The
Highway Addressable Remote Transducer () protocol provides digital communication to microprocessor-based analog process control instruments.
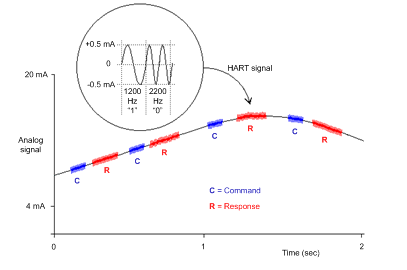
HART uses the Bell 202 frequency-shift-keying () standard to superimpose a digital signal on top of the 4-20mA current loop analog signal:
-
the analog signal communicates the primary measured process variable value
-
the digital signal communicates additional instrument information including instrument status, additional process variables, configuration data, and diagnostics
The digital signal shifts between a frequency of 1200 Hz (representing a binary 1) and a frequency of 2200 Hz (representing a binary 0):
These digital signal frequencies are higher than the typical analog signaling frequency range of 0...10 Hz. The digital signal is typically isolated using a passive with a cut-off frequency in the range of 400...800 Hz. The analog signal is likewise isolated using a passive .
The separation in frequency between HART and analog signaling allows both signals to coexist on the same . Because the HART digital signal is phase continuous, the HART digital signal:
-
does not interfere with the 4-20 mA signal, and
-
allows the analog process to continue operating during HART digital communication
Half-duplex Communication Protocol
HART communication is in design, which means that a HART-compliant instrument does not simultaneously transmit and receive.
HART is a master-slave protocol. A responds only when commanded by a . Examples of HART-compliant instruments include:
-
HART masters:
-
asset management software (AMS) running on a PC
-
a , for example, the HART modem feature of both the BMEAHI0812 input module and the BMEAHO0412 output module when communicating with a HART process control instrument (such as a HART-compliant sensor or actuator)
-
a hand-held device temporarily attached to the network
-
HART slaves:
-
a HART process control instrument
-
a , for example, the HART modem feature of both the BMEAHI0812 input module and the BMEAHO0412 output module when operating as a slave with asset management software (AMS) or a HART server