Operating States
The M580 safety PAC operating states are described below.
Operating State |
Applies to... |
Description |
|---|---|---|
AUTOTEST |
PAC |
The CPU is executing internal self-tests. NOTE: If extended racks are connected to the main local
rack and line terminators are not plugged into the unused connectors
on the rack extender module, the CPU remains in AUTOTEST after the
self-tests have completed.
|
NOCONF |
PAC |
The application program is not valid. |
STOP |
PAC or Task |
The PAC has a valid application and no error is detected, but operation has stopped because:
The CPU reads the inputs associated with each task, but does not refresh outputs, which enter their fallback state. The CPU can be restarted when you are ready. NOTE: Issuing a STOP
command in Control Expert stops all tasks.
The STOP event is recorded in the SYSLOG server of the CPU.
|
HALT |
Task |
The M580 safety PAC presents two independent HALT states:
In each case, task operations are halted because an unexpected blocking condition has been encountered, resulting in a recoverable condition. The CPU reads the inputs associated with each halted task, but does not refresh outputs, which are in fallback state. |
RUN |
PAC or Task |
With a valid application and no error detected, the CPU reads the inputs associated with each task, executes the code associated with each task, and refreshes the associated outputs.
NOTE: Issuing a RUN command in Control Expert starts all tasks. The RUN event is recorded in
the SYSLOG server of the CPU
|
WAIT |
PAC |
The CPU is in a transitory state while it backs up data when a power down condition is detected. The CPU starts again only when power is restored and the supply reserve is replenished. Because WAIT is a transitory state, it may not be visible. The CPU performs a warm restart to exit the WAIT state. |
ERROR |
PAC |
The CPU is stopped because an non-recoverable hardware or system error is detected. The ERROR state triggers the safety function. When the system is ready to be restarted, perform a cold start of the CPU to exit the ERROR state, either by cycling power or performing a RESET. |
OS DOWNLOAD |
PAC |
A CPU or COPRO firmware download is in progress. |
Refer to the M580 CPU LED Diagnostics and M580 Safety Coprocessor LED Diagnostics topics for information on the operating states of the PAC.
Operating State Transitions
The transitions between the several states in an M580 safety PAC are described, below:
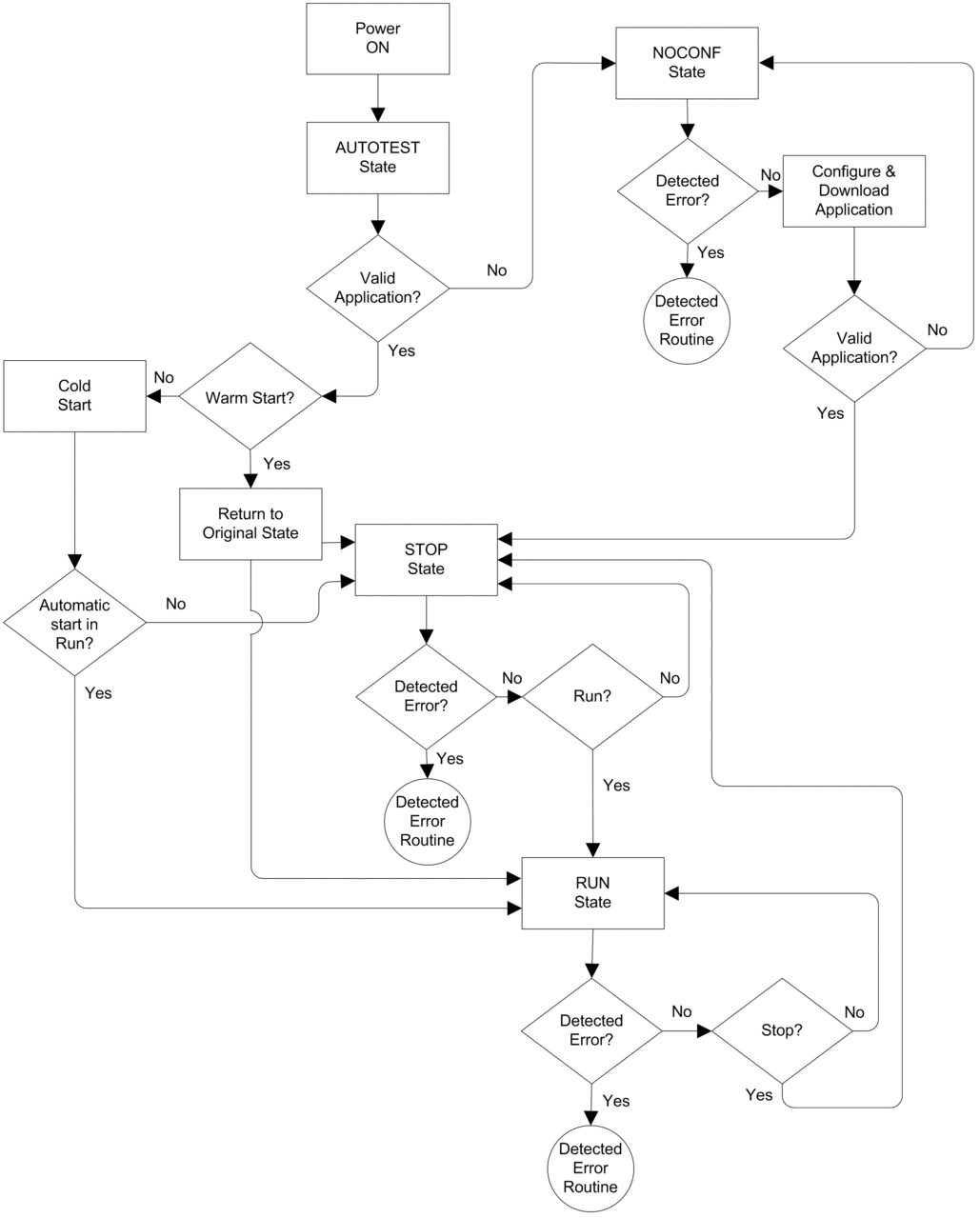
Refer to the topic Detected Error Processing for information on how the safety system handles detected errors.
