Introducing the Safety Library
When you install Control Expert Safety, a safety library of elementary functions (EFs), elementary function blocks (EFBs), and derived function blocks, (DFBs) are automatically included. These EFs, EFBs, and DFBs are identified by the prefix “S_” and are reserved for use in code sections managed by the SAFE task.
For a description of the blocks included in the M580 safety library, refer to the Control Expert Safety Block Library document.
Certified Safety Functions and Function Blocks
| WARNING | |
|---|---|
Unity Pro is the former name of Control Expert for version 13.1 or earlier.
These are the subset of EFs and Functions Blocks, which can be used inside safety logic. These are provided in the Safety Library:
Family |
Group or Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Logic |
S_AND_*, S_OR_*, S_XOR_*, S_NOT_*, S_SHL_*, S_SHR_*, S_ROR_*, S_ROL_* |
EF |
Type specific, e.g. S_AND with 2 to 32 inputs (inline code) |
Logic |
S_RS, S_SR, S_F_TRIG, S_R_TRIG |
EFB |
– |
Mathematics |
S_ADD_*, S_MUL_*, S_SUB_*, S_DIV_*, S_ABS_*, S_SIGN_*, S_NEG_*, S_MOVE, S_SQRT_REAL |
EF |
Type specific detected error handling (e.g. overflow) to be considered (inline code) |
Comparison |
S_GT_*, S_GE_*, S_LT_*, S_LE_*, S_NE_*, S_EQ_* |
EF |
Type specific (inline code) |
Statistical |
S_LIMIT_*, S_MAX_*, S_MIN_*, S_MUX_*, S_SEL |
EF |
Type specific (inline code) |
Type To Type |
S_BIT_TO*, S_BOOL_TO_*, S_BYTE_TO_*, S_DINT_TO_*, S_DWORD_TO_*, S_INT_TO_*, S_REAL_TO_*, S_TIME_TO_*, S_UDINT_TO_*, S_UINT_TO_*, S_WORD_TO_* |
EF |
Type specific (inline code) |
Timers & Counters |
S_CTU_*, S_CTD_*, S_CTUD_* |
EFB |
Type specific |
Timers & Counters |
S_TON, S_TOF, S_TP |
EFB |
– |
Peer to peer |
S_RD_ETH_MX, S_WR_ETH_MX, S_RD_ETH_MX2, S_WR_ETH_MX2 |
DFB |
Functions to perform a Safety peer to peer communication |
Actuator Connection |
S_EDM, S_ENABLE_SWITCH, S_ESPE, S_OUTCONTROL, S_GUARD_LOCKING, S_GUARD_MONITORING, S_MODE_SELECTOR |
DFB |
Machine Safety Function Blocks linked to actuators |
Sensor Connection |
S_EQUIVALENT, S_ANTIVALENT, S_EMERGENCYSTOP, S_TWO_HAND_CONTROL_TYPE_II, S_TWO_HAND_CONTROL_TYPE_III, S_MUTING_SEQ, S_MUTING_PAR, S_AI_COMP |
DFB |
Machine Safety Function Blocks linked to sensors |
System |
S_SYST_STAT_MX, S_SYST_TIME_MX, S_SYST_CLOCK_MX, S_SYST_RESET_TASK_BIT_MX, S_SYST_READ_TASK_BIT_MX |
EFB |
System function blocks |
Non-Certified Safety Functions and Function Blocks
These are the subset of Derived Functions Blocks (DFBs), which can be used inside safety logic. These function blocks are not certified. Their purpose is to provide you sample safety function blocks that can be easily reused and adapted. You can copy and paste these function blocks into your application and change them to meet the requirements of your application.
Family |
Group or Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
High Availability MX |
S_DIHA, S_AIHA |
DFB |
Function for high availability SIL2 or SIL3 digital input modules (inline code) |
Sensor Connection |
AI_COMP |
DFB |
Machine Safety Function Blocks linked to sensors |
Viewing the Safety Library in Control Expert
You can access the safety library only from the SAFE task. When you open the safety library in the , the safety library presents groups of EFs, EFBs, and DFBs. Some of these groups include safety versions of functions and blocks found in non-safety tasks. Others groups, noted below, contain functions and blocks unique to the SAFE task:
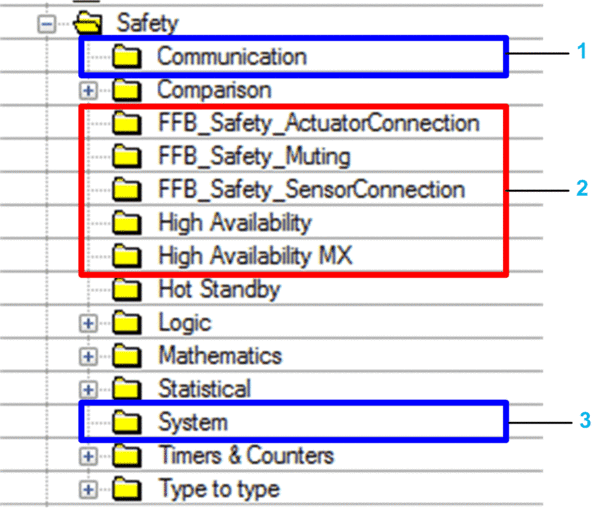
1 Blocks for reading and writing safety data values.
2 Blocks for performing safety-specific tasks.
3 Blocks for reading and writing safety system values.
For an example of how some of the safety blocks are implemented, refer to the PAC-to-PAC communication configuration example, which includes S_RD_ETH_MX and S_WR_ETH_MX.
Also refer to the EcoStruxure™ Control Expert Safety Block Library for a description of each available safety function and block.


