makes direct readings and comparisons of the value very difficult for a human user. However, it is possible to copy a SourceSafeSignature value and paste it into an appropriate text tool to make comparisons. The SourceSafeSignature value can be found in the following Control Expert locations:
Comparing the SourceSafeSignature and the SAId
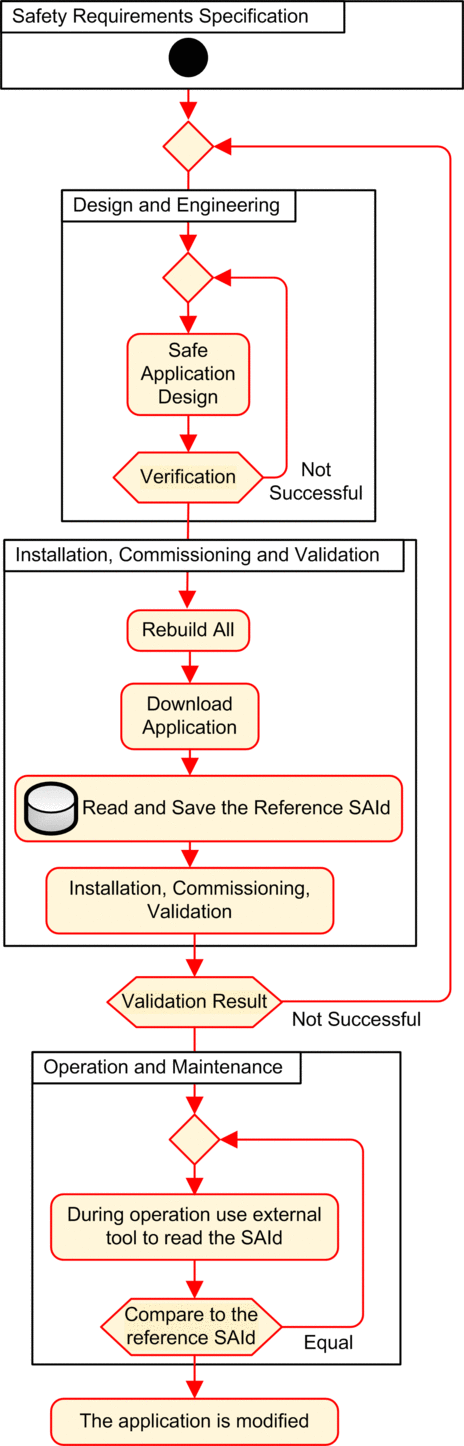
The SourceSafeSignature was introduced to provide an a priori verification that the safe application is unchanged. It is recommended to use this feature each time the process application is modified to avoid unintended modification of the safe application.
The SourceSafeSignature is a reliable mechanism, but is not sufficient for safety applications because the same source code may correspond to different binary (executable) codes, depending on the kind of build used after the last modification of the safe code.
The SAId can be evaluated only at run time. Its calculation is double executed and compared by both the CPU and the COPRO, based on the binary code that is executed by the safe application. Because the SAId is sensitive to all modifications, including those that may be introduced by a command after a build change, it is recommended that you use a command to generate a reference version of the safe application. This process lets you use any form of build (, online or offline) for the process application changes without any change made to the SAId.
The SAId is the recommended method used to confirm that the safe application is the one that was validated. The SAId value is not automatically tested by the application. For this reason, it is recommended that you regularly verify the SAId by any convenient mean (for example, using Control Expert or an HMI) by reading the output of the S_SYST_STAT_MX function block or the content of system word %SW169.
Modification of the Process Application Simplified Process
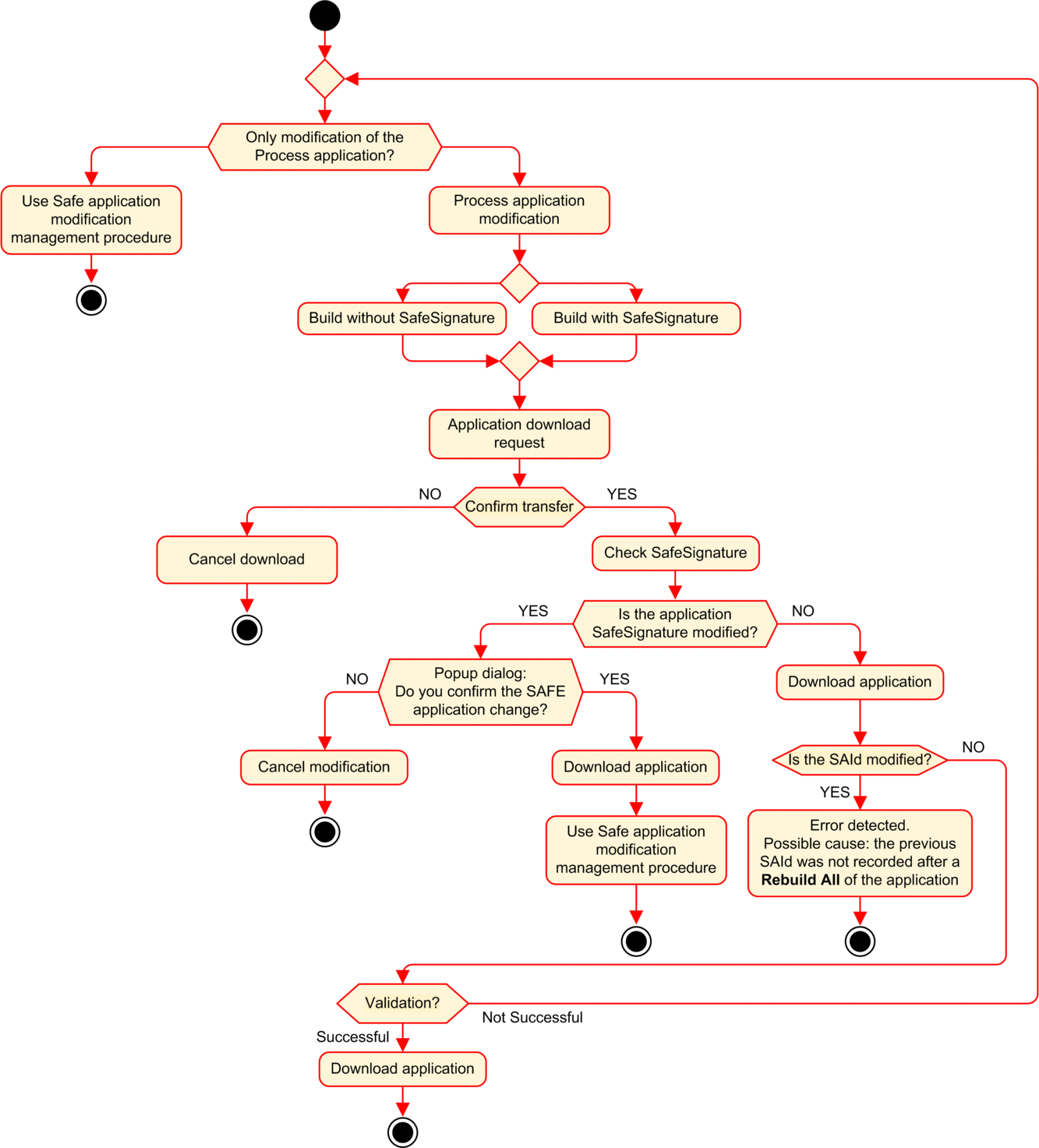
SAId Management