Introduction
This topic discusses the interactions between the following safety CPU originator states/operations and the target device connection:
System Reaction Time
Run state
Stop / Halt state
Power Cycle / Restart
Init Safety command
Maintenance mode
CCOTF
Connecting / disconnecting / replacing a device
System Reaction Time
The time consumed by CIP Safety communication–called network time expectation–is added to and becomes part of the M580 safety system reaction time. Refer to the topic Impact of CIP Safety Communications on Safety System Reaction Time for additional information.
Run State
When the CIP Safety system is operating in Run state:
Health bits in the CIP Safety device communication DDDT are updated at the beginning of the SAFE task cycle.
Input values are updated at the beginning of the SAFE task cycle, based on the value most recently received.
Output values are updated and transmitted after execution of the SAFE task program.
The Run_Idle bit for outputs in the CIP Safety device communication DDDT is set to 1.
Health bits in the CIP Safety device communication DDDT are updated.
Stop State
When the SAFE task enters Stop state, for example if the SAFE task is stopped or has reached a breakpoint:
The originator to target connection remains open.
Data exchanges between the CPU and CIP Safety device are performed.
Health bits in the CIP Safety device communication DDDT continue to be updated.
The Run_Idle bit for outputs in the CIP Safety device communication DDDT is set to 0, and output devices apply their configured fallback setting.
Halt State
In Halt state, output values are not sent from the CPU to the CIP Safety device, and the device CIP Safety device health bits are set to 0.
Power Cycle or Reset
On a power cycle or reset:
The safety part of the application performs a cold start.
The PAC executes the same sequence of operations that is performed for application download.
Init Safety Command
Executing the command in Control Expert initializes the values of the CIP Safety device communication DDDT, by setting them to their factory default values.
Maintenance Mode
Operating the M580 safety CPU in maintenance mode does not impact CIP Safety device operations. The CPU will continue to compare calculations separately performed by the CPU and the Copro. However, there will be no additional comparison to values in the target DDDT. Hence, operating the PAC in maintenance mode is not deemed safe.
CCOTF
The change configuration on the fly (CCOTF) function is not supported for CIP Safety devices. Because a CIP Safety device gets its configuration settings from a vendor provided safety network configuration tool (SNCT) – and not the originator CPU – changes to device settings cannot be made from the CPU.
Connecting / Disconnecting / Replacing a CIP Safety Device
By default, upon application startup or execution of a command, the CTRL_IN and CTRL_OUT bits in the DDDT are set to Enabled (1). When a device is connected to a PAC in Stop or Run mode and the device CTRL_IN or CTRL_OUT bit is set to Enabled (1), the device automatically initiates data exchanges.
| WARNING | |
|---|---|
When the PAC detects an error requiring the termination of a device connection, the PAC sets the corresponding CTRL_IN or CTRL_OUT bit to Disabled (0). The device remains in the disabled state and only enters the Enabled (1) state if the transition is intended. For example, if the error is cleared and the a re-open connection request is executed.
You can execute a re-open connection request by re-setting the corresponding control bit (CTRL_IN or CTRL_OUT) from Disabled (0) to Enabled (1) in the DDDT.
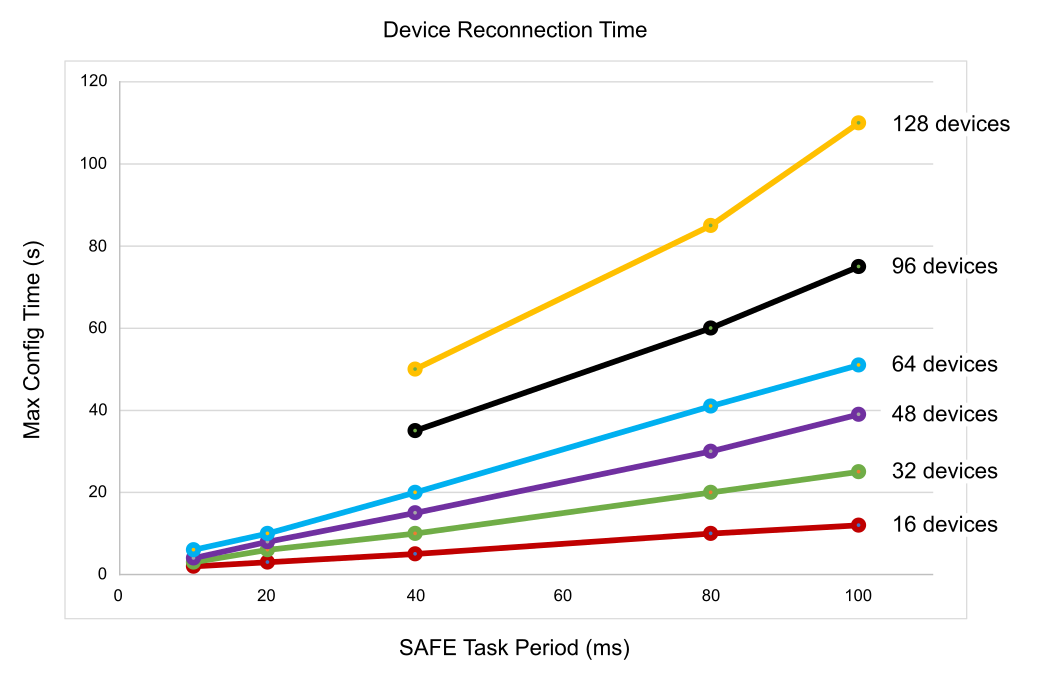
When reconnecting a device, the time to connect depends on the SAFE task period and the number of devices being connected:
For a single device with a SAFE task period less than 100 ms, the estimated reconnection time is less than 2 seconds.
For multiple devices, refer to the following chart for estimated reconnection times.
The CIP Safety PAC treats device replacement in the same manner as a device disconnection and reconnection. The operations to reconfigure the new device with the same settings as the replaced device are local to the device and do not involve the PAC.


