Introduction
In the following examples, the defined architectures restrict the number of hops a packet takes from an RIO drop to the CPU. By restricting the number of hops, the application response time (ART) for the system can be calculated.
In any M580 network topology, the hop count is used as a factor in calculating network delay. To determine the hop count from the perspective of an RIO drop, count the number of switches from the remote drop to the CPU.
Simple Daisy Chain Loop
In this example of a simple daisy chain loop topology, the CPU with Ethernet I/O scanner service on the local rack is connected to the main ring. Two BM•CRA312•0 X80 EIO adapter modules connect two Ethernet RIO drops to the main ring:
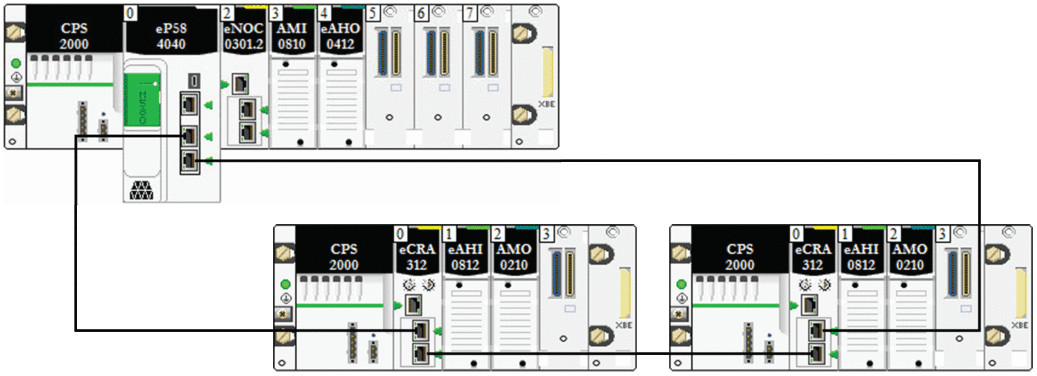
These restrictions apply to the simple daisy-chain loop topology above (which consists of only the local rack and RIO drops):
the maximum hop count = 17
the maximum number of RIO modules:
one (1) CPU with Ethernet I/O scanner service on the local rack
up to sixteen X80 EIO adapter modules (BM•CRA312•0)
In this design, the traffic is transmitted through the port with the shortest path to the CPU.