Detected Error Processing
The M580 safety PAC handles the following kinds of CPU detected errors:
Recoverable application detected errors: These events cause the related task(s) to enter the HALT state.
NOTE: Because the MAST, FAST, and AUX tasks operate in the same memory area, an event that causes one of these tasks to enter HALT state causes the other non-safe tasks also to enter HALT state. Because the SAFE task operates in a separate memory area, the non-safe tasks are not affected if the SAFE task enters HALT state.Non-recoverable application detected errors: Internal CPU or coprocessor detected errors: These events cause the PAC to enter the ERROR state. The safety function is applied to the affected portion of the safety loop.
The logic of the detected error handling process is described below:
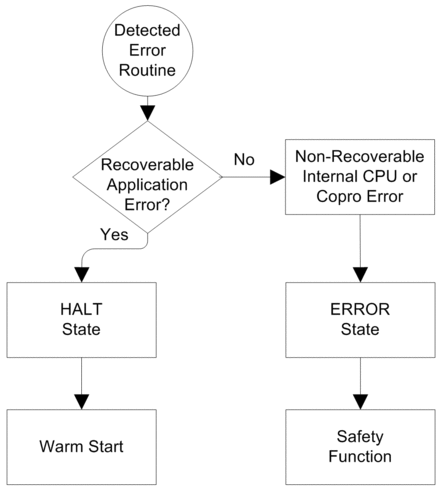
The impact of detected errors on individual tasks is described below:
Detected Error Type |
Task State |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
FAST |
SAFE |
MAST |
AUX |
|
FAST task watchdog overrun |
HALT |
RUN1 |
HALT |
HALT |
SAFE task watchdog overrun |
RUN |
HALT2 |
RUN |
RUN |
MAST task watchdog overrun |
HALT |
RUN |
HALT |
HALT |
AUX task watchdog overrun |
HALT |
RUN |
HALT |
HALT |
CPU dual code execution detected error |
RUN |
HALT2 |
RUN |
RUN |
Safety watchdog overrun3 |
ERROR |
ERROR2 |
ERROR |
ERROR |
CPU internal detected error |
ERROR |
ERROR2 |
ERROR |
ERROR |
1.Because FAST task has a higher priority than the SAFE task, delay of the FAST task may cause the SAFE task to enter HALT or ERROR state instead of RUN state. 2. The ERROR and HALT states on the SAFE task causes the safe outputs to be set to their user configurable state (fallback or maintain). 3. The safety watchdog is set equal to 1.5 times the SAFE task watchdog. |
||||
Task Bar Safety Status Viewer
When Control Expert is connected to the M580 safety PAC, the task bar includes a field describing the combined operating states of the SAFE task and the process tasks (MAST, FAST, AUX0, AUX1), as follows:
Process task(s) state |
SAFE task state |
Message |
|---|---|---|
STOP (all process tasks in STOP state) |
STOP |
STOP |
STOP (all process tasks in STOP state) |
RUN |
RUN |
STOP (all process tasks in STOP state) |
HALT |
SAFE HALT |
RUN (at lease one process task in RUN state) |
STOP |
RUN |
RUN (at lease one process task in RUN state) |
RUN |
RUN |
RUN (at lease one process task in RUN state) |
HALT |
SAFE HALT |
HALT |
STOP |
PROC HALT |
HALT |
RUN |
PROC HALT |
HALT |
HALT |
HALT |


